MySQL之自增
我们发现,当我们的mysql表插入一些数据然后删除这些数据后,我们下一次插入数据时,表的id仍然是接着数据删除之前id后面增长的,这是MySQL默认的,但是我们能不能修改呢,当然是可以的。当我们输入语句show create table 表名G;时,可以查看表的创建语句,我们插入一些数据后,比如五条数据,我们查看表的创建语句会发现多了一个AUTO_INCREMENT=6,再次插入一条数据会发现这个值变成了7,我们会发现这个值,和下一条数据的id值是一样的,经过验证,果然可以通过修改这个值来修改id,修改语句如下:
alter table 表名 AUTO_INCREMENT=数字;
经过查阅资料发现,MySQL可以修改自增字段的自增步长,并且有基于会话级别和全局级别两种,会话级别就是当前会话登录,重新登录一下失效了,全局级别就是只要修改了,那么每一次修改的自增步长都是修改的值,一般不建议修改全局级别的自增步长。
注意:1、对于自增列,必须是索引(含主键) 2、对于自增可以设置步长和起始值 show session variables like 'auto_inc%'; #查看当前会话的步长和起始值 set session auto_increment_increment=2; #设置当前会话的步长 set session auto_increment_offset=10; #设置当前会话的起始值 show global variables like 'auto_inc%'; #查看全局的步长和起始值 set global auto_increment_increment=2; #设置全局的步长 set global auto_increment_offset=10; #设置全局的起始值
唯一索引
create table t1( id int primary key auto_increment, num int, cid int, unique 唯一索引名称 (列名), #()里面可以写多列,作为联合唯一索引 )
PS:唯一索引作用:1、约束不能重复
2、加速查找
外键的变种
一对多(MySQL默认创建的外键就是一对多)

create table userinfo1( id int primary key auto_increment, name char(32), age int, gender enum('男','女') )engine=innodb default charset=utf8; create table admin( id int primary key auto_increment, username char(32), password char(32), user_id int, constraint fk5 foreign key (user_id) references userinfo1(id) )engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
一对一(一对一就是在一对多的基础上加入了唯一索引的约束)

create table userinfo1( id int primary key auto_increment, name char(32), age int, gender enum('男','女') )engine=innodb default charset=utf8; create table admin( id int primary key auto_increment, username char(32), password char(32), user_id int, unique uq1(user_id), constraint fk5 foreign key (user_id) references userinfo1(id) )engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
多对多(多对多需要创建第三张表来维护表的关系)

create table userinfo2( id int primary key auto_increment, name char(32), age int, gender enum('男','女') )engine=innodb default charset=utf8; create table host( id int primary key auto_increment, hostname char(32) )engine=innodb default charset=utf8; create table userhost( id int primary key auto_increment, user_id int, host_id int, unique uq2(user_id,host_id), constraint fk6 foreign key (user_id) references userinfo2(id), constraint fk7 foreign key (host_id) references host(id) )engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
MySQL语句的补充
增
insert into tb11(name,age) values('wusir',12); #插入单条数据 insert into tb11(name,age) values('wusir',12),('root',18); #插入多条数据 insert into tb12(name,age) select name,age from tb11; #从另一张表中查出数据插入这张表
删
delete from tb12; #清空整个表 delete from tb12 where id !=2; #清空id不为2的数据 delete from tb12 where id =2; #清空id为2的数据 delete from tb12 where id > 2; #清空id大于2的数据 delete from tb12 where id >=2; #清空id大于等于2的数据 delete from tb12 where id >=2 or name='wusir'; #清空id大于等于2或者name为wusir的数据
delete from tb12 where id >=2 and name='wusir'; #清空id大于等于2并且name为wusir的数据
改
update tb12 set name='wusir' where id>12 and name='xx' update tb12 set name='wusir',age=19 where id>12 and name='xx'
查
a、条件 select * from 表 where id > 1 and name != 'wusir' and num = 12; select * from 表 where id between 5 and 16; select * from 表 where id in (11,22,33) select * from 表 where id not in (11,22,33) select * from 表 where id in (select nid from 表) b、通配符 select * from 表 where name like 'ale%' #ale开头的所有(多个字符串) select * from 表 where name like 'ale_' #ale开头的所有(一个字符) c、限制 select * from 表 limit 5; - 前5行 select * from 表 limit 4,5; - 从第4行开始的5行 select * from 表 limit 5 offset 4 - 从第4行开始的5行 d、排序 select * from 表 order by 列 asc - 根据 “列” 从小到大排列 select * from 表 order by 列 desc - 根据 “列” 从大到小排列 select * from 表 order by 列1 desc,列2 asc - 根据 “列1” 从大到小排列,如果相同则按列2从小到大排序 e、分组 select num from 表 group by numselect num from 表 where id > 10 group by num order by nid desc select num,min(score) from 表 group by num
group分组经常配合下面的聚合函数使用:
count()
max()
min()
sum()
avg()
select num from 表 group by num having max(id) > 10 特别的:group by 必须在where之后(where中不能有聚合函数),order by之前,如果二次筛选用到了聚合函数,就不能使用where,要使用having,且having要放在group by之后。
连表查询
select * from userinfo5,department5 where userinfo5.part_id = department5.id; #一般不推荐使用这种连表查询的方式 select * from userinfo5 left join department5 on userinfo5.part_id = department5.id; #左连接(调换两个表的顺序相当于右连接) #左边的表全部显示,如果对应右边的表有空数据的话显示null select * from userinfo5 right join department5 on userinfo5.part_id = department5.id; #右连接(调换两个表的顺序相当于左连接) #右边的表全部显示,如果对应左边的表右空数据的话显示null select * from userinfo5 innder join department5 on userinfo5.part_id = department5.id #内连接 将出现null时的一行隐藏
PS:一般连表查询不用*,需要查哪个字段就写哪个字段,字段前最好加上表名,避免不同的表中出现相同的字段,连表后还可以接着连表。
数据库的导入导出
作用:作数据备份
导出现有数据库数据: mysqldump -u用户名 -p密码 数据库名称 > 导出文件路径 # 导出结构+数据 mysqldump -u用户名 -p密码 -d 数据库名称 > 导出文件路径 # 只导出结构 导入现有数据库数据: mysqldump -uroot -p密码 数据库名称 < 文件路径 #导入之前先要保证要导入的数据库存在
MySQL之临时表
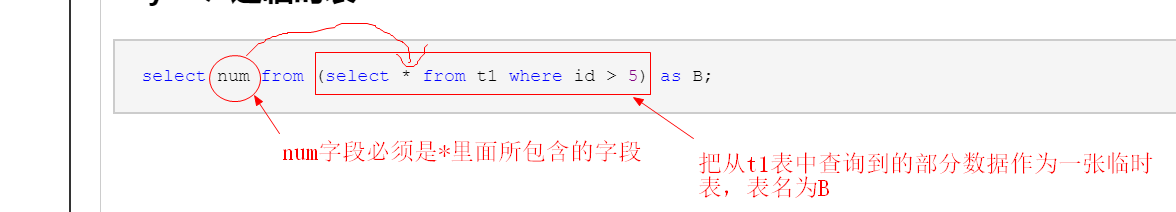
select num from (select * from t1 where id > 5) as B;
MySQL补充用法
select course_id,avg(num),sum(case when num <60 THEN 0 ELSE 1 END)/sum(1) as jgl from score GROUP BY course_id;

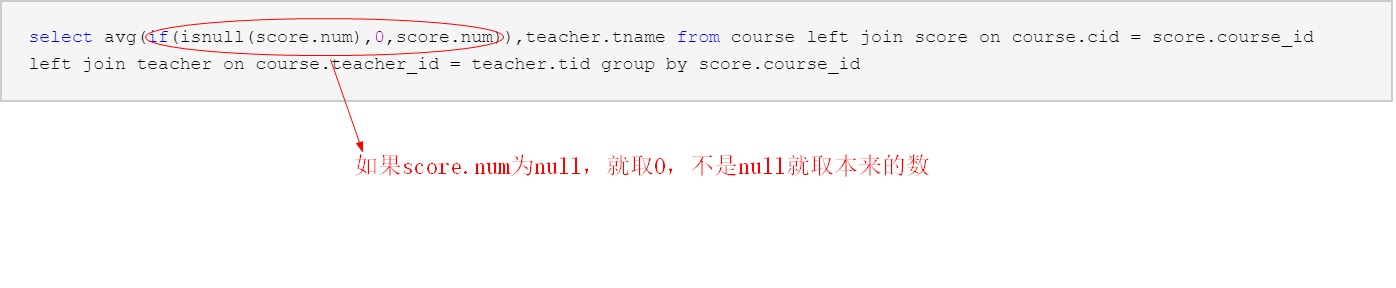
select avg(if(isnull(score.num),0,score.num)),teacher.tname from course left join score on course.cid = score.course_id left join teacher on course.teacher_id = teacher.tid group by score.course_id