一.调用类的公有方法
String str = "aa"; Class<? extends String> clazz = str.getClass(); Method concat = clazz.getMethod("concat", String.class); Object bb = concat.invoke(str,"bb"); System.out.println(bb);
运行结果:

二.调用类的私有方法
1.测试类
package reflex; public class Test { private String a; private Test(){ } public Test(String a) { this.a = a; } public String getA() { return a; } public void setA(String a) { this.a = a; } private String concatStr(String b){ return this.a.concat(b); } }
2.调用该类的concatStr方法
@Test public void testInvoke() throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException { reflex.Test testStr = new reflex.Test("aa"); Class<? extends reflex.Test> clazz = testStr.getClass(); //获取到该私有方法的Method对象 Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("concatStr", String.class); //忽略访问修饰符的检查 method.setAccessible(true); Object obj = method.invoke(testStr, "bb"); System.out.println(obj); }
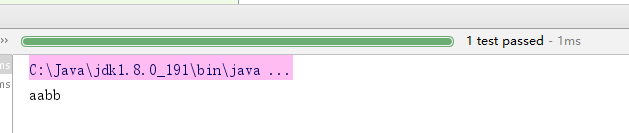
调用结果:
三.调用类的公有构造方法
@Test public void testConstructor() throws Exception { Class<reflex.Test> clazz = reflex.Test.class; //获取该类的Constructor对象 Constructor<reflex.Test> constructor = clazz.getConstructor(String.class); //Constructor.newInstance方法可以创建该类的实例 reflex.Test hello = constructor.newInstance("hello"); System.out.println(hello.getA()); }
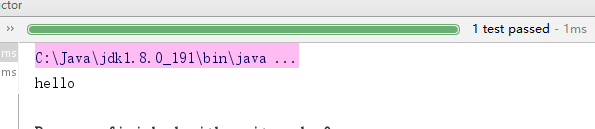
运行结果:
四.调用类的私有构造方法
@Test public void testConstructor2() throws Exception { Class<reflex.Test> clazz = reflex.Test.class; Constructor<reflex.Test> constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(); //忽略访问修饰符的检查 constructor.setAccessible(true); reflex.Test test = constructor.newInstance(); System.out.println(test); }
运行结果:
