#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Singleton
{
static Singleton s;
int i;
Singleton(int x) :i(x)
{};
Singleton& operator=(Singleton&);//不允许赋值
Singleton(const Singleton&);//不允许拷贝
public:
static Singleton& instance()//为了后面可以用引用接收,所以这里要返回引用
{
return s;
}
int getValue()
{
return i;
}
void setValue(int x)
{
i = x;
}
};
Singleton Singleton::s(47);
int main()
{
Singleton& s = Singleton::instance();//防止调用拷贝构造函数,所以这里用引用
cout << s.getValue() << endl;
cout << &s << endl;
Singleton& s2 = Singleton::instance();
//Singleton s3;不存在默认构造函数,即该类不能继续实例化
s2.setValue(9);
cout << &s2 << endl;
cout << s.getValue() << endl;
return 0;
}
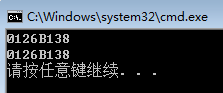
运行结果:从输出结果我们可以知道,对象地址是一样的,即这都是同一个对象
上述实现通过返回一个引用实现单例模式。如果返回的是指针而不是引用,用户可能会不小心删除此指针,因此上述实现比返回指针更安全。
问:在上面我们把拷贝构造函数和赋值操作符都声明为私有,为什么要声明为私有?仅仅把构造函数声明为私有不久可以了吗?
答:不可以的,如果不把拷贝构造函数声明为私有那么还是可以通过拷贝构造函数来创造一个类新的对象。
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Singleton
{
static Singleton s;
int i;
Singleton(int x) :i(x)
{};
//Singleton& operator=(Singleton&);//不允许赋值
//Singleton(const Singleton&);//不允许拷贝
public:
static Singleton instance()
{
return s;
}
int getValue()
{
return i;
}
void setValue(int x)
{
i = x;
}
};
Singleton Singleton::s(47);
int main()
{
Singleton s = Singleton::instance();//调用了拷贝构造函数
//cout << s.getValue() << endl;
cout << &s << endl;
Singleton s2 = Singleton::instance();
//Singleton s3;不存在默认构造函数,即该类不能继续实例化
//s2.setValue(9);
cout << &s2 << endl;
//cout << s.getValue() << endl;
return 0;
}
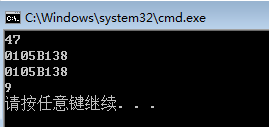
运行结果:
从截图我们可以知道,这是两个不同的对象,因为我们调用了拷贝构造函数。
从这里也可以知道,我们要做一个单实例模式时需要采用引用的方法这样才不会调用拷贝构造函数。
此外对于赋值操作符声明为私有主要是为了证明这个类产生的对象都是同一个对象是调用了类的构造函数后的结果而不是因为其中调用了赋值操作符产生的结果。
最简单的单实例例子:
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Singleton
{
static Singleton a;
Singleton() {};
Singleton(Singleton&) {};
public:
static Singleton& instance()
{
return a;
}
};
Singleton Singleton::a;//静态数据成员需要在类外定义
int main()
{
Singleton& temp = Singleton::instance();//这里用引用,是为了不调用拷贝构造函数
cout << &temp << endl;
Singleton &temp1 = Singleton::instance();
cout << &temp1 << endl;
return 0;
}
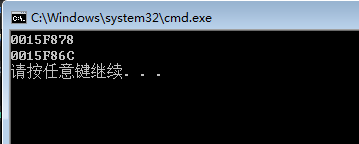
运行结果: