avro官网
1、Avro历史
Avro是Hadoop的一个数据序列化系统,由Hadoop的创始人Doug Cutting(也是Lucene,Nutch等项目的创始人)开发,设计用于支持大批量数据交换的应用。
它的主要特点有:
- 支持二进制序列化方式,可以便捷,快速地处理大量数据;
- 动态语言友好,Avro提供的机制使动态语言可以方便地处理Avro数据
Hadoop现存的RPC系统遇到一些问题,
- 性能瓶颈(当前采用IPC系统,它使用Java自带的DataOutputStream和DataInputStream);
- 需要服务器端和客户端必须运行相同版本的Hadoop;
- 只能使用Java开发等。
对比其他序列化系统,如Google的Protocol Buffers, Facebook的Thrift可以完全可以满足普通应用的需求。但现存的这些序列化系统自身也有毛病
以Protocol Buffers为例:
- 它需要用户先定义数据结构,然后根据这个数据结构生成代码,再组装数据。如果需要操作多个数据源的数据集,那么需要定义多套数据结构并重复执行多次上面的流程,这样就不能对任意数据集做统一处理。
- 对于Hadoop中Hive和Pig这样的脚本系统来说,使用代码生成是不合理的。并且Protocol Buffers在序列化时考虑到数据定义与数据可能不完全匹配,在数据中添加注解,这会让数据变得庞大并拖慢处理速度。
其它序列化系统有如Protocol Buffers类似的问题。所以为了Hadoop的前途考虑,Doug Cutting主导开发一套全新的序列化系统,这就是Avro于09年加入Hadoop项目族中。
2、Avro的结构
(1)Avro依赖模式(Schema)来实现数据结构定义。可以把模式理解为Java的类,它定义每个实例的结构,可以包含哪些属性。可以根据类来产生任意多个实例对象(比较抽象不过可以看到)。对实例序列化操作时必须需要知道它的基本结构,也就需要参考类的信息。这里,根据模式产生的Avro对象类似于类的实例对象。每次序列化/反序列化时都需要知道模式的具体结构。所以,在Avro可用的一些场景下,如文件存储或是网络通信,都需要模式与数据同时存在。Avro数据以模式来读和写(文件或是网络),并且写入的数据都不需要加入其它标识,这样序列化时速度快且结果内容少。由于程序可以直接根据模式来处理数据,所以Avro更适合于脚本语言的发挥。
Avro的模式主要由JSON对象来表示,它可能会有一些特定的属性,用来描述某种类型(Type)的不同形式。Avro支持八种基本类型(Primitive Type)和六种混合类型(Complex Type)。基本类型可以由JSON字符串来表示。每种不同的混合类型有不同的属性(Attribute)来定义,有些属性是必须的,有些是可选的,如果需要的话,可以用JSON数组来存放多个JSON对象定义。在这几种Avro定义的类型的支持下,可以由用户来创造出丰富的数据结构来,支持用户纷繁复杂的数据。
(2) Avro支持两种序列化编码方式:二进制编码和JSON编码。
- 使用二进制编码会高效序列化,并且序列化后得到的结果会比较小。而JSON一般用于调试系统或是基于WEB的应用。
- 对Avro数据序列化/反序列化时都需要对模式以深度优先(Depth-First),从左到右(Left-to-Right)的遍历顺序来执行。
- 基本类型的序列化容易解决,混合类型的序列化会有很多不同规则。对于基本类型和混合类型的二进制编码在文档中规定,按照模式的解析顺序依次排列字节。对于JSON编码,联合类型(Union Type)就与其它混合类型表现不一致。
(3)Avro为了便于MapReduce的处理定义了一种容器文件格式(Container File Format)。
- 文件中只能有一种模式,所有需要存入这个文件的对象都需要按照这种模式以二进制编码的形式写入。
- 对象在文件中以块(Block)来组织,并且这些对象都是可以被压缩的。
- 块和块之间会存在同步标记符(Synchronization Marker),以便MapReduce方便地切割文件用于处理。
下图是根据文档描述画出的文件结构图(将Avro对象序列化到文件的操作):
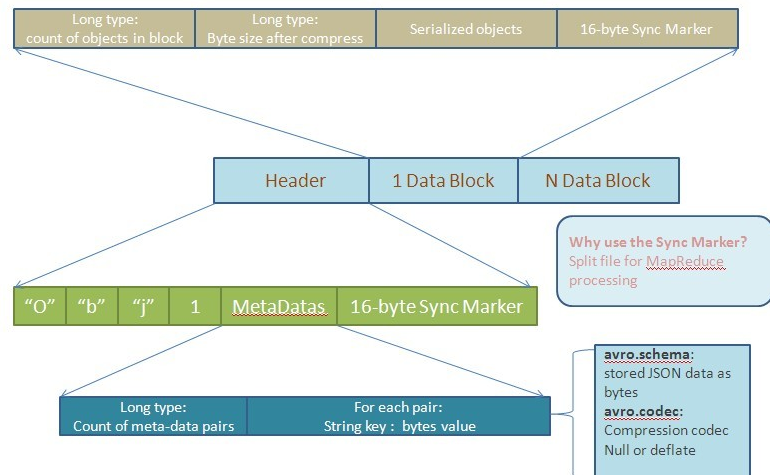
一个存储文件由两部分组成:头信息(Header)和数据块(Data Block)。
(1)头信息又由三部分构成:四个字节的前缀(类似于Magic Number),文件Meta-data信息和随机生成的16字节同步标记符。这里的Meta-data信息让人有些疑惑,它除了文件的模式外,还能包含schema和codec。文档中指出当前Avro认定的就两个Meta-data:schema和codec。这里的codec表示对后面的文件数据块(File Data Block)采用何种压缩方式。Avro的实现都需要支持下面两种压缩方式:null(不压缩)和deflate(使用Deflate算法压缩数据块)。除了文档中认定的两种Meta-data,用户还可以自定义适用于自己的Meta-data。这里用long型来表示有多少个Meta-data数据对,也是让用户在实际应用中可以定义足够的Meta-data信息。对于每对Meta-data信息,都有一个string型的key(需要以“avro.”为前缀)和二进制编码后的value。
(2)每个数据块,结构如下:一个long值记录当前块有多少个对象,一个long值用于记录当前块经过压缩后的字节数,真正的序列化对象和16字节长度的同步标记符。由于对象可以组织成不同的块,使用时就可以不经过反序列化而对某个数据块进行操作。还可以由数据块数,对象数和同步标记符来定位损坏的块以确保数据完整性。
3、RPC框架
Avro也被作为一种RPC框架来使用。客户端希望同服务器端交互时,就需要交换双方通信的协议,它类似于模式,需要双方来定义,在Avro中被称为消息(Message)。通信双方都必须保持这种协议,以便于解析从对方发送过来的数据,这也就是RPC握手阶段。
消息从客户端发送到服务器端需要经过传输层(Transport Layer),它发送消息并接收服务器端的响应。到达传输层的数据就是二进制数据。通常以HTTP作为传输模型,数据以POST方式发送到对方去。在Avro中,它的消息被封装成为一组缓冲区(Buffer),类似于下图的模型:
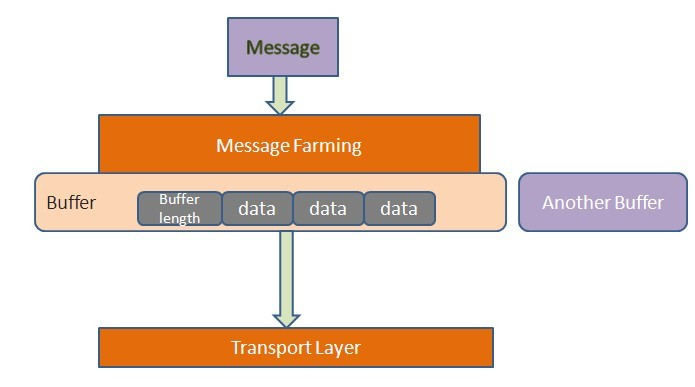
如上图,每个缓冲区以四个字节开头,中间是多个字节的缓冲数据,最后以一个空缓冲区结尾。这种机制的好处在于,发送端在发送数据时可以很方便地组装不同数据源的数据,接收方也可以将数据存入不同的存储区。 当往缓冲区中写数据时,大对象可以独占一个缓冲区,而不是与其它小对象混合存放,便于接收方方便地读取大对象。
Protocol Buffer在传输数据时,往数据中加入注释(annotation),以应对数据结构与数据不匹配的问题。但直接导致数据量变大,解析困难等缺点。那Avro是如何应对模式与数据的不同呢?
为了保证Avro的高效,假定模式至少大部分是匹配的,然后定义一些验证规则,如果在规则满足的前提下,做数据验证。
如果模式不匹配就会报错。相同模式,交互数据时,如果数据中缺少某个域(field),用规范中的默认值设置;如果数据中多了些与模式不匹配的数据。则忽视这些值。
Avro列出的优点中还有一项是:可排序的。一种语言支持的Avro程序在序列化数据后,可由其它语言的Avro程序对未反序列化的数据排序。
4.Avro数据序列化/反序列化
1、下载avro-1.8.2.jar and avro-tools-1.8.2.jar两个jar包,放到指定文件目录。下载地址 http://www.trieuvan.com/apache/avro/1.8.2./java/
2、
在avro中,它是用Json格式来定义模式的。模式可以由基础类型(null, boolean, int, long, float, double, bytes, and string)和复合类型(record, enum, array, map, union, and fixed)的数据组成。这里定义了一个简单的模式User.avsc:
{ "namespace": "com.wqb.hdfs.avro", "type": "record", "name": "User", "fields": [ {"name": "name", "type": "string"}, {"name": "id", "type": "int"}, {"name": "salary", "type": "int"}, {"name": "age", "type": "int"}, {"name": "address", "type": "string"} ] }
3、打开cmd,进入到该目录,执行命令生成User类
在该文件夹下的res 文件下的目录下就会生成 com/wqb/hdfs/avro/User.java 文件。

4、使用eclipse新建maven项目,在pom.xml加入avro的依赖。
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.avro</groupId> <artifactId>avro</artifactId> <version>1.8.2</version> </dependency>
5、把生成的User.java类复制到工程中,注意这个User.java里面生成的User类及其内部类的包名默认是user.avsc文件中的namespace的值。

/** * Autogenerated by Avro * * DO NOT EDIT DIRECTLY */ package com.wqb.hdfs.avro; import org.apache.avro.specific.SpecificData; import org.apache.avro.message.BinaryMessageEncoder; import org.apache.avro.message.BinaryMessageDecoder; import org.apache.avro.message.SchemaStore; @SuppressWarnings("all") @org.apache.avro.specific.AvroGenerated public class User extends org.apache.avro.specific.SpecificRecordBase implements org.apache.avro.specific.SpecificRecord { private static final long serialVersionUID = -8252366833275661088L; public static final org.apache.avro.Schema SCHEMA$ = new org.apache.avro.Schema.Parser().parse("{"type":"record","name":"User","namespace":"com.wqb.hdfs.avro","fields":[{"name":"name","type":"string"},{"name":"id","type":"int"},{"name":"salary","type":"int"},{"name":"age","type":"int"},{"name":"address","type":"string"}]}"); public static org.apache.avro.Schema getClassSchema() { return SCHEMA$; } private static SpecificData MODEL$ = new SpecificData(); private static final BinaryMessageEncoder<User> ENCODER = new BinaryMessageEncoder<User>(MODEL$, SCHEMA$); private static final BinaryMessageDecoder<User> DECODER = new BinaryMessageDecoder<User>(MODEL$, SCHEMA$); /** * Return the BinaryMessageDecoder instance used by this class. */ public static BinaryMessageDecoder<User> getDecoder() { return DECODER; } /** * Create a new BinaryMessageDecoder instance for this class that uses the specified {@link SchemaStore}. * @param resolver a {@link SchemaStore} used to find schemas by fingerprint */ public static BinaryMessageDecoder<User> createDecoder(SchemaStore resolver) { return new BinaryMessageDecoder<User>(MODEL$, SCHEMA$, resolver); } /** Serializes this User to a ByteBuffer. */ public java.nio.ByteBuffer toByteBuffer() throws java.io.IOException { return ENCODER.encode(this); } /** Deserializes a User from a ByteBuffer. */ public static User fromByteBuffer( java.nio.ByteBuffer b) throws java.io.IOException { return DECODER.decode(b); } @Deprecated public CharSequence name; @Deprecated public int id; @Deprecated public int salary; @Deprecated public int age; @Deprecated public CharSequence address; /** * Default constructor. Note that this does not initialize fields * to their default values from the schema. If that is desired then * one should use <code>newBuilder()</code>. */ public User() {} /** * All-args constructor. * @param name The new value for name * @param id The new value for id * @param salary The new value for salary * @param age The new value for age * @param address The new value for address */ public User(CharSequence name, Integer id, Integer salary, Integer age, CharSequence address) { this.name = name; this.id = id; this.salary = salary; this.age = age; this.address = address; } public org.apache.avro.Schema getSchema() { return SCHEMA$; } // Used by DatumWriter. Applications should not call. public Object get(int field$) { switch (field$) { case 0: return name; case 1: return id; case 2: return salary; case 3: return age; case 4: return address; default: throw new org.apache.avro.AvroRuntimeException("Bad index"); } } // Used by DatumReader. Applications should not call. @SuppressWarnings(value="unchecked") public void put(int field$, Object value$) { switch (field$) { case 0: name = (CharSequence)value$; break; case 1: id = (Integer)value$; break; case 2: salary = (Integer)value$; break; case 3: age = (Integer)value$; break; case 4: address = (CharSequence)value$; break; default: throw new org.apache.avro.AvroRuntimeException("Bad index"); } } /** * Gets the value of the 'name' field. * @return The value of the 'name' field. */ public CharSequence getName() { return name; } /** * Sets the value of the 'name' field. * @param value the value to set. */ public void setName(CharSequence value) { this.name = value; } /** * Gets the value of the 'id' field. * @return The value of the 'id' field. */ public Integer getId() { return id; } /** * Sets the value of the 'id' field. * @param value the value to set. */ public void setId(Integer value) { this.id = value; } /** * Gets the value of the 'salary' field. * @return The value of the 'salary' field. */ public Integer getSalary() { return salary; } /** * Sets the value of the 'salary' field. * @param value the value to set. */ public void setSalary(Integer value) { this.salary = value; } /** * Gets the value of the 'age' field. * @return The value of the 'age' field. */ public Integer getAge() { return age; } /** * Sets the value of the 'age' field. * @param value the value to set. */ public void setAge(Integer value) { this.age = value; } /** * Gets the value of the 'address' field. * @return The value of the 'address' field. */ public CharSequence getAddress() { return address; } /** * Sets the value of the 'address' field. * @param value the value to set. */ public void setAddress(CharSequence value) { this.address = value; } /** * Creates a new User RecordBuilder. * @return A new User RecordBuilder */ public static Builder newBuilder() { return new Builder(); } /** * Creates a new User RecordBuilder by copying an existing Builder. * @param other The existing builder to copy. * @return A new User RecordBuilder */ public static Builder newBuilder(Builder other) { return new Builder(other); } /** * Creates a new User RecordBuilder by copying an existing User instance. * @param other The existing instance to copy. * @return A new User RecordBuilder */ public static Builder newBuilder(User other) { return new Builder(other); } /** * RecordBuilder for User instances. */ public static class Builder extends org.apache.avro.specific.SpecificRecordBuilderBase<User> implements org.apache.avro.data.RecordBuilder<User> { private CharSequence name; private int id; private int salary; private int age; private CharSequence address; /** Creates a new Builder */ private Builder() { super(SCHEMA$); } /** * Creates a Builder by copying an existing Builder. * @param other The existing Builder to copy. */ private Builder(Builder other) { super(other); if (isValidValue(fields()[0], other.name)) { this.name = data().deepCopy(fields()[0].schema(), other.name); fieldSetFlags()[0] = true; } if (isValidValue(fields()[1], other.id)) { this.id = data().deepCopy(fields()[1].schema(), other.id); fieldSetFlags()[1] = true; } if (isValidValue(fields()[2], other.salary)) { this.salary = data().deepCopy(fields()[2].schema(), other.salary); fieldSetFlags()[2] = true; } if (isValidValue(fields()[3], other.age)) { this.age = data().deepCopy(fields()[3].schema(), other.age); fieldSetFlags()[3] = true; } if (isValidValue(fields()[4], other.address)) { this.address = data().deepCopy(fields()[4].schema(), other.address); fieldSetFlags()[4] = true; } } /** * Creates a Builder by copying an existing User instance * @param other The existing instance to copy. */ private Builder(User other) { super(SCHEMA$); if (isValidValue(fields()[0], other.name)) { this.name = data().deepCopy(fields()[0].schema(), other.name); fieldSetFlags()[0] = true; } if (isValidValue(fields()[1], other.id)) { this.id = data().deepCopy(fields()[1].schema(), other.id); fieldSetFlags()[1] = true; } if (isValidValue(fields()[2], other.salary)) { this.salary = data().deepCopy(fields()[2].schema(), other.salary); fieldSetFlags()[2] = true; } if (isValidValue(fields()[3], other.age)) { this.age = data().deepCopy(fields()[3].schema(), other.age); fieldSetFlags()[3] = true; } if (isValidValue(fields()[4], other.address)) { this.address = data().deepCopy(fields()[4].schema(), other.address); fieldSetFlags()[4] = true; } } /** * Gets the value of the 'name' field. * @return The value. */ public CharSequence getName() { return name; } /** * Sets the value of the 'name' field. * @param value The value of 'name'. * @return This builder. */ public Builder setName(CharSequence value) { validate(fields()[0], value); this.name = value; fieldSetFlags()[0] = true; return this; } /** * Checks whether the 'name' field has been set. * @return True if the 'name' field has been set, false otherwise. */ public boolean hasName() { return fieldSetFlags()[0]; } /** * Clears the value of the 'name' field. * @return This builder. */ public Builder clearName() { name = null; fieldSetFlags()[0] = false; return this; } /** * Gets the value of the 'id' field. * @return The value. */ public Integer getId() { return id; } /** * Sets the value of the 'id' field. * @param value The value of 'id'. * @return This builder. */ public Builder setId(int value) { validate(fields()[1], value); this.id = value; fieldSetFlags()[1] = true; return this; } /** * Checks whether the 'id' field has been set. * @return True if the 'id' field has been set, false otherwise. */ public boolean hasId() { return fieldSetFlags()[1]; } /** * Clears the value of the 'id' field. * @return This builder. */ public Builder clearId() { fieldSetFlags()[1] = false; return this; } /** * Gets the value of the 'salary' field. * @return The value. */ public Integer getSalary() { return salary; } /** * Sets the value of the 'salary' field. * @param value The value of 'salary'. * @return This builder. */ public Builder setSalary(int value) { validate(fields()[2], value); this.salary = value; fieldSetFlags()[2] = true; return this; } /** * Checks whether the 'salary' field has been set. * @return True if the 'salary' field has been set, false otherwise. */ public boolean hasSalary() { return fieldSetFlags()[2]; } /** * Clears the value of the 'salary' field. * @return This builder. */ public Builder clearSalary() { fieldSetFlags()[2] = false; return this; } /** * Gets the value of the 'age' field. * @return The value. */ public Integer getAge() { return age; } /** * Sets the value of the 'age' field. * @param value The value of 'age'. * @return This builder. */ public Builder setAge(int value) { validate(fields()[3], value); this.age = value; fieldSetFlags()[3] = true; return this; } /** * Checks whether the 'age' field has been set. * @return True if the 'age' field has been set, false otherwise. */ public boolean hasAge() { return fieldSetFlags()[3]; } /** * Clears the value of the 'age' field. * @return This builder. */ public Builder clearAge() { fieldSetFlags()[3] = false; return this; } /** * Gets the value of the 'address' field. * @return The value. */ public CharSequence getAddress() { return address; } /** * Sets the value of the 'address' field. * @param value The value of 'address'. * @return This builder. */ public Builder setAddress(CharSequence value) { validate(fields()[4], value); this.address = value; fieldSetFlags()[4] = true; return this; } /** * Checks whether the 'address' field has been set. * @return True if the 'address' field has been set, false otherwise. */ public boolean hasAddress() { return fieldSetFlags()[4]; } /** * Clears the value of the 'address' field. * @return This builder. */ public Builder clearAddress() { address = null; fieldSetFlags()[4] = false; return this; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public User build() { try { User record = new User(); record.name = fieldSetFlags()[0] ? this.name : (CharSequence) defaultValue(fields()[0]); record.id = fieldSetFlags()[1] ? this.id : (Integer) defaultValue(fields()[1]); record.salary = fieldSetFlags()[2] ? this.salary : (Integer) defaultValue(fields()[2]); record.age = fieldSetFlags()[3] ? this.age : (Integer) defaultValue(fields()[3]); record.address = fieldSetFlags()[4] ? this.address : (CharSequence) defaultValue(fields()[4]); return record; } catch (Exception e) { throw new org.apache.avro.AvroRuntimeException(e); } } } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") private static final org.apache.avro.io.DatumWriter<User> WRITER$ = (org.apache.avro.io.DatumWriter<User>)MODEL$.createDatumWriter(SCHEMA$); @Override public void writeExternal(java.io.ObjectOutput out) throws java.io.IOException { WRITER$.write(this, SpecificData.getEncoder(out)); } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") private static final org.apache.avro.io.DatumReader<User> READER$ = (org.apache.avro.io.DatumReader<User>)MODEL$.createDatumReader(SCHEMA$); @Override public void readExternal(java.io.ObjectInput in) throws java.io.IOException { READER$.read(this, SpecificData.getDecoder(in)); } }
6、实现序列化avro文件。
package com.wqb.hdfs.avro; import org.apache.avro.file.DataFileWriter; import org.apache.avro.io.DatumWriter; import org.apache.avro.specific.SpecificDatumWriter; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; public class testAvro { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 声明并初始化User对象 // 方式一 User user1 = new User(); user1.setName("wqbin"); user1.setId(1); user1.setSalary(1000); user1.setAge(20); user1.setAddress("beijing"); // 方式二 使用构造函数 // Alternate constructor User user2 = new User("wang", 2, 1000, 19, "guangzhou"); // 方式三,使用Build方式 // Construct via builder User user3 = User.newBuilder() .setName("bin") .setId(3) .setAge(21) .setSalary(2000) .setAddress("shenzhen") .build(); String path = "E:\avro\fuxi\User.avro"; // avro文件存放目录 DatumWriter<User> userDatumWriter = new SpecificDatumWriter<User>(User.class); DataFileWriter<User> dataFileWriter = new DataFileWriter<User>(userDatumWriter); dataFileWriter.create(user1.getSchema(), new File(path)); // 把生成的user对象写入到avro文件 dataFileWriter.append(user1); dataFileWriter.append(user2); dataFileWriter.append(user3); dataFileWriter.close(); } }


7、实现avro反序列化
@Test public void testDeSerial() throws IOException { DatumReader<User> reader = new SpecificDatumReader<User>(User.class); DataFileReader<User> dataFileReader = new DataFileReader<User>(new File("E:\avro\fuxi\User.avro"), reader); User user = null; while (dataFileReader.hasNext()) { user = dataFileReader.next(); System.out.println(user); } }

