题目链接:
题目描述
根据 逆波兰表示法,求表达式的值。
有效的算符包括 +、-、*、/ 。每个运算对象可以是整数,也可以是另一个逆波兰表达式。
说明:
-
整数除法只保留整数部分。
-
给定逆波兰表达式总是有效的。换句话说,表达式总会得出有效数值且不存在除数为 0 的情况。
示例 1:
输入:tokens = ["2","1","+","3","*"]
输出:9
解释:该算式转化为常见的中缀算术表达式为:((2 + 1) * 3) = 9
示例 2:
输入:tokens = ["4","13","5","/","+"]
输出:6
解释:该算式转化为常见的中缀算术表达式为:(4 + (13 / 5)) = 6
示例 3:
输入:tokens = ["10","6","9","3","+","-11","*","/","*","17","+","5","+"]
输出:22
解释:
该算式转化为常见的中缀算术表达式为:
((10 * (6 / ((9 + 3) * -11))) + 17) + 5
= ((10 * (6 / (12 * -11))) + 17) + 5
= ((10 * (6 / -132)) + 17) + 5
= ((10 * 0) + 17) + 5
= (0 + 17) + 5
= 17 + 5
= 22
提示:
-
1 <= tokens.length <= 104
-
tokens[i] 要么是一个算符("+"、"-"、"*" 或 "/"),要么是一个在范围 [-200, 200] 内的整数
逆波兰表达式:
逆波兰表达式是一种后缀表达式,所谓后缀就是指算符写在后面。
-
平常使用的算式则是一种中缀表达式,如 ( 1 + 2 ) * ( 3 + 4 ) 。
-
该算式的逆波兰表达式写法为 ( ( 1 2 + ) ( 3 4 + ) * ) 。
逆波兰表达式主要有以下两个优点:
-
去掉括号后表达式无歧义,上式即便写成 1 2 + 3 4 + * 也可以依据次序计算出正确结果。
-
适合用栈操作运算:遇到数字则入栈;遇到算符则取出栈顶两个数字进行计算,并将结果压入栈中。
题解
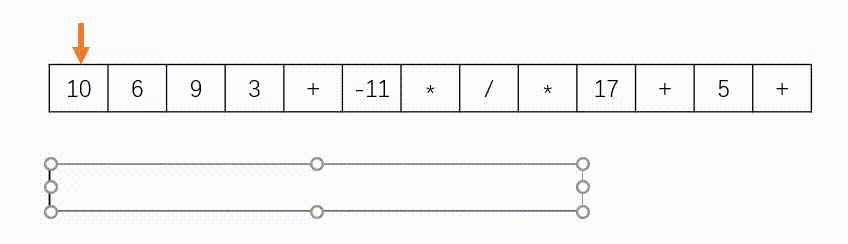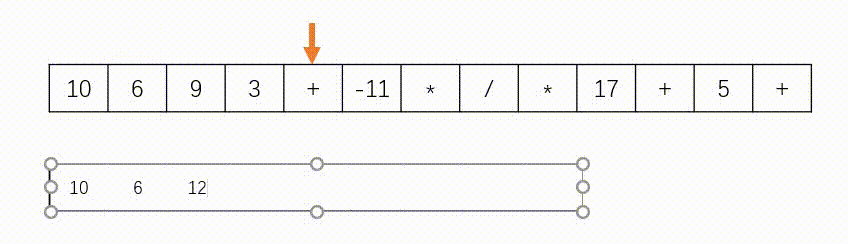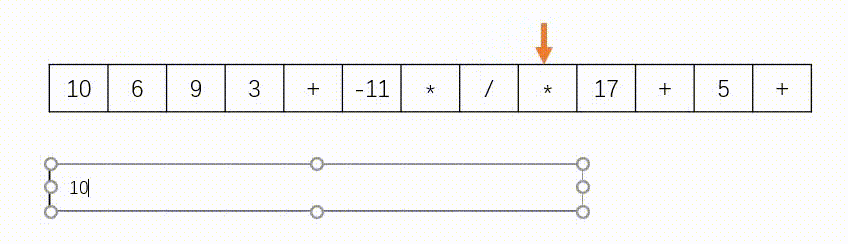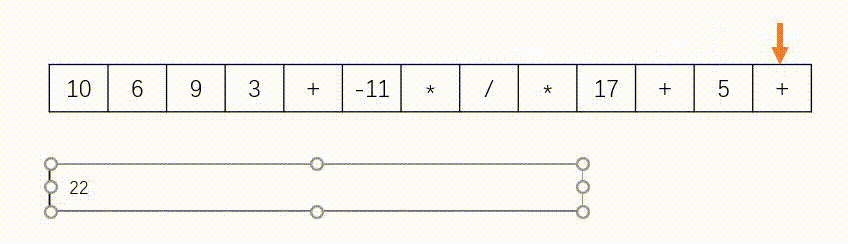
思路:此题使用”栈“实现,如下图所示。遇到数字则入栈,遇到字符则去除栈顶的两个数字进行计算在将结果压入栈中。另外,题目中说了给定的逆波兰表达式总是有效的,所以不需要判断式子是否有效。
代码(C++)
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) { stack<string> sta; for (string t : tokens) { if (t == "+") { string temp1 = sta.top(); sta.pop(); string temp2 = sta.top(); sta.pop(); //stoi() 将 n 进制的字符串转化为十进制 int result = stoi(temp2) + stoi(temp1); sta.push(to_string(result)); } else if (t == "-") { string temp1 = sta.top(); sta.pop(); string temp2 = sta.top(); sta.pop(); int result = stoi(temp2) - stoi(temp1); sta.push(to_string(result)); } else if (t == "*") { string temp1 = sta.top(); sta.pop(); string temp2 = sta.top(); sta.pop(); int result = stoi(temp2) * stoi(temp1); sta.push(to_string(result)); } else if (t == "/") { string temp1 = sta.top(); sta.pop(); string temp2 = sta.top(); sta.pop(); int result = stoi(temp2) / stoi(temp1); sta.push(to_string(result)); } else { sta.push(t); } } return stoi(sta.top()); }
分析:
-
时间复杂度:O(N),N为vector的长度。
-
空间复杂度:O(N)。
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) { stack<int> sta; for (string t : tokens) { if (t == "+" || t == "-" || t == "*" ||t == "/") { int temp1 = sta.top(); sta.pop(); int temp2 = sta.top(); sta.pop(); int result; if (t == "+") result = temp2 + temp1; else if (t == "-") result = temp2 - temp1; else if (t == "*") result = temp2 * temp1; else if (t == "/") result = temp2 / temp1; sta.push(result); } else { sta.push(stoi(t)); } } return sta.top(); }