测试环境
机器配置
linux container
- 4C/16G/300GSSD
- 8C/32G/300GSSD
测试对象
| 版本 | 引擎 | 参数配置 | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
4C/16G |
8C/32G | ||
| mongodb3.2.6 | wiredTiger |
|
|
| tokumx1.5 | tokumx |
cacheSize=12G syncdelay=5 |
cacheSize=24G syncdelay=5 |
| tokumx2.0.2 | tokumx | cacheSize=12G checkpointPeriod=10 cleanerIterations=10 directio=false cleanerPeriod=2 syncdelay=5 |
cacheSize=24G |
测试场景
- 测试单节点环境
- 100%insert
- 单节点_50%update50%read
- 5%update5%insert90%read
- 100%read
- wiredtiger_syncPeriodSecs_60与1比较
- sharding集群性能压测
- 说明
- 场景1-4每次加载1000W数据,数据大小约13G
- 场景5加载5000W数据,数据大小约75G
测试方法
- YCSB压测
测试结果
场景1:单节点_100%insert (load data)
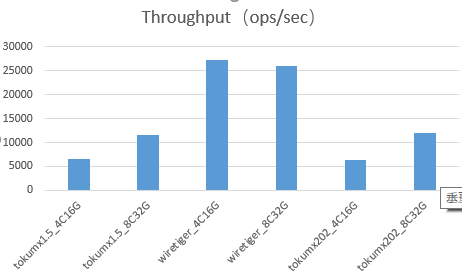

场景2:单节点_50%update50%read


场景3:单节点_5%update5%insert90%read
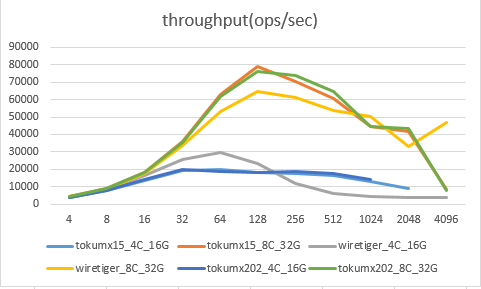
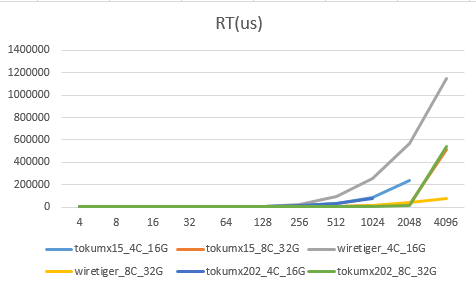
场景4:单节点_100%read

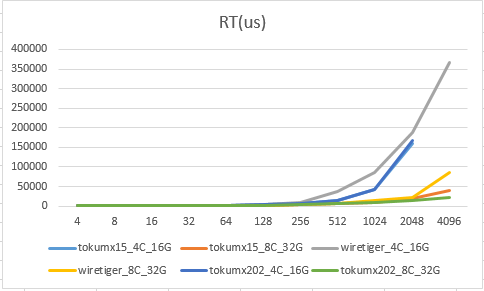
场景5:wiredtiger_syncPeriodSecs_60_1
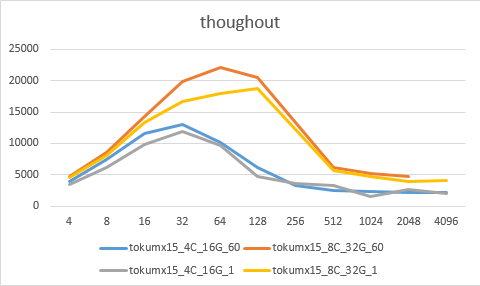
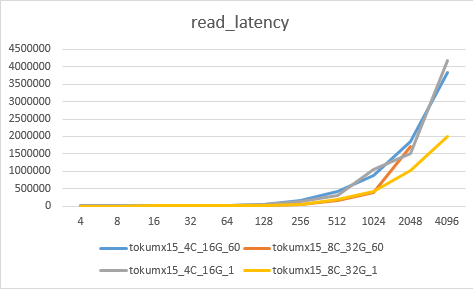
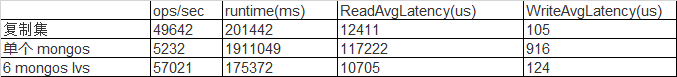
场景6:sharding集群性能测试
结论
- load性能比较,wiredtiger优势十分明显,速度大约是同配置tokumx的5倍,且RT较短
- 只读性能,wiredTiger性能和tokumx,比较,性能较差,但稳定;
- 复杂情况下,wiredTiger性能较好,可支撑更高并发度的线程调用;
- 如果不基于磁盘和网络吞吐量考虑,三个以下节点的 sharding 从性能上没有价值,现阶段结果看来,尽可能多的部署 mongos,能有效提升总体的集群利用率。