Springboot学习06-Spring AOP封装接口自定义校验
关键字
BindingResult、Spring AOP、自定义注解、自定义异常处理、ConstraintValidator
前言
在实际项目中,对接口的传如的参数需要做校验处理,原来都是在接口里面直接进行if判断,虽然简单,但是每个接口都要重复写,显得冗余;并且返回的数据也无法很好的自定义说明校验情况;如下;
@RequestMapping(value = { "/get/authcode" }, method = {RequestMethod.POST })
public Object getSignInAuthCode(@RequestBody AuthCodeReq authCodeReq) throws Exception {
//每个数据都要这样重复写
if(StringUtils.isBlank(authCodeReq.getMobile())){
//返回数据也是固定格式,无法知道究竟是什么数据校验没通过
return ResponseMessageEnum.ARGUMENT_EXCEPTION.toString();
}
//业务逻辑略
}

正文
0-封装全局数据校验功能的目的
1-避免每个接口重复使用if判断,显得冗余
2-可以自定义返回数据,告诉前端什么数据检验失败
1-POST请求业务逻辑(且数据以json格式放在body中传入)
1-将数据校验的具体内容放在POJO中,通过注解进行,见源码-01
2-当前端URL请求(POST请求,且数据以json格式放在body中传入),且有数据校验失败时,传参BindException exception会接收校验失败的结果,见源码-02
3-使用Spring AOP的前置方法处理数据检验,见源码-03
3-1-自定义注解MyValidateAopAnnotation(见源码-04),用于定位AOP的Pointcut(见源码-03)
3-2-AOP前置方法,根据joinPoint获取接口方法BindingResult参数值(见源码-03)
3-3-如果bindingResult.hasErrors()为true,则表明数据校验没有通过(见源码-03),则直接抛出BindException异常()
3-4-在GlobalExceptionHandler类中的BindExceptionHandler方法,专门处理BindException异常,返回json数据(见源码-05)
2-GET请求
3-源码分析
//1-POJO import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.NotEmpty; import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull; public class ValidateAuthCodeReq { @NotEmpty(message = "手机号不能为空")//message将在接口返回数据中得以体现 private String mobile;//手机号 @NotEmpty(message = "验证码不能为空") private String code;//验证码 public String getMobile() { return mobile; } public void setMobile(String mobile) { this.mobile = mobile; } public String getCode() { return code; } public void setCode(String code) { this.code = code; } } //2-controller层接口方法 @RestController @RequestMapping(value="/api/shop/login") public class ApiShopLoginController extends ApiShopBaseController { //2-2-校验并绑定手机号 @MyValidateAopAnnotation//自定义注解,用户AOP定位方法 @RequestMapping(value = { "/validate/authcode" }, method = {RequestMethod.POST }) public Object validateAndBind( @Valid @RequestBody ValidateAuthCodeReq validateAuthCodeReq,BindingResult bindingResult) throws Exception { //BindingResult封装了数据校验结果 //业务逻辑略 } } //3-AOP方法,统一处理数据校验 @Aspect @Component public class ExceptionAspect { //根据自定义注解MyValidateAopAnnotation定位方法 @Pointcut("@annotation(com.hs.web.common.exception.MyValidateAopAnnotation)") public void bindPointCut() { } @Before("bindPointCut()") public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) throws BindException { // 接收到请求 ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes(); //获取请求的request HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest(); //获取BindingResult,并进行判断 Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs(); BindingResult bindingResult = (BindingResult)args[args.length-1]; if(bindingResult.hasErrors()){ throw new BindException(bindingResult); } System.out.println("args[args.length-1]: "+ args[args.length-1]); System.out.println("bindingResult" + bindingResult); } } //4-自定义注解MyValidateAopAnnotation-目的是为了AOP定位 @Target({ METHOD, FIELD, CONSTRUCTOR, PARAMETER }) @Retention(RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface MyValidateAopAnnotation { } //5-全局异常处理类 import com.hs.common.util.json.JsonUtil; @ControllerAdvice @ResponseBody public class GlobalExceptionHandler { //数据校验 @ExceptionHandler(value=BindException.class) public String BindExceptionHandler(HttpServletRequest request,BindException exception) throws Exception{ logger.warn(exception); //1-封装异常说明 List<ObjectError> errorList = exception.getAllErrors(); StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); for(ObjectError error : errorList){ sb.append("参数" + exception.getFieldError().getField() + "异常:" + exception.getFieldError().getDefaultMessage() + ";"); } //2-封装返回参数 ExceptionResponseBean detailBean = new ExceptionResponseBean( GlobalExceptionEnum.ERROR_DATA_VALIDATION.getCode(), GlobalExceptionEnum.ERROR_DATA_VALIDATION.getMsg(), sb.toString()); //3-以Json格式返回数据 return JsonUtil.toJson(detailBean).toString(); } } //6-异常情况枚举 import com.hs.common.util.json.JsonUtil; public enum GlobalExceptionEnum { OTHER_EXCEPTION(800, "出现异常", "其它异常,待识别", Exception.class), ERROR_DATA_VALIDATION(801, "数据校验异常", "请求参数数据校验异常", BindException.class), ; private int code; private String msg; private ExceptionResponseDetailBean data; private Class exception; private GlobalExceptionEnum(int code, String msg, String data, Class exception) { this.code = code; this.msg = msg; this.data = new ExceptionResponseDetailBean(data); this.exception = exception; } public int getCode() { return code; } public String getMsg() { return msg; } public ExceptionResponseDetailBean getData() { return data; } public Class getException() { return exception; } } //7-ExceptionResponseBean异常返回POJO public class ExceptionResponseBean { private int code; private String msg; private ExceptionResponseDetailBean data; public ExceptionResponseBean() { super(); } public ExceptionResponseBean(int code, String msg, String detail) { super(); this.code = code; this.msg = msg; this.data = new ExceptionResponseDetailBean(detail); } public int getCode() { return code; } public void setCode(int code) { this.code = code; } public String getMsg() { return msg; } public void setMsg(String msg) { this.msg = msg; } public ExceptionResponseDetailBean getData() { return data; } public void setData(ExceptionResponseDetailBean data) { this.data = data; } } //8-ExceptionResponseDetailBean异常返回明细POJO public class ExceptionResponseDetailBean { private String detail; public ExceptionResponseDetailBean() { super(); } public ExceptionResponseDetailBean(String detail) { super(); this.detail = detail; } public String getDetail() { return detail; } public void setDetail(String detail) { this.detail = detail; } }
4-应用示例
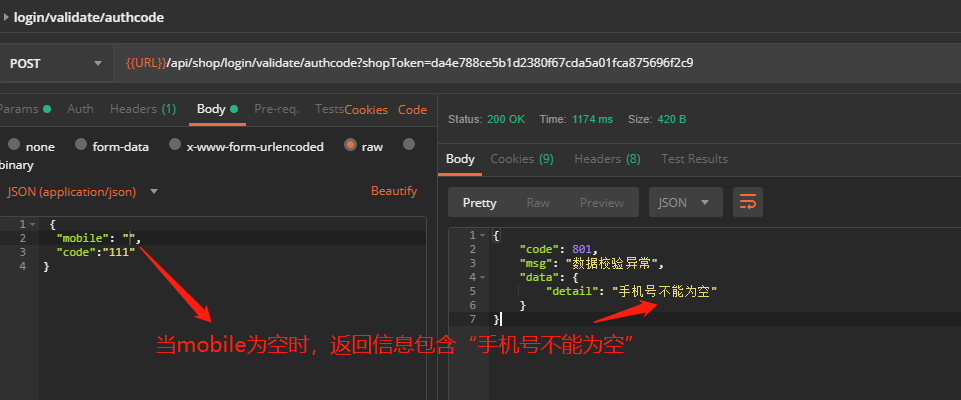
5-进一步优化校验
5-1-优点和问题
- 上面的数据校验已经进行分装,实现了和接口业务低耦合要求,并且可以自定义结果;但有一个问题:对于每一个POJO要校验的参数,都要重复指定message值,
- 示例:@NotEmpty(message = "手机号不能为空") ;如果多个POJO对手机号验证,又会出现冗余情况
5-2-优化思路
- 自定义校验注解,对相同或类似的参数使用相同的自定义注解(见源码-01)
- 自定义注解需要,自定义一个注解类(见源码-03)和一个ConstraintValidator实现类(见源码-03)
5-3-源码分析
//1-POJO package com.hs.api.shopapp.entity.commom; import com.hs.web.common.annotation.validation.MobileFormat; public class AuthCodeReq { @MobileFormat//使用自定义校验注解 private String mobile;//手机号 public String getMobile() { return mobile; } public void setMobile(String mobile) { this.mobile = mobile; } } //2-自定义注解MobileFormat @Documented @Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Constraint(validatedBy = MobileConstraintValidator.class) public @interface MobileFormat { String message() default "手机号格式不正确"; Class<?>[] groups() default {}; Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default {}; @Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE, ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.PARAMETER}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface List { NotBlank[] value(); } } //3-重写ConstraintValidator接口,自定义校验规则 public class MobileConstraintValidator implements ConstraintValidator<MobileFormat,String>{ @Override public void initialize(MobileFormat constraintAnnotation) { } //在当前方法指定校验规则 @Override public boolean isValid(String value, ConstraintValidatorContext context) { if(StringUtil.isBlank(value)){ return false; } return true; } } //4-测试接口 @RestController @RequestMapping(value="/api/shop/login") public class ApiShopLoginController extends ApiShopBaseController { @MyValidateAopAnnotation @RequestMapping(value = { "/get/authcode" }, method = {RequestMethod.POST }) public Object getSignInAuthCode(@Valid @RequestBody AuthCodeReq authCodeReq,BindingResult bindingResult) throws Exception { //业务逻辑略 } }
5-4-应用示例
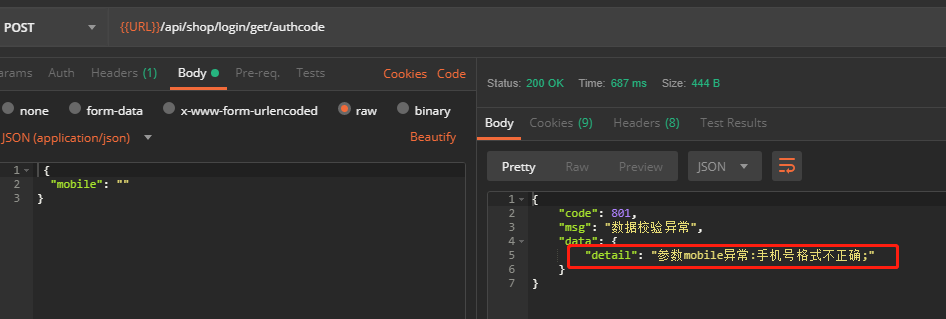
6-备注
6-1-@NotEmpty、@NotNull、@NotBlank 的区别
- @NotEmpty 用在集合上面(不能注释枚举)
- @NotBlank用在String上面
- @NotNull用在所有类型上面
参考文献
1-https://blog.csdn.net/ranshenyi/article/details/79548188
2-https://www.cnblogs.com/NeverCtrl-C/p/8185576.html