Android实现入门界面布局
开发工具:Andorid Studio 1.3
运行环境:Android 4.4 KitKat
代码实现
首先是常量的定义,安卓中固定字符串应该定义在常量中。
strings.xml
<resources>
<string name="app_name">Exp1</string>
<string name="title_activity_personal_info">PersonalInfo</string>
<string name="welcome_info">Welcome to first Android Class</string>
<string name="personal_info">个人信息</string>
<string name="submit">提交</string>
<string name="student_id">学号</string>
<string name="name">姓名</string>
<string name="man">男</string>
<string name="woman">女</string>
<string name="register">Register</string>
<string name="login">Login</string>
<string name="user">user:</string>
<string name="input_hint">Input Your User Account Here</string>
<string name="input_password">password:</string>
<string name="pick_aspect">选择你的方向</string>
<string name="pick_birthday">选择你的生日</string>
</resources>
color.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<color name="green">#0eff2e</color>
<color name="purple">#ff18c5</color>
</resources>
arrays.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<string-array name="aspect">
<item>移动</item>
<item>软院</item>
<item>管理</item>
<item>政务</item>
<item>环境</item>
</string-array>
</resources>
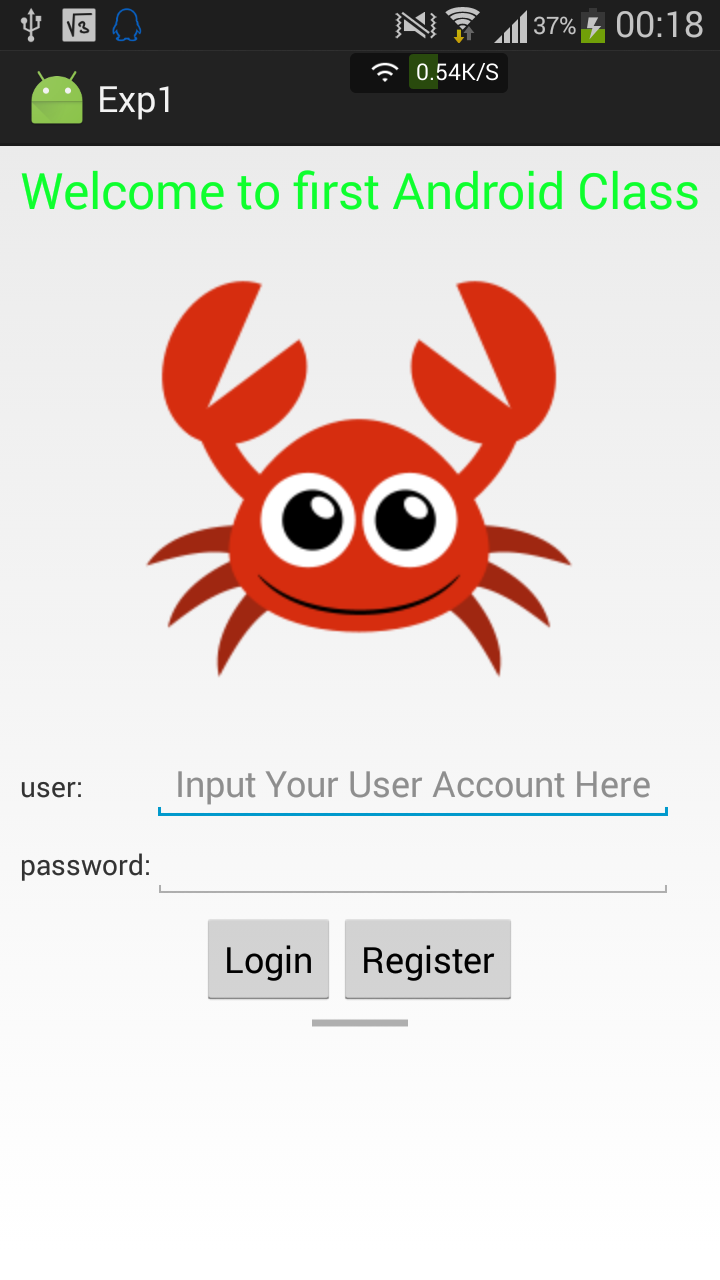
界面一:(LinearLayout、TableLayout)
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingLeft="5dp"
android:paddingRight="5dp"
android:paddingTop="5dp"
android:paddingBottom="5dp"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceSmall"
android:text="@string/welcome_info"
android:id="@+id/title"
android:textColor="@color/green"
android:textSize="25sp"
android:gravity="center"/>
<ImageView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/logoImage"
android:src="@mipmap/crab"/>
<TableLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingLeft="5dp"
android:paddingRight="5dp"
android:paddingTop="5dp"
android:paddingBottom="5dp"
>
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/user"
/>
<EditText
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:hint="@string/input_hint"/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/input_password"/>
<EditText
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/login"
android:id="@+id/btn_login" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/register"
android:id="@+id/btn_register" />
</LinearLayout>
<ProgressBar
style="?android:attr/progressBarStyleHorizontal"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/progressBar"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" />
</LinearLayout>
注意:
- 外层的定义可以使用LinearLayout,加上属性android:orientation="vertical",就变成了线性垂直布局,这是安卓开发中比较常用的基本布局。
- TableLayout中实现占据一行剩余空间还有另一种实现方法,
<EditText android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_weight="1" />,重点就在于layout_weight这上面。 - 两个button水平居中的实现使用的是嵌套布局,也就是在Layout中还有Layout,但要合理使用Layout,避免区域重复渲染,安卓开发者人员调试工具中可以看到渲染情况。
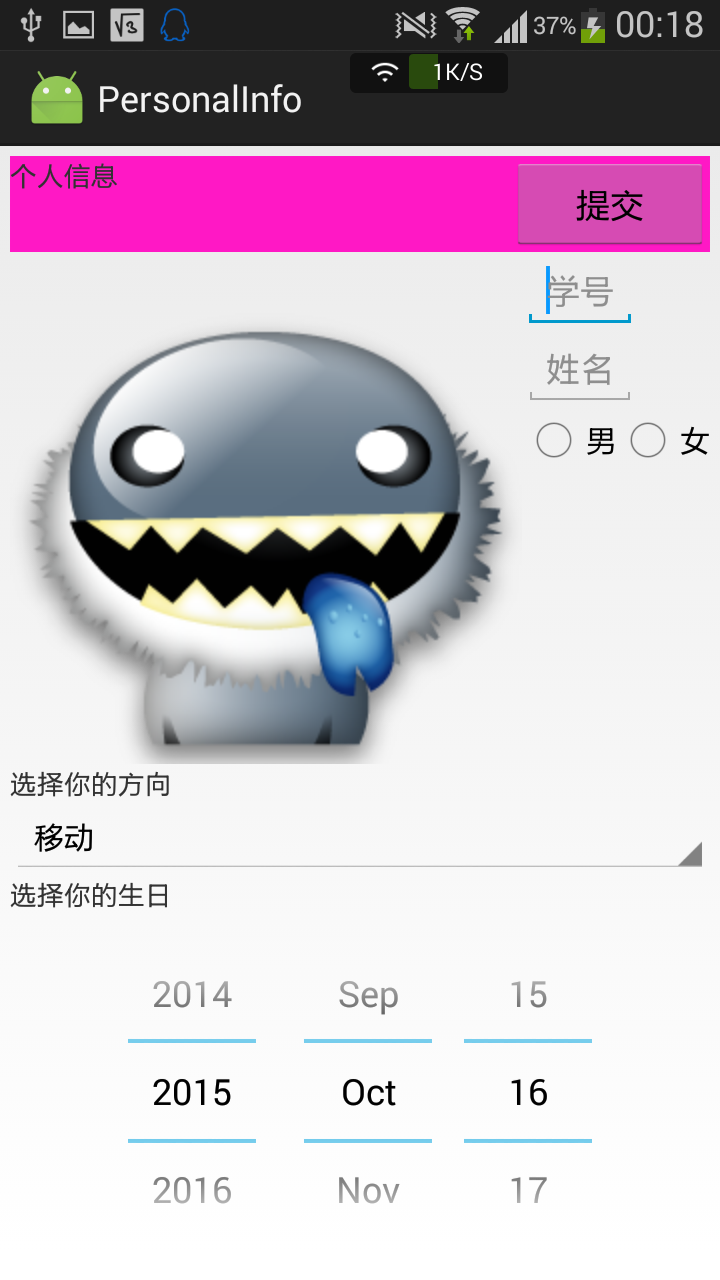
界面二:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingLeft="5dp"
android:paddingRight="5dp"
android:paddingTop="5dp"
android:paddingBottom="5dp"
android:orientation="vertical">
<FrameLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@color/purple">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/personal_info"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="end"
android:text="@string/submit"
android:minWidth="100dp"
android:id="@+id/submit"/>
</FrameLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@mipmap/avatar"
android:id="@+id/avatar" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<EditText
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="@string/student_id"/>
<EditText
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="@string/name"/>
<RadioGroup
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<RadioButton
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/man"/>
<RadioButton
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/woman"/>
</RadioGroup>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/pick_aspect"/>
<Spinner
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/aspect"
android:entries="@array/aspect"
android:prompt="@string/pick_aspect">
</Spinner>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/pick_birthday"/>
<DatePicker
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:calendarViewShown="false">
</DatePicker>
</LinearLayout>
注意:
- FrameLayout会将所有的子元素放在整个布局的左上角,后面的子元素会直接覆盖前面的子元素,因此需要添加layout_gravity参数控制方向。
效果图
由于是真机测试,因此给两个按钮加入了跳转响应,这些内容在后面的博客中再讲实现。
一些总结
学到的东西:
- android:orientation="vertical"
布局的方向 - android:layout_width="match_parent"
和父级元素同样的宽度 - android:layout_width="fill_parent"
填充父级元素剩余的宽度 - android:layout_height="wrap_content"
根据内容来决定高度 - android:gravity="center"
决定自动靠拢的位置 - android:textColor="@color/green"
修改文本中文字的颜色 - android:src="@mipmap/crab"
图片的源地址 - android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
水平居中 - android:minWidth="100dp"
最小的宽度设置 - android:background="@color/purple"
布局控件的底色 - android:entries="@array/aspect"
Spinner控件的静态内容 - android:calendarViewShown="false"
DataPicker隐藏日历的方法
不同的Layout的简要不同:
| Layout名称 | 区别 |
|---|---|
| LinearLayout | 按照水平或垂直的顺序将子元素(可以是控件或布局)依次按照顺序排列,每一个元素都位于前面一个元素之后 |
| TableLayout | 适用于多行多列的布局格式,每个TableLayout是由多个TableRow组成,一个TableRow就表示TableLayout中的每一行,这一行可以由多个子元素组成 |
| RelativeLayout | 按照子元素之间的位置关系完成布局 |
| FrameLayout | 将所有的子元素放在整个界面的左上角,后面的子元素直接覆盖前面的子元素 |
| AbsoluteLayou | 将所有的子元素通过设置android:layout_x 和 android:layout_y属性,将子元素的坐标位置固定下来 |
| GridLayout | 使用虚细线将布局划分为行、列和单元格,也支持一个控件在行、列上都有交错排列 |
工程下载
传送门:下载