特性(Attribute)
用于在运行时传递程序中各种元素(比如类、方法、结构、枚举、组件等)的行为信息的声明性标签。您可以通过使用特性向程序添加声明性信息。一个声明性标签是通过放置在它所应用的元素前面的方括号([ ])来描述的。
特性(Attribute)用于添加元数据,如编译器指令和注释、描述、方法、类等其他信息。功能类似JAVA中的注解(Annotation)。
约定
所有特性名称都以单词“Attribute”结束,以便将它们与“.NET Framework”中的其他项区分。但是,在代码中使用特性时,不需要指定 attribute 后缀。例如,[DllImport] 虽等效于 [DllImportAttribute],但 DllImportAttribute 才是该特性在 .NET Framework 中的实际名称。
Attribute类
所有特性都由Attribute类派生。Attribute 类的细节:
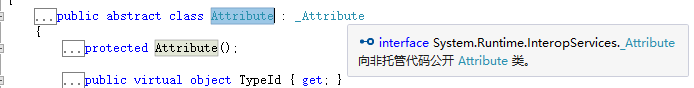
protected Attribute(): 保护的构造器,只能被Attribute的派生类调用。
三个静态方法
static Attribute GetCustomAttribute():这个方法有8种重载的版本,它被用来取出施加在类成员上指定类型的Attribute。
static Attribute[] GetCustomAttributes(): 这个方法有16种重载版本,用来取出施加在类成员上指定类型的Attribute数组。
static bool IsDefined(): 这个方法有八种重载版本,看是否指定类型的定制attribute被施加到类的成员上面。
实例方法
bool IsDefaultAttribute(): 如果Attribute的值是默认的值,那么返回true。
bool Match():表明这个Attribute实例是否等于一个指定的对象。
公共属性
TypeId: 得到一个唯一的标识,这个标识被用来区分同一个Attribute的不同实例。
.Net 框架提供了两种类型的特性:预定义特性和自定义特性。
预定义特性
.Net 框架提供了三种预定义特性:
- AttributeUsage
- Conditional
- Obsolete
AttributeUsage
预定义特性 AttributeUsage 描述了如何使用一个自定义特性类。它规定了特性可应用到的项目的类型。
规定该特性的语法如下:
[AttributeUsage( validon, AllowMultiple=allowmultiple, Inherited=inherited )]
其中:
- 参数 validon 规定特性可被放置的语言元素。它是枚举器 AttributeTargets 的值的组合。默认值是 AttributeTargets.All。
- 参数 allowmultiple(可选的)为该特性的 AllowMultiple 属性(property)提供一个布尔值。如果为 true,则该特性是多用的。默认值是 false(单用的)。
- 参数 inherited(可选的)为该特性的 Inherited 属性(property)提供一个布尔值。如果为 true,则该特性可被派生类继承。默认值是 false(不被继承)。
例如:
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class | AttributeTargets.Constructor | AttributeTargets.Field | AttributeTargets.Method | AttributeTargets.Property, AllowMultiple = true)]
Conditional
这个预定义特性标记了一个条件方法,其执行依赖于它顶的预处理标识符。
它会引起方法调用的条件编译,取决于指定的值,比如 Debug 或 Trace。例如,当调试代码时显示变量的值。
规定该特性的语法如下:
[Conditional( conditionalSymbol )]
例如:
public class Myclass
{
[Conditional("DEBUG")]
public static void Message(string msg)
{
Console.WriteLine(msg);
}
}
class Test
{
static void function1()
{
Myclass.Message("In Function 1.");
function2();
}
static void function2()
{
Myclass.Message("In Function 2.");
}
public static void Main()
{
Myclass.Message("In Main function.");
function1();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
In Main function In Function 1 In Function 2
Obsolete
这个预定义特性标记了不应被使用的程序实体。它可以让您通知编译器丢弃某个特定的目标元素。例如,当一个新方法被用在一个类中,但是您仍然想要保持类中的旧方法,您可以通过显示一个应该使用新方法,而不是旧方法的消息,来把它标记为 obsolete(过时的)。
规定该特性的语法如下:
[Obsolete( message )] [Obsolete( message, iserror )]
其中:
- 参数 message,是一个字符串,描述项目为什么过时的原因以及该替代使用什么。
- 参数 iserror,是一个布尔值。如果该值为 true,编译器应把该项目的使用当作一个错误。默认值是 false(编译器生成一个警告)。
创建自定义特性(Attribute)
.Net 框架允许创建自定义特性,用于存储声明性的信息,且可在运行时被检索。该信息根据设计标准和应用程序需要,可与任何目标元素相关。
创建并使用自定义特性包含四个步骤:
- 声明自定义特性
- 构建自定义特性
- 在目标程序元素上应用自定义特性
- 通过反射访问特性
声明自定义特性
一个新的自定义特性应派生自 System.Attribute 类。例如:
// 一个自定义特性 BugFix 被赋给类及其成员 [AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class | AttributeTargets.Constructor | AttributeTargets.Field | AttributeTargets.Method | AttributeTargets.Property, AllowMultiple = true)] public class DeBugInfo : System.Attribute
在上面的代码中,我们已经声明了一个名为 DeBugInfo 的自定义特性。
构建自定义特性
让我们构建一个名为 DeBugInfo 的自定义特性,该特性将存储调试程序获得的信息。它存储下面的信息:
- bug 的代码编号
- 辨认该 bug 的开发人员名字
- 最后一次审查该代码的日期
- 一个存储了开发人员标记的字符串消息
我们的 DeBugInfo 类将带有三个用于存储前三个信息的私有属性(property)和一个用于存储消息的公有属性(property)。所以 bug 编号、开发人员名字和审查日期将是 DeBugInfo 类的必需的定位( positional)参数,消息将是一个可选的命名(named)参数。
每个特性必须至少有一个构造函数。必需的定位( positional)参数应通过构造函数传递。下面的代码演示了 DeBugInfo 类:
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class |
AttributeTargets.Constructor |
AttributeTargets.Field |
AttributeTargets.Method |
AttributeTargets.Property,
AllowMultiple = true)]
public class DeBugInfo : Attribute
{
public int BugNo { get; private set; }
public string Developer { get; private set; }
public string LastReview { get; private set; }
public string Message { get; set; }
public DeBugInfo(int bg, string dev, string d)
{
this.BugNo = bg;
this.Developer = dev;
this.LastReview = d;
}
}
应用自定义特性
通过把特性放置在紧接着它的目标之前,来应用该特性:
[DeBugInfo(45, "Zara Ali", "12/8/2012",
Message = "Return type mismatch")]
[DeBugInfo(49, "Nuha Ali", "10/10/2012",
Message = "Unused variable")]
public class Rectangle
{
// 成员变量
protected double length;
protected double width;
public Rectangle(double length, double width)
{
this.length = length;
this.width = width;
}
[DeBugInfo(55, "Zara Ali", "19/10/2012",
Message = "Return type mismatch")]
public double GetArea()
{
return length * width;
}
[DeBugInfo(56, "Zara Ali", "19/10/2012")]
public void Display()
{
Console.WriteLine("Length: {0}", length);
Console.WriteLine("Width: {0}", width);
Console.WriteLine("Area: {0}", GetArea());
}
}
访问特性
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Rectangle r = new Rectangle(4.5, 7.5);
r.Display();
Console.WriteLine("
遍历 Rectangle 类的属性");
Type type = typeof(Rectangle);
// 遍历 Rectangle 类的属性
foreach (Attribute a in type.GetCustomAttributes(false))
{
Console.WriteLine("Name: {0},TypeId:{1}", a.GetType().Name, a.TypeId);
if (a is DeBugInfo)
{
DeBugInfo dbi = (DeBugInfo)a;
Console.WriteLine("Bug no: {0}", dbi.BugNo);
Console.WriteLine("Developer: {0}", dbi.Developer);
Console.WriteLine("Last Reviewed: {0}",
dbi.LastReview);
Console.WriteLine("Remarks: {0}", dbi.Message);
}
}
Console.WriteLine("
遍历方法属性");
// 遍历方法属性
foreach (MethodInfo m in type.GetMethods())
{
foreach (Attribute a in m.GetCustomAttributes(true))
{
Console.WriteLine("Name: {0},TypeId:{1}", a.GetType().Name, a.TypeId);
if (a is DeBugInfo)
{
DeBugInfo dbi = (DeBugInfo)a;
Console.WriteLine("Bug no: {0}, for Method: {1}",
dbi.BugNo, m.Name);
Console.WriteLine("Developer: {0}", dbi.Developer);
Console.WriteLine("Last Reviewed: {0}",
dbi.LastReview);
Console.WriteLine("Remarks: {0}", dbi.Message);
}
}
}
Console.ReadKey();
}