Linux进程管理
编辑a.c 文件
#include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> int main() { printf( "Message aaaa " ); if ( fork() ) { sleep(4); printf( "Message bbbb " ); if ( fork() ) { sleep(2); printf( "Message cccc " ); }else{ sleep(1); printf( "Message dddd " ); } }else{ sleep(1); printf( "Message eeee " ); if ( fork() ) { sleep(2); printf( "Message ffff " ); }else{ sleep(6); printf( "Message gggg " ); } } return 0; }
编译 a.c 文件
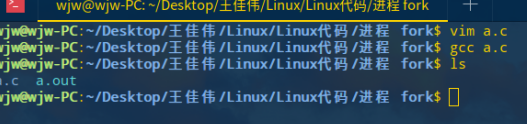
运行 a.out
./a.out
Linux信号处理
编辑 a.c 文件
编译 a.c 文件
gcc a.c
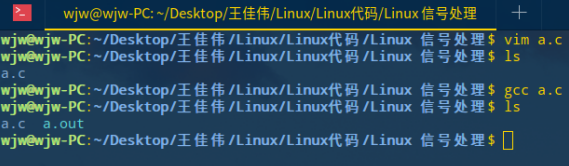
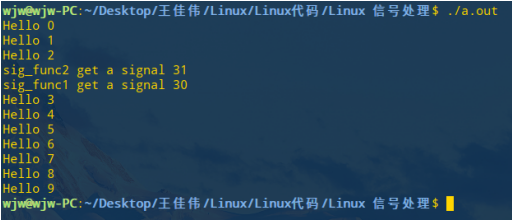
运行 a.out 文件
./a.out
Linux多线程
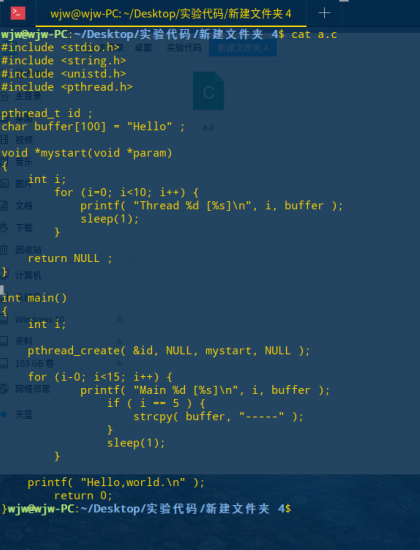
Lin编辑 a.c
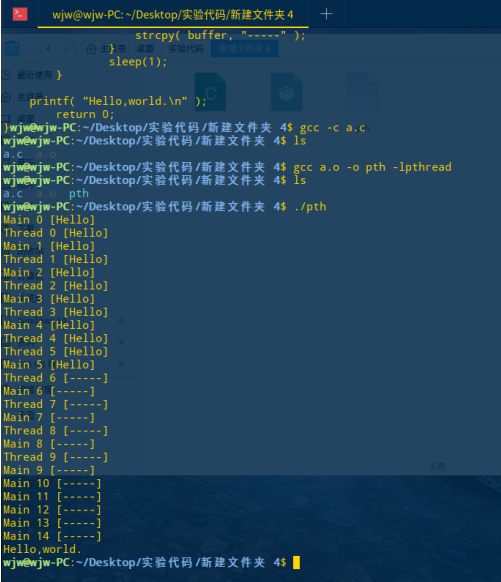
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <pthread.h> char buffer[100] = "Hello" ; pthread_t id ; void *mystart(void *param) { int i; for (i=0; i<10; i++) { printf( "Thread %d [%s] ", i, buffer ); sleep(1); } return NULL ; } int main() { int i; pthread_create( &id, NULL, mystart, NULL ); for (i-0; i<15; i++) { printf( "Main %d [%s] ", i, buffer ); if ( i == 5 ) { strcpy( buffer, "-----" ); } sleep(1); } printf( "Hello,world. " ); return 0; }
编译运行
Linux 管道
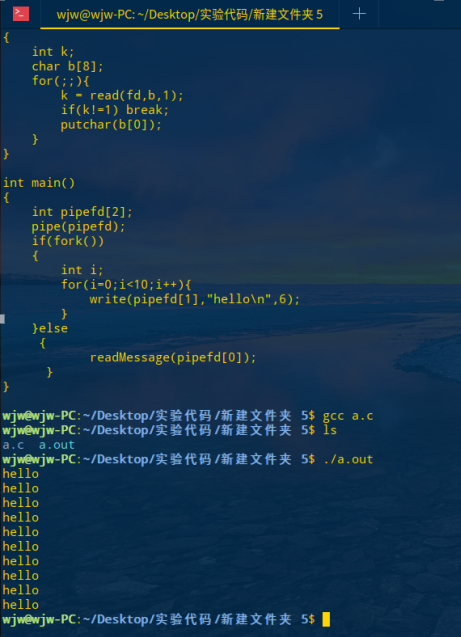
#include <stdio.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdlib.h> void readMessage(int fd) { int k; char b[8]; for(;;){ k = read(fd,b,1); if(k!=1) break; putchar(b[0]); } } int main() { int pipefd[2]; pipe(pipefd); if(fork()) { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++){ write(pipefd[1],"hello ",6); } }else { readMessage(pipefd[0]); } }
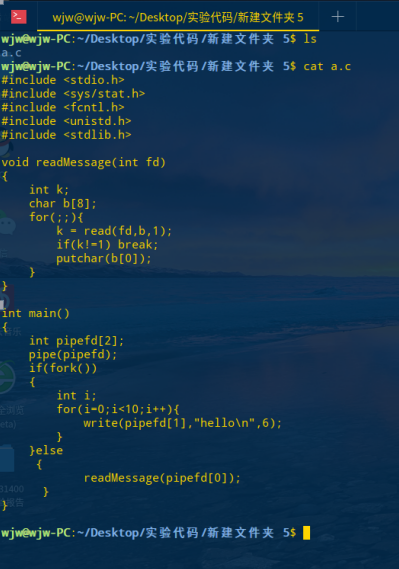
编译运行
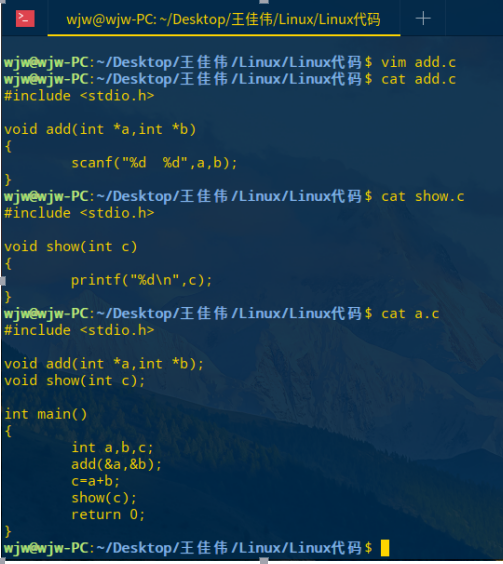
Linux makefile文件
编写 add.c show.c a.c 三个文件
// add.c文件: #include <stdio.h> void add(int *a,int *b) { scanf("%d %d",a,b); } // show.c 文件: #include <stdio.h> void show(int c) { printf("%d ",c); } // a.c 文件: #include <stdio.h> void add(int *a,int *b); void show(int c); int main() { int a,b,c; add(&a,&b); c=a+b; show(c); return 0; }
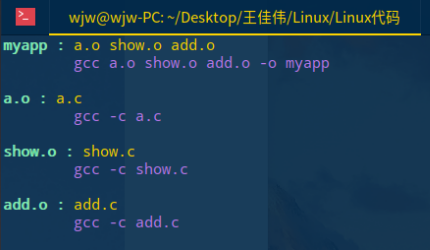
编写makefile文件
myapp : a.o show.o add.o gcc a.o show.o add.o -o myapp a.o : a.c gcc -c a.c show.o : show.c gcc -c show.c add.o : add.c gcc -c add.c
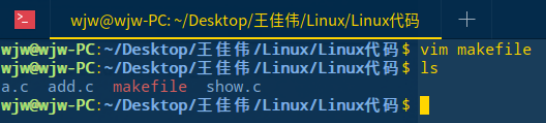
运行 makefile 文件
make
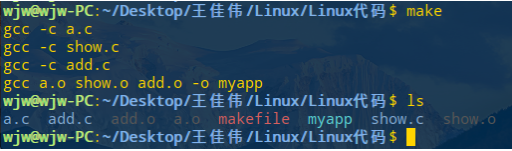
运行 myapp
./myapp

基本I/O文件操作
编写w.c写文件:
#include <stdio.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <unistd.h> int main() { int fd = open("myfile.txt",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT,0644); if(fd<0) { printf("File cannot open! "); return 1; } write(fd,"wjwwjwwjwwjwwjw",15); close(fd); return 0; }

运行 w.c 文件
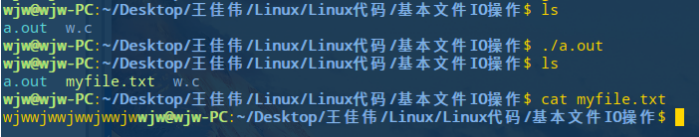
编写读文件r.c
#include <stdio.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <sys/types.h> int main() { int k; char b[1000]; int fd = open("myfile.txt",O_RDONLY); if(fd < 0){ perror("cannot open file!"); return 1; } k = read(fd,b,1000); printf("%d ",k); b[k]=0; printf("%d ",b); close(fd); return 0; }
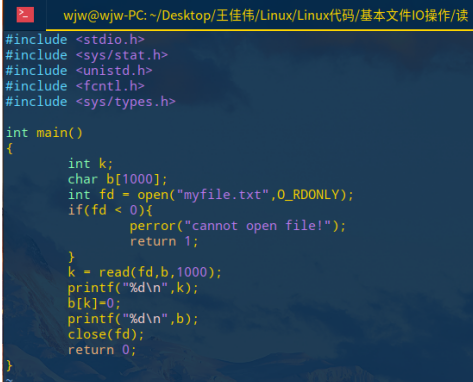
运行 a.out

完成!