1.字符串比较,是按照字符串(String)中每一个字符(char)的字段表顺序进行比较
/**
* Compares two strings lexicographically(字典序,按照字典顺序).
* The comparison is based on the Unicode value of each character in
* the strings. The character sequence represented by this
* {@code String} object is compared lexicographically to the
* character sequence represented by the argument string. The result is
* a negative integer if this {@code String} object
* lexicographically precedes(先于) the argument string. The result is a
* positive integer if this {@code String} object lexicographically
* follows the argument string. The result is zero if the strings
* are equal; {@code compareTo} returns {@code 0} exactly when
* the {@link #equals(Object)} method would return {@code true}.
* <p>
* This is the definition of lexicographic ordering. If two strings are
* different, then either they have different characters at some index
* that is a valid index for both strings, or their lengths are different,
* or both. If they have different characters at one or more index
* positions, let <i>k</i> be the smallest such index; then the string
* whose character at position <i>k</i> has the smaller value, as
* determined by using the < operator, lexicographically precedes the
* other string. In this case, {@code compareTo} returns the
* difference of the two character values at position {@code k} in
* the two string -- that is, the value:
* <blockquote><pre>
* this.charAt(k)-anotherString.charAt(k)
* </pre></blockquote>
* If there is no index position at which they differ, then the shorter
* string lexicographically precedes the longer string. In this case,
* {@code compareTo} returns the difference of the lengths of the
* strings -- that is, the value:
* <blockquote><pre>
* this.length()-anotherString.length()
* </pre></blockquote>
*
* @param anotherString the {@code String} to be compared.
* @return the value {@code 0} if the argument string is equal to
* this string; a value less than {@code 0} if this string
* is lexicographically less than the string argument; and a
* value greater than {@code 0} if this string is
* lexicographically greater than the string argument.
*/
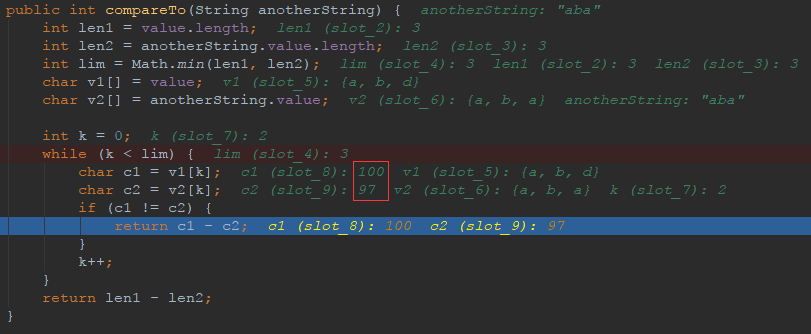
public int compareTo(String anotherString) {
int len1 = value.length;
int len2 = anotherString.value.length;
int lim = Math.min(len1, len2);
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int k = 0;
while (k < lim) {
char c1 = v1[k];
char c2 = v2[k];
if (c1 != c2) {
return c1 - c2;
}
k++;
}
return len1 - len2;
}
String str1 = "abd";
String str2 = "aba";
int res1 = str1.compareTo(str2);
//3
System.out.println(res1);
String str1 = "Abd";
String str2 = "aba";
int res1 = str1.compareTo(str2);
//-32
System.out.println(res1);
2.比较时忽略大小写
/**
* Compares two strings lexicographically, ignoring case
* differences. This method returns an integer whose sign is that of
* calling {@code compareTo} with normalized versions of the strings
* where case differences have been eliminated by calling
* {@code Character.toLowerCase(Character.toUpperCase(character))} on
* each character.
* <p>
* Note that this method does <em>not</em> take locale into account,
* and will result in an unsatisfactory ordering for certain locales.
* The java.text package provides <em>collators</em> to allow
* locale-sensitive ordering.
*
* @param str the {@code String} to be compared.
* @return a negative integer, zero, or a positive integer as the
* specified String is greater than, equal to, or less
* than this String, ignoring case considerations.
* @see java.text.Collator#compare(String, String)
* @since 1.2
*/
public int compareToIgnoreCase(String str) {
return CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER.compare(this, str);
}
String str1 = "Abd"; String str2 = "aba"; int res = str1.compareToIgnoreCase(str2); //3 System.out.println(res);