课下作业(选做)第八周
相关知识点的总结(代码检查)
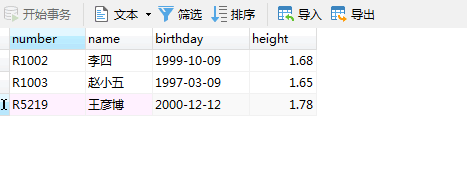
xampp 和数据库服务器建立连接 建立数据库 创建表 在idea上运行
结果截图(代码检查)
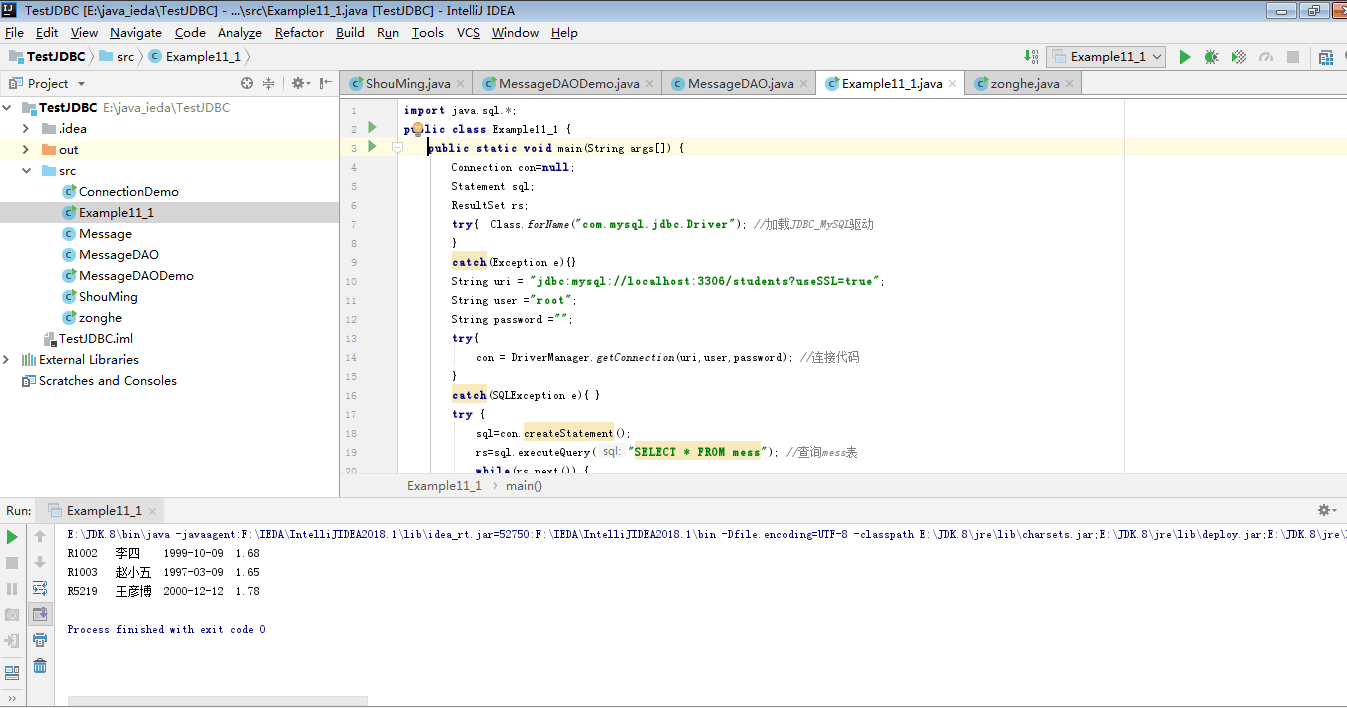
教材11.1-11.10的代码发分析
Example11_1
import java.sql.*;
public class Example11_1 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Connection con=null;
//初始化
Statement sql;
ResultSet rs;
//顺序查询,始终保持和数据库的连接,直到将对象中的数据查看完毕
try{ Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //加载JDBC_MySQL驱动
}
catch(Exception e){}
String uri = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/students?useSSL=true";
String user ="root";
String password ="";
try{
con = DriverManager.getConnection(uri,user,password); //连接代码
}
catch(SQLException e){ }
try {
sql=con.createStatement();
rs=sql.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM mess"); //查询mess表
while(rs.next()) { //读取数据
String number=rs.getString(1);
String name=rs.getString(2);
Date date=rs.getDate(3);
float height=rs.getFloat(4);
System.out.printf("%s ",number);
System.out.printf("%s ",name);
System.out.printf("%s ",date);
System.out.printf("%.2f
",height);
}
con.close();
}
catch(SQLException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
分析:查询students数据库中mess表中的全部记录
Example11_2
import java.sql.*;
public class Example11_2 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Connection con;
Statement sql;
ResultSet rs;
con = GetDBConnection.connectDB("students","root",""); //连接数据库
if(con == null ) return;
//若数据为空
try {
sql=con.createStatement(ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_SENSITIVE,
ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY); //为得到一个可滚动的结果集
rs = sql.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM mess ");
//根据参数ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_SENSITIVE和ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY的情况,sql返回相应类型的结果集
rs.last();
int max = rs.getRow();
System.out.println("表共有"+max+"条记录,随机抽取2条记录:");
int [] a =GetRandomNumber.getRandomNumber(max,2);//得到1-max之间2个不同随机数
for(int i:a){
rs.absolute(i);//油标移动到第i行
String number = rs.getString(1);
String name = rs.getString(2);
Date date = rs.getDate(3);
float h = rs.getFloat(4);
System.out.printf("%s ",number);
System.out.printf("%s ",name);
System.out.printf("%s ",date);
System.out.printf("%.2f
",h);
}
con.close();
}
catch(SQLException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
分析:随机查询student数据库中mess表的两条记录,首先将游标移动到最后一行,然后再获取最后一行的行号,以便获得表中的记录数目。
Example11_3
import java.sql.*;
public class Example11_3 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Connection con;
Statement sql;
ResultSet rs;
con = GetDBConnection.connectDB("students","root","");//连接数据库
if(con == null ) return;
//若数据为空
String c1=" year(birthday)<=2000 and month(birthday)>7";
//条件1:若出生的年份在2000年或者2000年之前,月份在7月之后
String c2=" name Like '张_%'";
//条件2:学生姓张
String c3=" height >1.65";
//条件3:身高大于1.65
String sqlStr =
"select * from mess where "+c1+" and "+c2+" and "+c3+"order by birthday";
//通过where查找和通过order by排序
try {
sql=con.createStatement();
rs = sql.executeQuery(sqlStr);
while(rs.next()) {
String number=rs.getString(1);
String name=rs.getString(2);
Date date=rs.getDate(3);
float height=rs.getFloat(4);
System.out.printf("%s ",number);
System.out.printf("%s ",name);
System.out.printf("%s ",date);
System.out.printf("%.2f
",height);
}
con.close();
}
catch(SQLException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
分析:
查询mess表中姓张,身高大于1.65,出生的年份在2000年或者2000年之前,月份在7月之后的学生,并按照出生日期排序。
Example11_4
import java.sql.*;
public class Example11_4 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Connection con;
Statement sql;
ResultSet rs;
con = GetDBConnection.connectDB("students","root",""); //连接数据库
if(con == null ) return;
String jiLu="('R11q','王三','2000-10-23',1.66),"+
"('R10q','李武','1989-10-23',1.76)"; //插入的2条记录
String sqlStr ="insert into mess values"+jiLu;
//通过insert into mess values语句进行插入记录
try {
sql=con.createStatement();
int ok = sql.executeUpdate(sqlStr);
rs = sql.executeQuery("select * from mess");
while(rs.next()) {
String number=rs.getString(1);
String name=rs.getString(2);
Date date=rs.getDate(3);
float height=rs.getFloat(4);
System.out.printf("%s ",number);
System.out.printf("%s ",name);
System.out.printf("%s ",date);
System.out.printf("%.2f
",height);
}
con.close();
}
catch(SQLException e) {
System.out.println("记录中number值不能重复"+e);
}
}
}
分析:向mess中插入两条记录
Example11_5
import java.sql.*;
public class Example11_5 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Connection con;
PreparedStatement preSql; //预处理语句对象preSql
ResultSet rs;
con = GetDBConnection.connectDB("students","root",""); //连接数据库
if(con == null ) return;
String sqlStr ="insert into mess values(?,?,?,?)";
//在对SQL进行预处理时可以使用通配符?来代替字段的值
try {
preSql = con.prepareStatement(sqlStr);//得到预处理语句对象preSql
preSql.setString(1,"A001"); //设置第1个?代表的值
preSql.setString(2,"刘伟"); //设置第2个?代表的值
preSql.setString(3,"1999-9-10"); //设置第3个?代表的值
preSql.setFloat(4,1.77f); //设置第4个?代表的值
int ok = preSql.executeUpdate();
sqlStr="select * from mess where name like ? ";
preSql = con.prepareStatement(sqlStr);//得到预处理语句对象preSql
preSql.setString(1,"张%"); //设置第1个?代表的值
rs = preSql.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()) {
String number=rs.getString(1);
String name=rs.getString(2);
Date date=rs.getDate(3);
float height=rs.getFloat(4);
System.out.printf("%s ",number);
System.out.printf("%s ",name);
System.out.printf("%s ",date);
System.out.printf("%.2f
",height);
}
con.close();
}
catch(SQLException e) {
System.out.println("记录中number值不能重复"+e);
}
}
}
分析:使用预处理语句向mess表添加记录并查询了姓张的记录。
Example11_6
import javax.swing.*;
public class Example11_6 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String [] tableHead;
String [][] content;
JTable table ;//定义表格
JFrame win= new JFrame();
Query findRecord = new Query();
findRecord.setDatabaseName("students");
findRecord.setSQL("select * from mess");
content = findRecord.getRecord();
//返回二维数组,即查询的全部记录
tableHead=findRecord.getColumnName();
//返回全部字段名
table = new JTable(content,tableHead);
//表格JTable
win.add(new JScrollPane(table));
win.setBounds(12,100,400,200);
win.setVisible(true);
win.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}
分析:将数据库的名字以及SQL语句传递给Query类的对象,用表格显示查询到的记录。
Example11_7
import java.sql.*;
public class Example11_7{
public static void main(String args[]){
Connection con = null;
//初始化
Statement sql;
ResultSet rs;
String sqlStr;
con = GetDBConnection.connectDB("students","root",""); //连接数据库
if(con == null ) return;
try{ float n = 0.02f;
con.setAutoCommit(false); //关闭自动提交模式
sql = con.createStatement();
sqlStr = "select name,height from mess where number='R1001'";
rs = sql.executeQuery(sqlStr);
rs.next();
float h1 = rs.getFloat(2);
System.out.println("事务之前"+rs.getString(1)+"身高:"+h1);
sqlStr = "select name,height from mess where number='R1002'";
rs = sql.executeQuery(sqlStr);
rs.next();
float h2 = rs.getFloat(2);
System.out.println("事务之前"+rs.getString(1)+"身高:"+h2);
h1 = h1-n; //R1001的height的值减少n
h2 = h2+n; //将减少的n增加到字段是R1002的height上
sqlStr = "update mess set height ="+h1+" where number='R1001'";
sql.executeUpdate(sqlStr);
sqlStr = "update mess set height ="+h2+" where number='R1002'";
sql.executeUpdate(sqlStr);
//更新数据
con.commit(); //开始事务处理,如果发生异常直接执行catch块
con.setAutoCommit(true); //恢复自动提交模式
String s = "select name,height from mess"+
" where number='R1001'or number='R1002'";
rs =
sql.executeQuery(s);
while(rs.next()){
System.out.println("事务后"+rs.getString(1)+
"身高:"+rs.getFloat(2));
}
con.close();
}
catch(SQLException e){
try{ con.rollback(); //撤销事务所做的操作
}
catch(SQLException exp){}
}
}
}
分析:将mess表中number字段是R1001的height的值减少n,并将减少的n增加到字段是R1002的height上。
Example11_8
import java.sql.*;
public class Example11_8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection con =null;
Statement sta = null;
//初始化
ResultSet rs;
String SQL;
try {
Class.forName("org.apache.derby.jdbc.EmbeddedDriver");//加载驱动
}
catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
return;
}
try {
String uri ="jdbc:derby:students;create=true";
con=DriverManager.getConnection(uri); //连接数据库
sta = con.createStatement();
}
catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
return;
}
try { SQL = "create table chengji(name varchar(40),score float)";
sta.execute(SQL);//创建表
}
catch(SQLException e) {
//System.out.println("该表已经存在");
}
SQL ="insert into chengji values"+
"('张三', 90),('李斯', 88),('刘二', 67)";
//向表中添加三条新的记录
try {
sta.execute(SQL);
rs = sta.executeQuery("select * from chengji "); // 查询表中的记录
while(rs.next()) {
String name=rs.getString(1);
System.out.print(name+" ");
float score=rs.getFloat(2);
System.out.println(score);
}
con.close();
}
catch(SQLException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
分析:用Derby数据库管理系统创建了名为students的数据库,并在数据库中建立了chengji表
11章编程题:
参照例子3,按出生日期排序mess表的记录
import java.sql.*;
public class test1 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Connection con;
Statement sql;
ResultSet rs;
con = GetDBConnection.connectDB("students","root","");
if(con == null ) return;
String sqlStr =
"select * from mess "+"order by birthday";
try {
sql=con.createStatement();
rs = sql.executeQuery(sqlStr);
while(rs.next()) {
String number=rs.getString(1);
String name=rs.getString(2);
Date date=rs.getDate(3);
float height=rs.getFloat(4);
System.out.printf("%s ",number);
System.out.printf("%s ",name);
System.out.printf("%s ",date);
System.out.printf("%.2f
",height);
}
con.close();
}
catch(SQLException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}