1个图1类3个知识点6个接口
JDK所提供的容器API位于java.util这个包

Collection:(单个往里装)
- Set没有顺序,不可以重复(两个对象他们之间的引用永远不可能重复,这里的重复指的是两个对象间相互equals就是重复)
- List有顺序,可以重复
Map:(成对往里装)

1 import java.util.*; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Collection c = new ArrayList(); 6 c.add("hello"); 7 c.add(new Name("f1", "l1")); 8 c.add(new Integer(100)); 9 System.out.println(c.size()); 10 System.out.println(c); 11 } 12 } 13 14 class Name { 15 private String str1; 16 private String str2; 17 Name(String str1, String str2) { 18 this.str1 = str1; 19 this.str2 = str2; 20 } 21 /* 22 System.out.println()调用toString()方法返回对象自身(地址), 23 重写toString()方法返回成员变量 24 */ 25 public String toString() { 26 return str1 + " " + str2; 27 } 28 }
Collection方法举例:
1、容器类对象在调用remove、contains等方法时需要比较对象是否相等,这会涉及到对象类型的equals
方法和hashCode方法
2、对于自定义的类型,需要重写equals和hashCode方法以实现自定义的对象相等规则
注意:相等的对象应该具有相等的hashCode
3、增加Name类的equals和hashCode方法如下:
原则:重写对象的equals方法,必须要重写对象的hashCode方法,两个对象之间相互equals,两个对象必须具备相同的hashCode
Object类的equals方法:
对于任何非空引用值x和y,当且仅当x和y引用同一个对象时,此方法才返回true(x == y具有值true)
1 import java.util.*; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Collection c = new HashSet(); 6 c.add("Hello"); 7 c.add(new Integer(100)); 8 c.add(new Name("f1", "f2")); 9 /* 10 会去除,当你remove这个对象的时候,它会挨着排的拿出把容器中的 11 每一个对象拿出来然后去比较它们两个是否equals。String重写了 12 equals方法(查API文档),如果给定对象表示的 String 与此 String 相等,则返回 true; 13 */ 14 c.remove("Hello"); 15 /* 16 虽然这是两个Integer对象,但也会被去除掉,因为Integer也重写了equals方法(查API文档) 17 如果对象相同,则返回 true,否则返回 false 18 */ 19 c.remove(new Integer(100)); 20 /* 21 未重写equals方法和hashCode方法时,不能去除,因为Name类没有重写equals方法的话,它们equals的唯一条件是它们指向了同一对象, 22 但它们并不指向同一对象 23 重写equals方法和hashCode方法,可以去除 24 */ 25 System.out.println(c.remove(new Name("f1", "f2"))); 26 System.out.println(c); 27 } 28 } 29 30 class Name { 31 private String firstName, lastName; 32 public Name(String firstName, String lastName) { 33 this.firstName = firstName; 34 this.lastName = lastName; 35 } 36 public String getFirstName() { return firstName; } 37 public String gerLastName() { return lastName; } 38 //重写toString的目的是输出name的对象为firstName + lastName的形式,否则System.out.println(c);输出对象地址 39 public String toString(){ 40 return firstName + " " + lastName; 41 } 42 43 //重写equals方法 44 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 45 if (obj instanceof Name) { 46 Name name = (Name)obj; 47 return (firstName.equals(name.firstName)) 48 && (lastName.equals(name.lastName)); 49 }else{ 50 return super.equals(obj); 51 } 52 } 53 //重写hashCode方法 54 public int hashCode() { 55 return firstName.hashCode(); 56 } 57 }
Iterator接口(遍历容器内元素)
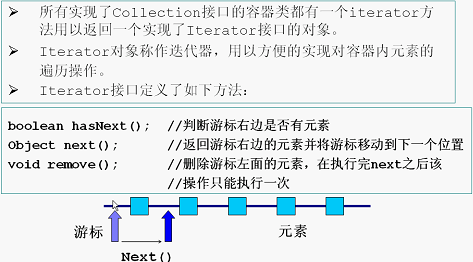
增强的for循环(遍历容器)
