Java深入学习15:Java线程池
一、线程池的作用
线程池提供一个线程队列,队列中保存着所有等待状态的线程。避免了创建与销毁等额外开销,提交了响应的速度。
二、类关系
Java线程池相关的接口和类均在 java.util.concurrent 包下,其相关关系(部分)如下
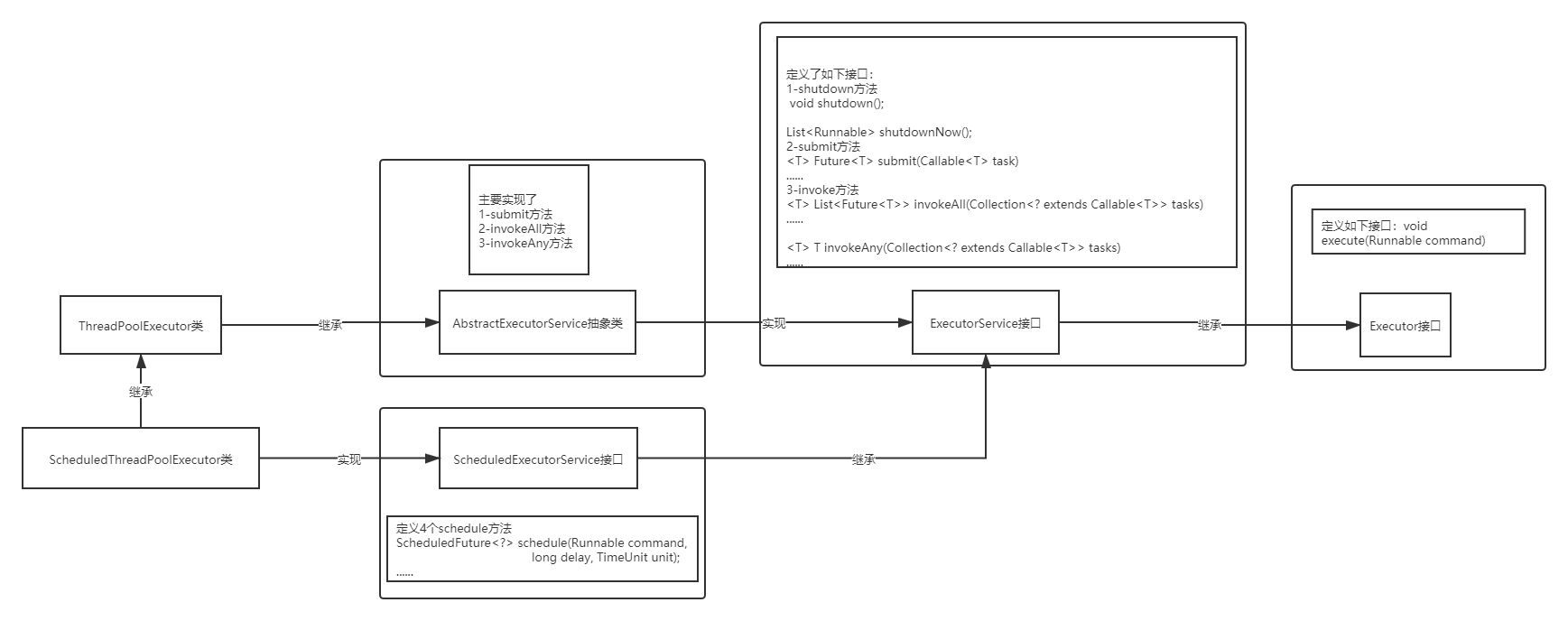
三、Executors类以及相关常用方法介绍
1-Executors类简介:简单的说是线程方法的工具类,提供了 创建线程池等方法。
2-ExecutorService 类创建线程池
//创建缓存线程池,线程数量不固定,可以自动调节线程数量 ExecutorService executor1 = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); //创建缓存线程池,并且只有一个线程数量 ExecutorService executor2 = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); //创建缓存线程池,并指定线程数量 ExecutorService executor3 = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
3-ExecutorService 类执行线程
public class ThreadPoolTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { //创建线程池 ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5); //方法1-1:Future<?> submit(Runnable task);有返回值 executor.submit(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " runnable"); } }); //方法1-2:<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);有返回值 Future<Object> future = executor.submit(new Callable<Object>() { @Override public Object call() throws Exception { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " callable"); return new Random().nextInt(100); } }); System.out.println(future.get()); //方法2-1:void execute(Runnable command)。没有返回值 executor.execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Runnable"); } }); //关闭线程池。ExecutorService executor.shutdown(); } }
4-ScheduledExecutorService 使用
public class ThreadPoolTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { //1-创建线程池 ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5); //2-执行线程,延迟2秒执行 for(int i=0; i<10; i++){ scheduledExecutor.schedule(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } },2,TimeUnit.SECONDS ); } //3-关闭线程池 scheduledExecutor.shutdown(); } } ------------------------------日志输出------------------------------ pool-1-thread-1 pool-1-thread-1 pool-1-thread-1 pool-1-thread-1 pool-1-thread-3 pool-1-thread-3 pool-1-thread-5 pool-1-thread-2 pool-1-thread-4 pool-1-thread-1 //日志说明:线程只有5个,并且会重复使用
5- submit()和execute()区别
1- 接收的参数不一样
2- submit有返回值,而execute没有。用到返回值的例子,比如说我有很多个做validation的task,我希望所有的task执行完,然后每个task告诉我它的执行结果,是成功还是失败,如果是失败,原因是什么。
3- submit方便Exception处理。意思就是如果你在你的task里会抛出checked或者unchecked exception,而你又希望外面的调用者能够感知这些exception并做出及时的处理,那么就需要用到submit,通过捕获Future.get抛出的异常。
END