Django如何使用logging打印日志
简介
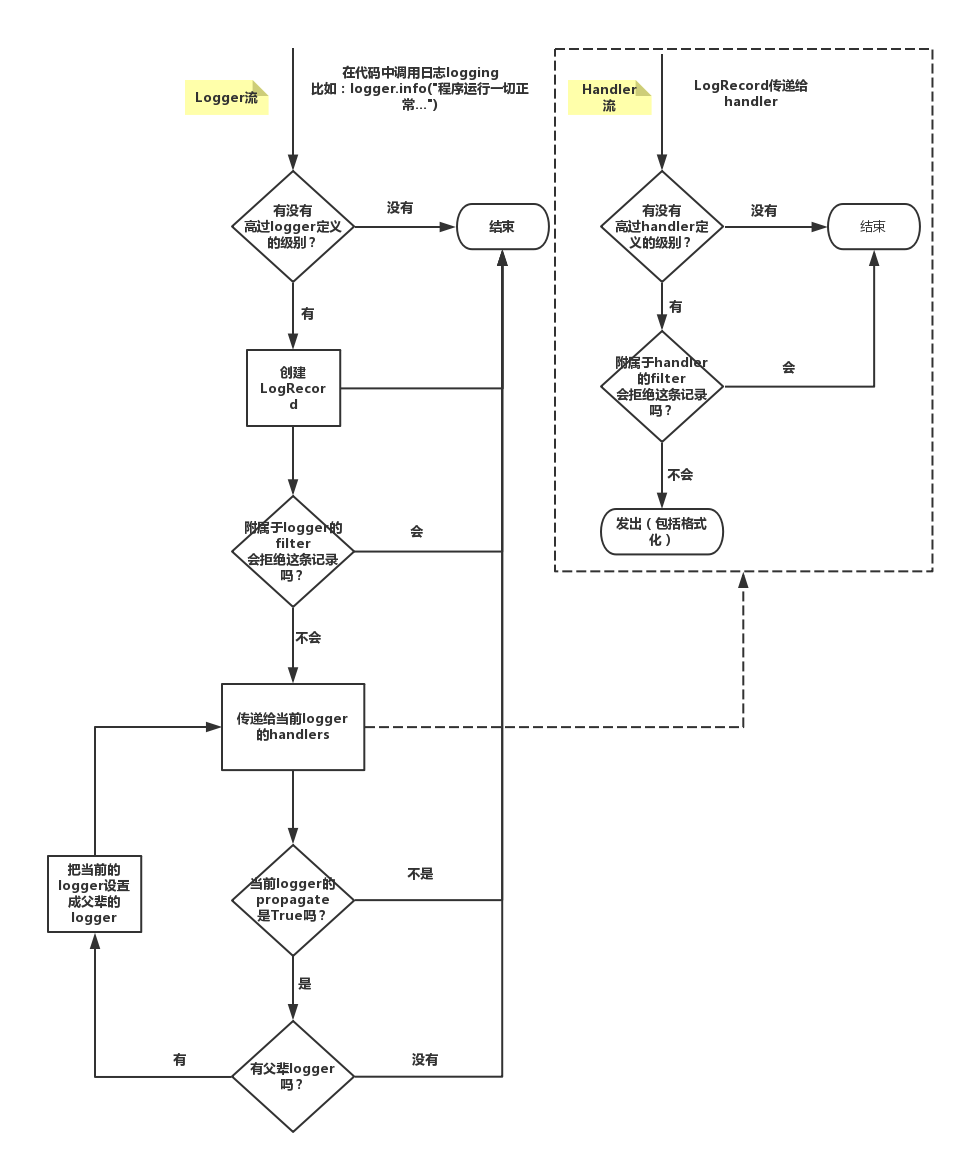
Django使用python自带的logging 作为日志打印工具。简单介绍下logging。
logging 是线程安全的,其主要由4部分组成:
"""
1. Logger 用户使用的直接接口,将日志传递给Handler
2. Handler 控制日志输出到哪里,console,file… 一个logger可以有多个Handler
3. Filter 控制哪些日志可以从logger流向Handler
4. Formatter 控制日志的格式
"""
使用
1.项目里sesetti.py里配置
Django通过在settings文件中使用LOGGING来定制日志输出(包括定义logger, handler, formatter等)
例如,settings文件中定义如下:
BASE_LOG_DIR = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "log")
LOGGING = {
```python
'version': 1, # 保留字
'disable_existing_loggers': False, # 禁用已经存在的logger实例
# 日志文件的格式
'formatters': {
# 详细的日志格式
'standard': {
'format': '[%(asctime)s][%(threadName)s:%(thread)d][task_id:%(name)s][%(filename)s:%(lineno)d]'
'[%(levelname)s][%(message)s]'
},
# 简单的日志格式
'simple': {
'format': '[%(levelname)s][%(asctime)s][%(filename)s:%(lineno)d]%(message)s'
},
# 定义一个特殊的日志格式
'collect': {
'format': '%(message)s'
}
},
# 过滤器
'filters': {
'require_debug_true': {
'()': 'django.utils.log.RequireDebugTrue',
},
},
# 处理器
'handlers': {
# 在终端打印
'console': {
'level': 'DEBUG',
'filters': ['require_debug_true'], # 只有在Django debug为True时才在屏幕打印日志
'class': 'logging.StreamHandler', #
'formatter': 'simple'
},
# 默认的
'default': {
'level': 'INFO',
'class': 'logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler', # 保存到文件,自动切
'filename': os.path.join(BASE_LOG_DIR, "xxx_info.log"), # 日志文件
'maxBytes': 1024 * 1024 * 50, # 日志大小 50M
'backupCount': 3, # 最多备份几个
'formatter': 'standard',
'encoding': 'utf-8',
},
# 专门用来记错误日志
'error': {
'level': 'ERROR',
'class': 'logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler', # 保存到文件,自动切
'filename': os.path.join(BASE_LOG_DIR, "xxx_err.log"), # 日志文件
'maxBytes': 1024 * 1024 * 50, # 日志大小 50M
'backupCount': 5,
'formatter': 'standard',
'encoding': 'utf-8',
},
# 专门定义一个收集特定信息的日志
'collect': {
'level': 'INFO',
'class': 'logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler', # 保存到文件,自动切
'filename': os.path.join(BASE_LOG_DIR, "xxx_collect.log"),
'maxBytes': 1024 * 1024 * 50, # 日志大小 50M
'backupCount': 5,
'formatter': 'collect',
'encoding': "utf-8"
}
},
'loggers': {
# 默认的logger应用如下配置
'': {
'handlers': ['default', 'console', 'error'], # 上线之后可以把'console'移除
'level': 'DEBUG',
'propagate': True, # 向不向更高级别的logger传递
},
# 名为 'collect'的logger还单独处理
'collect': {
'handlers': ['console', 'collect'],
'level': 'INFO',
}
},
```
### 2.views.py里使用
```python
import logging
#生成一个以当前文件名为名字的logger实例
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
# 生成一个名为collect的logger实例
collect_logger = logging.getLogger("collect")
def index(request):
logger.debug("一个萌萌的请求过来了。。。。")
logger.info("一个更萌的请求过来了。。。。")
logger.debug("这是app01里面的index视图函数")
collect_logger.info("用户1:河南")
return HttpResponse("OK")
```
## 流程