求单链表中有效节点的个数
代码实现
public static int countNode(HeroNode head) {
if(head.next == null) {
return 0;
}
int count = 0;
HeroNode current = head.next;
while(true) {
if(current == null) {
break;
}else {
count++;
current = current.next;
}
}
return count;
}
查找单向链表中的倒数第 k 个节点(新浪面试题)
思路分析
1. 接收一个index(倒数第几个的参数)
2. 获取当前链表中有效节点的个数 size
3. 遍历(size - index)次
4. 如果找到,返回节点,没找到,返回null
代码实现
public static HeroNode findLastHeroNode(HeroNode head, int index) {
// 判断链表是否为空
if(head.next == null) {
return null;
}
// 获取链表有效数据的个数
int size = CountNode.countNode(head);
// 校验index
if(index <= 0 || index > size) {
return null;
}
HeroNode current = head.next;
for(int i = 0; i < size - index; i++) {
current = current.next;
}
return current;
}
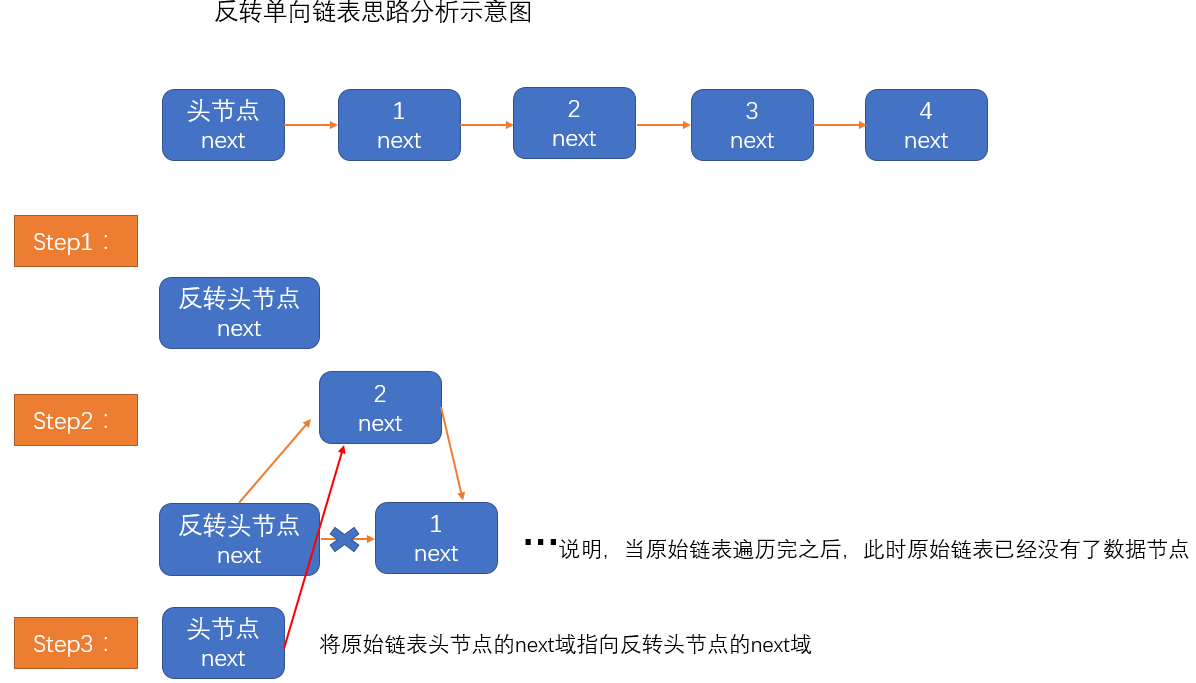
单向链表的反转(腾讯面试题)
思路分析
1. 定义一个反转链表的头节点
2. 遍历原始链表,每取出一个节点就插在反转链表头节点的下一个位置
3. 最后将原始链表的头节点指向反转链表的头节点即可
图解
代码实现
public static void reverse(HeroNode head) {
// 判断链表是否为空或者只有一个元素
if(head.next == null || head.next.next == null) {
return;
}
HeroNode temp = head.next; // 临时指针
HeroNode next = null; // 指向临时指针的下一个节点
HeroNode reverseHead = new HeroNode(0); // 反转链表的头
while(temp != null) {
next = temp.next; // 保存当前节点的下一个节点,后面遍历要用到
temp.next = reverseHead.next; // 当前节点指向反转列表头节点的下一个节点(理解在反转头之后插入当前节点)
reverseHead.next = temp; // 将反转链表的头节点指向当前节点(连接反转头和当前节点)
temp = next; // 后移
}
head.next = reverseHead.next; // 将原始链表的头指向反转之后链表的第一个元素
}
逆序打印单向链表(百度面试题)
代码实现(使用栈)
public static void reversePrint(HeroNode head) {
if(head.next == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空,不能打印");
}
Stack<HeroNode> stack = new Stack<HeroNode>();
HeroNode temp = head.next;
while(temp != null) {
stack.push(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println("逆序打印");
while(stack.size() > 0) {
System.out.println(stack.pop());
}
}
合并两个单向有序链表,要求合并完之后有序
思路分析(使用递归)
说明:两个链表的头节点分别为head1,head2,合并之后单位链表的头结点为newHead
1. 定义一个新的头结点newHead
2. 比较两个链表的头节点,假设head1 小于 head2,则newHead等于head1,然后用head1.next和head2继续比较,小的继续接在新链表的后面。反之亦然
代码实现
public static HeroNode merge(HeroNode head1, HeroNode head2) {
if(head1 == null && head2 == null) {
return null;
}
if(head2 == null) {
return head1;
}
if(head1 == null) {
return head2;
}
HeroNode newHead = null;
if(head1.no < head2.no) {
newHead = head1;
newHead.next = merge(head1.next, head2);
}else if(head1.no == head2.no) { // 如果两个链表的值相等,则选择其中一个即可,两链表同时后移
newHead = head1;
newHead.next = merge(head1.next, head2.next);
}else {
newHead = head2;
newHead.next = merge(head1, head2.next);
}
return newHead;
}
