A Famous City
Time Limit: 10000/3000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 372 Accepted Submission(s): 162
Problem Description
After Mr. B arrived in Warsaw, he was shocked by the skyscrapers and took several photos. But now when he looks at these photos, he finds in surprise that he isn't able to point out even the number of buildings in it. So he decides to work it out as follows:
- divide the photo into n vertical pieces from left to right. The buildings in the photo can be treated as rectangles, the lower edge of which is the horizon. One building may span several consecutive pieces, but each piece can only contain one visible building, or no buildings at all.
- measure the height of each building in that piece.
- write a program to calculate the minimum number of buildings.
Mr. B has finished the first two steps, the last comes to you.
- divide the photo into n vertical pieces from left to right. The buildings in the photo can be treated as rectangles, the lower edge of which is the horizon. One building may span several consecutive pieces, but each piece can only contain one visible building, or no buildings at all.
- measure the height of each building in that piece.
- write a program to calculate the minimum number of buildings.
Mr. B has finished the first two steps, the last comes to you.
Input
Each test case starts with a line containing an integer n (1 <= n <= 100,000). Following this is a line containing n integers - the height of building in each piece respectively. Note that zero height means there are no buildings in this piece at all. All the input numbers will be nonnegative and less than 1,000,000,000.
Output
For each test case, display a single line containing the case number and the minimum possible number of buildings in the photo.
Sample Input
3 1 2 3 3 1 2 1
Sample Output
Case 1: 3 Case 2: 2
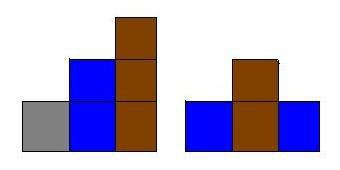
Hint
The possible configurations of the samples are illustrated below:
Source
题意是求最小的建筑物的个数 因为一开始老吴把题意给弄错了 所以没怎么做 后来比赛结束了才做出来的 悲剧啊 这题目很简单
用一个数组进行标记就行了 网后面遇到比他大的数不管 小的数只要往前面找一个最小的值 再与这个值进行比较 不相等就sum++
 View Code
View Code
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 4 int n, ans, test; 5 int a[100005], lk[100005]; 6 7 int main() { 8 while(scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) { 9 a[0] = -1; 10 for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) scanf("%d", &a[i]); 11 lk[1] = 0; 12 ans = (a[1]==0 ? 0 : 1); 13 for(int i=2; i<=n; i++) { 14 lk[i] = i-1; 15 while(a[lk[i]] > a[i]) lk[i] = lk[lk[i]]; 16 if(a[i] != 0 && a[lk[i]] != a[i]) ans++; 17 } 18 printf("Case %d: %d\n", ++test, ans); 19 } 20 return 0; 21 }
