1、

代码:
package class20191021; class Grandparent { public Grandparent() { System.out.println("GrandParent Created."); } public Grandparent(String string) { System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string); } } class Parent_2 extends Grandparent { public Parent_2() { //super("Hello.Grandparent."); System.out.println("Parent Created"); // super("Hello.Grandparent."); } } class Child_1 extends Parent_2 { public Child_1() { System.out.println("Child Created"); } } public class TestInherits { public static void main(String args[]) { Child_1 c = new Child_1(); } }
运行结果:
GrandParent Created.
Parent Created
Child Created
修改代码后的运行结果:
GrandParent Created.String:Hello.Grandparent.
Parent Created
Child Created
说明了GrandParent的另一个构造方法运行了,在运行子类前必先运行父类的构造方法,且super方法只能放在子类构造函数的第一句。

因为子类继承了父类的属性和方法,要想初始化子类的对象,则需要父类的属性和方法,所以需要先构造父类的属性和方法,所以要调用父类的构造方法,然后再构造自己在父类的基础上增加的属性和方法。
2、

反编译结果:
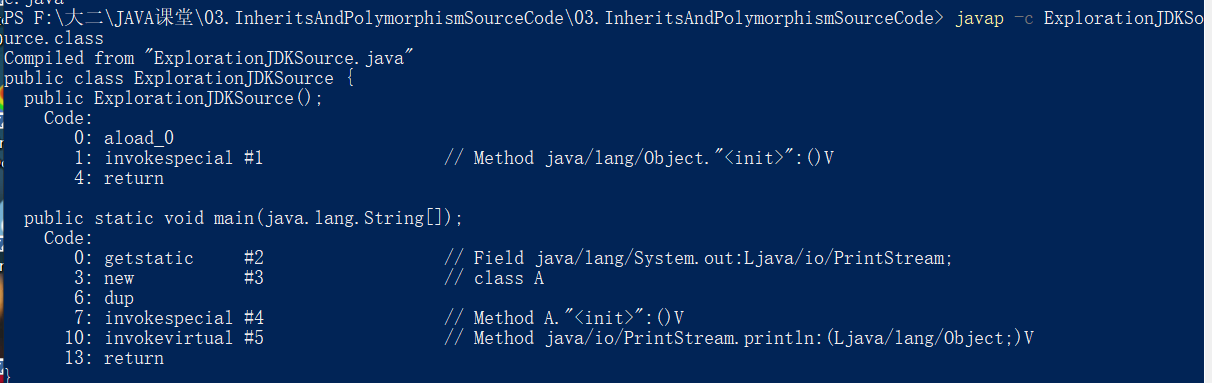
再查看jdk中的源码:

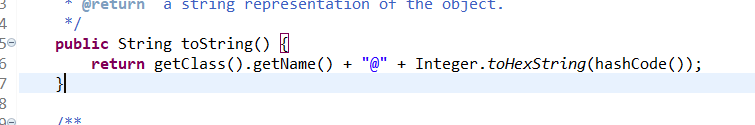
会发现输出的是object类,然而object类转换成字符串时会变成 类名@地址 的格式。
3、

编写的代码:
package class20191021; public class TestOverwrite { public static void main(String[] args) { BBB b = new BBB(); b.f1(); b.f2(); } } class AAA{ public void f1() { System.out.println("A run!"); } } class BBB extends AAA{ public void f1() { System.out.println("B run!"); } public void f2() { super.f1(); } }
运行结果:
B run!
A run!
4、


猜测:
第二句会出错。
结果:

结果是第二句和第四句会出错。说明了父类可以向子类类型转换,而不同的子类直接不能类型转换。
5、

运行结果:
Parent.printValue(),myValue=100 Child.printValue(),myValue=200 Child.printValue(),myValue=200 Child.printValue(),myValue=200 Child.printValue(),myValue=201
6、

不合理的地方:
都是同一个操作--喂养,但是要写三个不同的方法。
7、

代码:
package class20191021; public class TestDuotai { public static void main(String[] args) { Feeder feeder = new Feeder(); feeder.feed(new lion()); feeder.feed(new cat_1()); } } class Feeder{ public void feed(Animal m) { m.eat(); } } interface Animal{ public void eat(); } class lion implements Animal{ public void eat() { System.out.println("狮子要吃肉!"); } } class cat_1 implements Animal { public void eat() { System.out.println("猫咪爱吃鱼!"); } }
运行结果:
狮子要吃肉!
猫咪爱吃鱼!