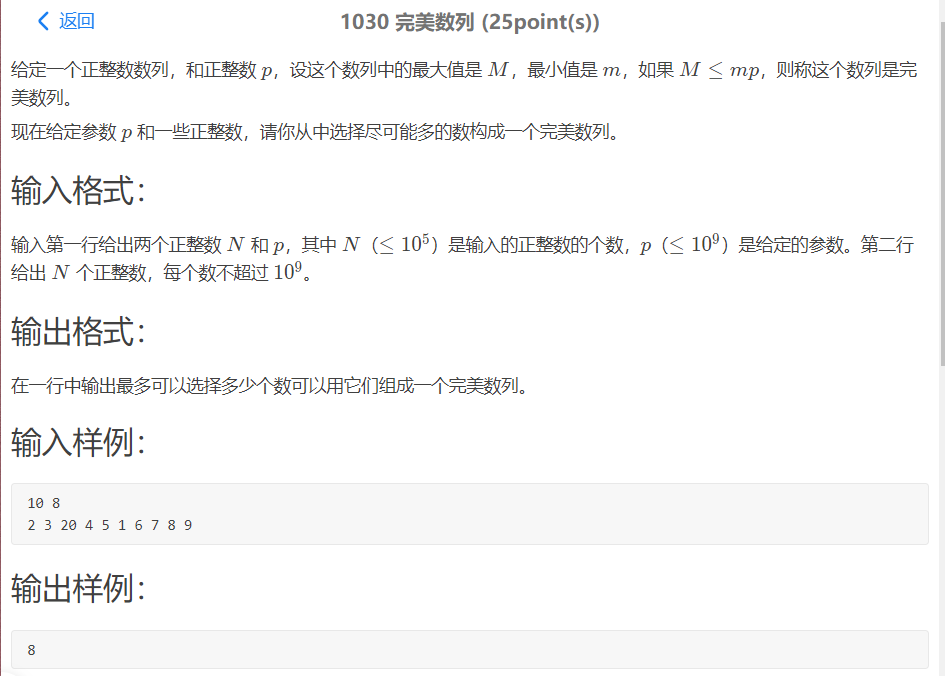
首先说一下这道题的坑点
1:p是一个10^9的数,所以要用long long的数据类型存储,否则会wa的一塌糊涂(教训orz)
2: 测试点4的样例的数据应该非常多,所以在找数字的时候不要用for循环从1-n遍历,否则不给过,这里我使用的是lower_bound函数,在使用这个函数之前首先得让查询数组是从小到大排序。(代码之后会详细讲解,有兴趣可以看看)
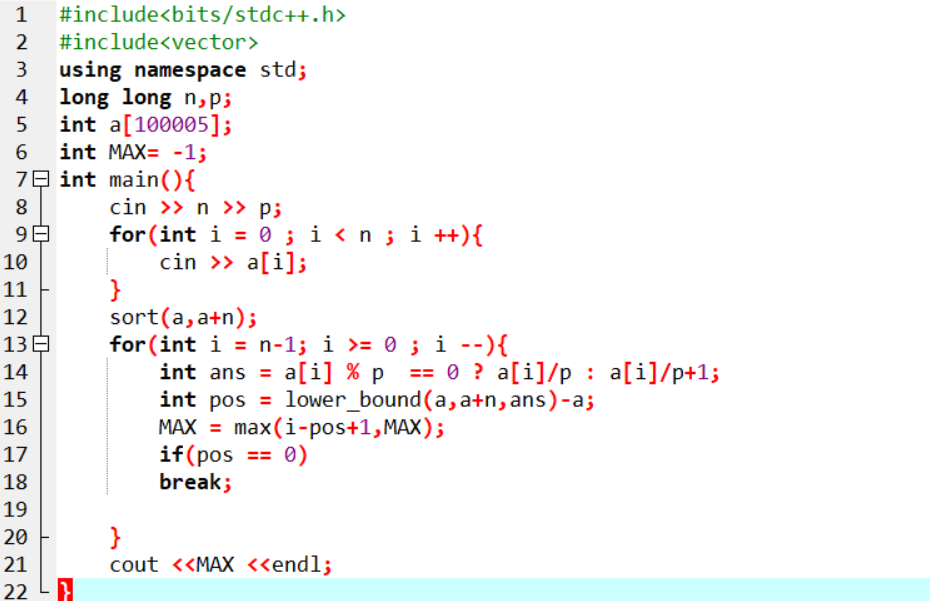
现在来介绍一下,lower_bound(),upper_bound()常见用法
lower_bound(),upper_bound()都是利用二分查找的方法在一个排好序的数组中进行查找
数组从小到大排序:
- lower_bound(begin,end,num): 从数组的begin位置到end-1位置二分查找第一个大于或等于num的数字,找到返回该数字的地址,不存在则返回end。通过返回地址减去起始地址begin,得到所找出的数字在数组中的下标
- upper_bound(begin,end,num):从数组的begin位置到end-1位置二分查找第一个大于num的数字,找到返回该数字的地址,不存在则返回end。通过返回地址减去起始地址begin,得到所找出的数字在数组中的下标
数组从大到小:
- lower(begin,end,num,greater<int> ()):从数组的begin位置到end-1位置二分查找第一个小于或等于num的数字,找到返回该数字的地址,不存在则返回end。通过返回的地址减去起始地址begin,得到找到数字在数组中的下标。
- upper_bound( begin,end,num,greater<type>() ):从数组的begin位置到end-1位置二分查找第一个小于num的数字,找到返回该数字的地址,不存在则返回end。通过返回的地址减去起始地址begin,得到找到数字在数组中的下标。
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 int a[10]= {2,3,8,9,10,1,12,8,4,7}; 4 int cmp(int a,int b){ 5 return a > b; 6 } 7 int main(){ 8 sort(a,a+10); 9 int l_index = lower_bound(a,a+10,8) - a; 10 cout << l_index << " " << a[l_index] << endl; // 5 8 11 int h_index = upper_bound(a,a+10,8) - a; 12 cout << h_index << " " << a[h_index] << endl; // 7 9 13 sort(a,a+10,cmp); 14 int down = lower_bound(a,a+10,11,greater<int>()) - a; 15 cout << " "<< down << " "<< a[down]<<endl; // 1 10 16 int up = upper_bound(a,a+10,10,greater<int>()) - a; 17 cout << " " << up << " " << a[up] << endl; // 2 9 18 }