【问题:sizeof 与 length(string的成员函数) 区别?】
sizeof :是C/C++中的一个操作符(operator),简单的说其作用就是返回一个对象或者类型所占的内存字节数。
size : 一般是容器当前拥有多少元素(注意区分与 capacity)
如果说:
capacity 相当于 _array[sizeof(_array) / sizeof(int) 容积 , 那么
strlen 相当于 size 当前占有【实际使用时候, strlen的参数是 char或者char*】
1 // sizeof例子 2 int _array[] = { 0,2,9,1,2,3,2 }; 3 int* _begin = _array;//指针指向首元素 4 int* _end = &(_array[sizeof(_array) / sizeof(int)]); 5 6 //******************************************************** 7 #include<iostream> 8 #include<string> 9 10 using namespace std; 11 12 int main() 13 { 14 string str = "shi rui yu"; 15 size_t length_ = str.length();//10 16 size_t size_ = str.size();//10 17 int sizeof_ = sizeof(str)/sizeof(int);//10 18 19 char str_[20] = "0123456789"; 20 int a = strlen(str_); //a=10; 21 int b = sizeof(str_); //而b=20; 22 return 1; 23 }




1
// 定义一个 零 矩阵 最简单的方法
int const rows = 5; 2 int const cols = 5; 3 vector<vector<int>> array_; 4 vector<int> vec_; 5 vec_.resize(cols, 0); 6 array_.resize(rows, vec_);



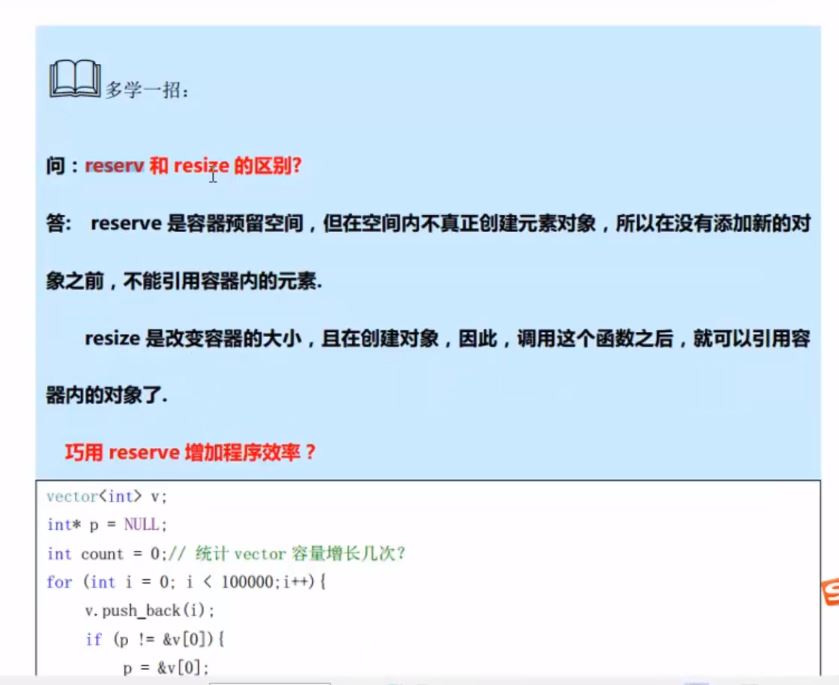
1 #include<vector> 2 #include<iostream> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 template <typename T> 7 void printf(vector<T>& vec) 8 { 9 if (!vec.empty()) 10 { 11 for (auto itr : vec) 12 { 13 cout << itr << ", "; 14 } 15 cout << endl; 16 } 17 else 18 { 19 cout << "容器是空的啦~~" << endl; 20 } 21 } 22 //大小操作 23 void test03() 24 { 25 cout << "===== test03()=====" << endl; 26 int arry1[] = { 100, 200, 300, 400 }; 27 vector<int> v4(arry1, arry1 + sizeof(arry1)/sizeof(int)); 28 cout << " v4.size = " << v4.size() << endl; // size表示元素个数 29 cout << " v4.capacity() = " << v4.capacity() << endl; // capatity表示容器的容量,比如:这个容器可以容纳100个元素,那么它的容量 = 100;但是其中只有50个元素,那么它的size = 50 30 // 为什么有容量这个说法,比如:当你发现容量不够时,你可以resize一下 31 if (!v4.empty()) 32 { 33 cout << "不是空" << endl; 34 } 35 else 36 { 37 cout << "空" << endl; 38 } 39 printf(v4);// 100 200 300 400 40 v4.resize(2);//将size改为2,如果改为6则会补充两个0 41 printf(v4);// 100 200 42 } 43 44 //vector 存取数据 45 void test04() 46 { 47 cout << "===== test04()=====" << endl; 48 int arry1[] = { 100, 200, 300, 400 }; 49 vector<int> v4(arry1, arry1 + sizeof(arry1) / sizeof(int)); 50 int a = v4.at(3); 51 int b = v4[3]; 52 int c = v4.front();//第一个元素 53 int d = v4.back(); 54 cout << "第一个元素 v4.front() = " << v4.front() << endl; 55 cout << "最后一个元素 v4.back() = " << v4.back() << endl; 56 } 57 58 //vector 插入与删除 59 void test05() 60 { 61 cout << "===== test05()=====" << endl; 62 vector<int> v1; 63 v1.push_back(10); 64 v1.push_back(20); 65 //[注:insert的效率比较低,慎用] 66 v1.insert(v1.begin(), 999); 67 v1.insert(v1.end(), 9999); 68 v1.insert(v1.begin() + 2, 30); // 一般,支持[]访问元素的容器都支持随机访问 69 printf(v1); // 999, 10, 30, 20, 9999 70 71 //删除操作 72 v1.erase(v1.begin()); 73 printf(v1);// 10, 30, 20, 9999 74 v1.erase(v1.begin() + 1, v1.end());// 10 75 printf(v1); 76 v1.clear();// [注:对string没卵用] 77 printf(v1); 78 } 79 80 //巧用swap收缩空间 81 void test06() 82 { 83 cout << "===== test06()=====" << endl; 84 vector<int> v1; 85 for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) 86 { 87 v1.push_back(i); 88 } 89 90 cout << " size = " << v1.size() << endl; // 1000 91 cout << "capatity = " << v1.capacity() << endl; // 1066 92 93 v1.resize(10); 94 cout << " size = " << v1.size() << endl; // 10 95 cout << "capatity = " << v1.capacity() << endl; // 1066 96 97 vector<int>(v1).swap(v1); //这样可以节省内存 98 cout << " size = " << v1.size() << endl; // 10 99 cout << "capatity = " << v1.capacity() << endl; // 10 100 } 101 102 void test07() 103 { 104 cout << "===== test07()=====" << endl; 105 vector<int> v1; 106 int num = 0; 107 int* address = nullptr; 108 // reserve 并没有像resize那样给空间经行初始化 109 v1.reserve(10000);//reserve预留空间,理论上,加这一步操作,预留空间会使得对象v1的构造和析构次数极大减少,但是这里不加这一句貌似 MS-build 给自动优化了 110 for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) 111 { 112 v1.push_back(i); 113 } 114 if (address != &(v1[0])) 115 { 116 address = &(v1[0]); 117 ++num; 118 } 119 cout << " 对象 v1 申请和释放次数 num = " << num << endl; 120 } 121 122 //find 123 void test08() 124 { 125 cout << "===== test08()=====" << endl; 126 vector<int> v1; 127 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) 128 { 129 v1.push_back(i);//0123456789 130 } 131 vector<int>::iterator itr = find(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 88); 132 if ( itr != v1.end()) // be found 133 { 134 cout << "be fonud!" << endl; 135 } 136 else 137 { 138 cout << "not be found!" << endl; 139 } 140 vector<int> v2, v3; 141 v2.assign(v1.begin(), v1.begin() + 3); 142 printf(v2);// 0 1 2 143 v3.assign(10, 1); 144 printf(v3); // 1~10 145 vector<int> v4(10,1); 146 printf(v4);// 1~10 147 } 148 149 int main() 150 { 151 //<1>用数组初始化vector 152 int arry[] = { 10, 20, 30, 40 }; 153 vector<int> vec1(arry, arry + sizeof(arry) / sizeof(int)); 154 printf(vec1); 155 vector<int> vec2(vec1.begin(), vec1.end()); 156 printf(vec2); 157 vector<int> vec3(vec1); 158 printf(vec3); 159 //<2>赋值 160 vector<int> vec4; 161 vec4 = vec3; // 这是深度拷贝 162 printf(vec3); 163 vec3.push_back(50); 164 printf(vec4); 165 printf(vec3); 166 //<3>大小操作 167 168 test03(); 169 test04(); 170 test05(); 171 test06(); 172 test07(); 173 test08(); 174 return 1; 175 }
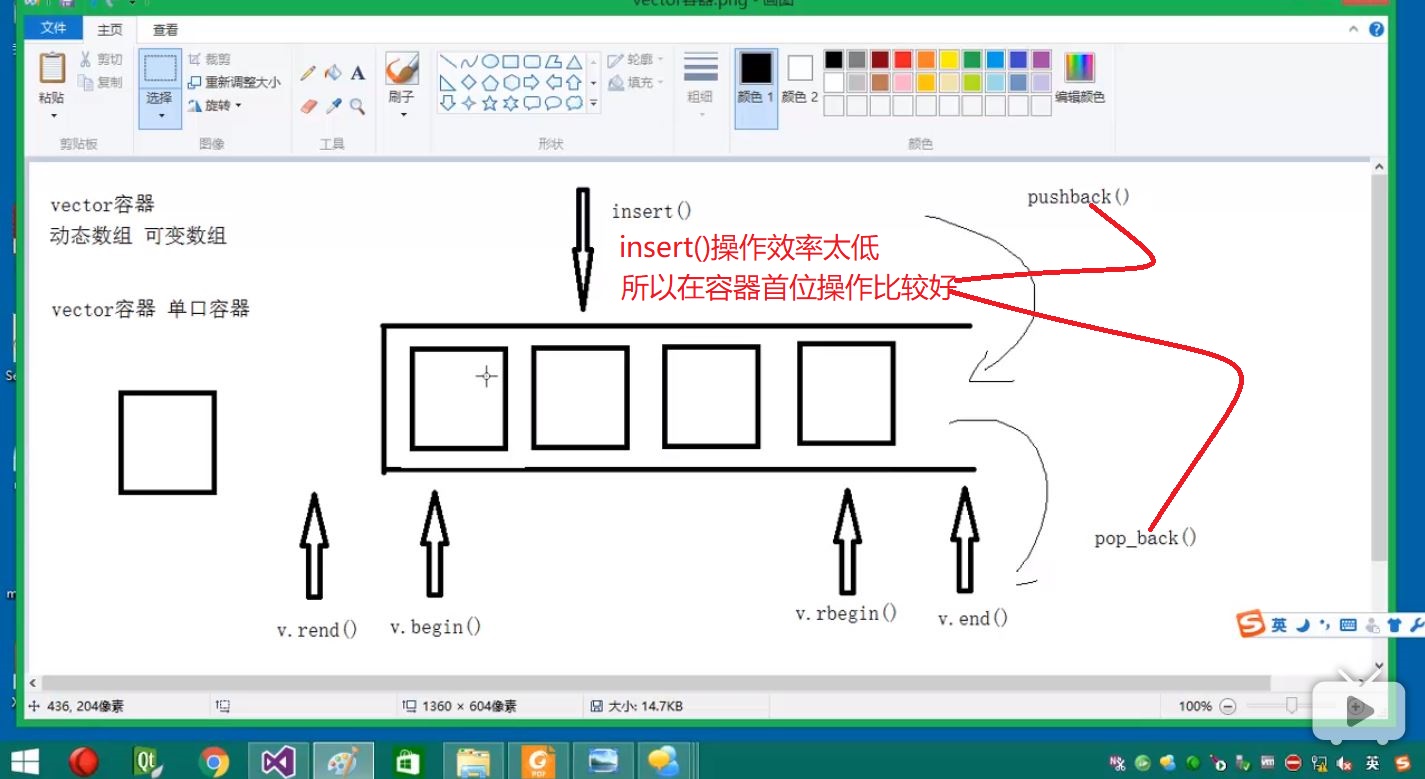
insert:
1 // inserting into a vector 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <vector> 4 5 int main() 6 { 7 std::vector<int> myvector(3, 100);// 100 100 100 8 std::vector<int>::iterator it; 9 10 it = myvector.begin(); 11 it = myvector.insert(it, 200); // 200 100 100 100 12 13 myvector.insert(it, 2, 300);// 300 300 200 100 100 100 14 15 // "it" no longer valid, get a new one: 16 it = myvector.begin(); 17 18 std::vector<int> anothervector(2, 400); 19 myvector.insert(it + 2, anothervector.begin(), anothervector.end()); // 300 300 400 400 200 100 100 100 20 21 int myarray[] = { 501,502,503 }; 22 myvector.insert(myvector.begin(), myarray, myarray + 3); // 501 502 503 300 300 400 400 200 100 100 100 23 24 std::cout << "myvector contains:"; 25 for (it = myvector.begin(); it<myvector.end(); it++) 26 std::cout << ' ' << *it; 27 std::cout << ' '; 28 29 return 0; 30 }
erase
1 // erasing from vector 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <vector> 4 5 int main() 6 { 7 std::vector<int> myvector; 8 9 // set some values (from 1 to 10) 10 for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) myvector.push_back(i); // 123456789 10 11 12 // erase the 6th element 13 myvector.erase(myvector.begin() + 5);// 12345 789 10 14 15 // erase the first 3 elements: 16 myvector.erase(myvector.begin(), myvector.begin() + 3);// [ , ) 17 18 std::cout << "myvector contains:"; 19 for (unsigned i = 0; i<myvector.size(); ++i) 20 std::cout << ' ' << myvector[i]; 21 std::cout << ' '; 22 23 return 0; 24 }
//********************************************以下是手动实现一个动态数组的代码
1 #include<iostream> 2 3 using namespace std; 4 5 namespace MY 6 { 7 class Vector 8 { 9 public: 10 Vector(); 11 ~Vector(); 12 void push_back(int value); 13 void removeByPose(int pos); 14 void removeByValue(int value); 15 int find(int value); 16 int& operator[](int index)// 可以是返回引用 17 { 18 return array_[index]; 19 } 20 void show() const; 21 void clear() 22 { 23 size_ = 0; 24 } 25 bool empty() 26 { 27 if (array_ == nullptr) 28 return true; 29 else 30 return false; 31 } 32 public: 33 int* array_; 34 int size_; 35 int capacity_; 36 }; 37 38 Vector::Vector() 39 { 40 size_ = 0; 41 capacity_ = 10; 42 array_ = new int[capacity_]; 43 } 44 Vector::~Vector() 45 { 46 delete[] array_; 47 cout << "free " << array_ << endl; 48 } 49 void MY::Vector::push_back(int value) 50 { 51 if (empty()) return; 52 //判断空间是否足够 53 if (size_ == capacity_) 54 { 55 int* newspace = new int[capacity_ * 2]; // 扩容 56 memcpy(newspace, array_, capacity_ * sizeof(int));// 备份 - > newsapce 57 delete[] array_;// 删除旧空间 58 capacity_ *= 2;//扩容 59 array_ = newspace;//转移旧空间的值 - > 新空间 60 } 61 //在末尾插入元素 62 array_[size_] = value; 63 size_++; 64 } 65 void MY::Vector::show() const 66 { 67 cout << "size_ = " << size_ << " ||"; 68 for (int i = 0; i < size_; i++) 69 { 70 cout << array_[i] << " "; 71 } 72 cout << endl; 73 } 74 void MY::Vector::removeByPose(int pos) 75 { 76 if (empty()) return; 77 if (pos < 0 || pos >= size_)//越界 78 { 79 cout << "out of range!" << endl; 80 return; 81 } 82 for (int i = pos; i < (size_ - 1); i++) //注意越界 83 { 84 array_[i] = array_[i + 1]; 85 } 86 size_--; 87 } 88 int MY::Vector::find(int value) 89 { 90 if (empty()) return -1; 91 int pos = -1; 92 for (int i = 0; i < size_; i++) 93 { 94 if (array_[i] == value) 95 { 96 pos = i; 97 break; 98 } 99 } 100 return pos; 101 } 102 void MY::Vector::removeByValue(int value) 103 { 104 if (empty()) return; 105 int pos = find(value); 106 if (pos == -1) 107 { 108 cout << "没有元素:" << value << endl; 109 return; 110 } 111 removeByPose(pos); 112 } 113 } 114 115 int main() 116 { 117 // 参考别人博客:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_26816591/article/details/52214313 118 //// 我的博客: https://www.cnblogs.com/winslam/articles/9146832.html 119 //int *p1 = new int; //在自由存储区开辟一个int变量 120 //int *p2 = new int[10];//在自由存储区开辟一个int数组,有10个元素 121 //for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) 122 //{ 123 // p2[i] = i; 124 // cout << "p2 = " << p2[i] << endl; 125 //} 126 //p2[2] = p2[1]; 127 //int *p3 = new int(10);//在自由存储区开辟一个int变量,并初始化为10 128 //cout << "*p3 = " << *p3 << endl; 129 130 MY::Vector vec; 131 for (int i = 0; i < 12; i++) 132 { 133 vec.push_back(i*i); 134 } 135 vec.push_back(88); 136 vec.show(); 137 vec.removeByPose(1); 138 vec.show(); 139 vec.removeByPose(2); 140 vec.show(); 141 vec.removeByValue(49); 142 vec.show(); 143 int position = vec.find(25); 144 //测试重载 145 cout << "test for overload " << endl; 146 for (int i = 0; i < vec.size_; i++) 147 { 148 cout << vec[i] << " "; 149 } 150 cout << endl; 151 152 vec.clear(); 153 vec.show(); 154 return 1; 155 }