PANDAS 数据合并与重塑(concat篇)
最后发布:2016-09-13 19:26:30首发:2016-09-13 19:26:30
<div id="article_content" class="article_content clearfix">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://csdnimg.cn/release/phoenix/template/css/ck_htmledit_views-211130ba7a.css">
<div id="content_views" class="markdown_views">
<!-- flowchart 箭头图标 勿删 -->
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" style="display: none;">
<path stroke-linecap="round" d="M5,0 0,2.5 5,5z" id="raphael-marker-block" style="-webkit-tap-highlight-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);"></path>
</svg>
<p>pandas作者Wes McKinney 在【PYTHON FOR DATA ANALYSIS】中对pandas的方方面面都有了一个权威简明的入门级的介绍,但在实际使用过程中,我发现书中的内容还只是冰山一角。谈到pandas数据的行更新、表合并等操作,一般用到的方法有concat、join、merge。但这三种方法对于很多新手来说,都不太好分清使用的场合与用途。今天就pandas<a href="http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/merging.html" rel="nofollow">官网中</a>关于数据合并和重述的章节做个使用方法的总结。</p>
- 文中代码块主要有pandas官网教程提供。
1 concat
concat函数是在pandas底下的方法,可以将数据根据不同的轴作简单的融合
- 1
pd.concat(objs, axis=0, join='outer', join_axes=None, ignore_index=False,
keys=None, levels=None, names=None, verify_integrity=False)- 1
- 2
参数说明
objs: series,dataframe或者是panel构成的序列lsit
axis: 需要合并链接的轴,0是行,1是列
join:连接的方式 inner,或者outer
其他一些参数不常用,用的时候再补上说明。
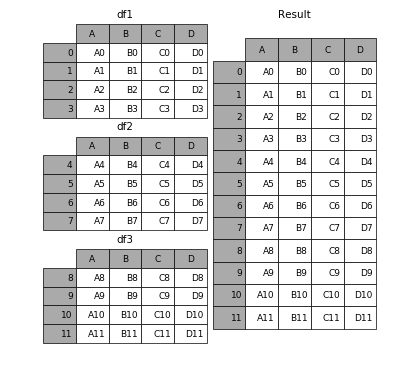
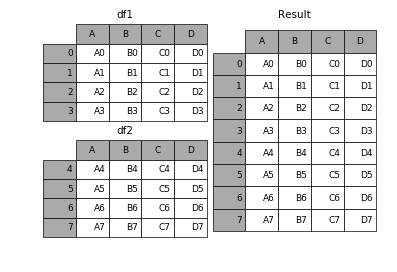
1.1 相同字段的表首尾相接
# 现将表构成list,然后在作为concat的输入
In [4]: frames = [df1, df2, df3]
In [5]: result = pd.concat(frames)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
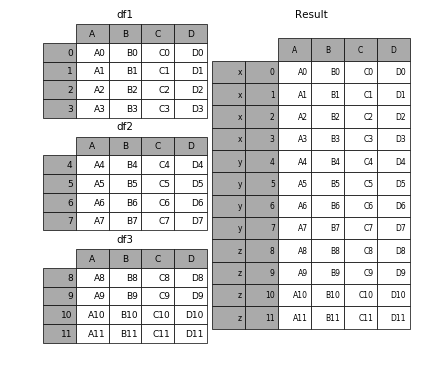
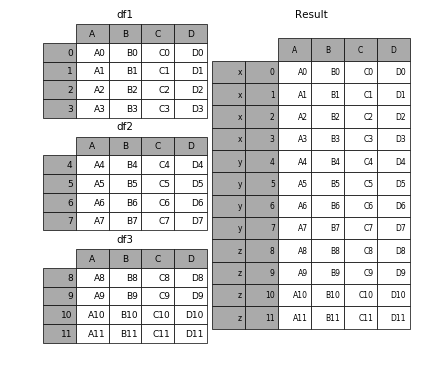
要在相接的时候在加上一个层次的key来识别数据源自于哪张表,可以增加key参数
In [6]: result = pd.concat(frames, keys=['x', 'y', 'z'])- 1
效果如下
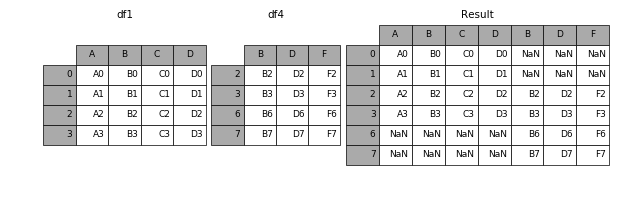
1.2 横向表拼接(行对齐)
1.2.1 axis
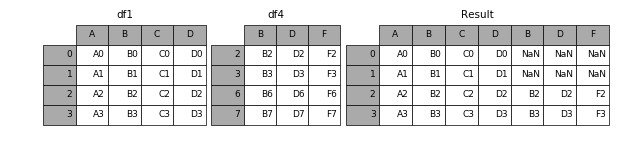
当axis = 1的时候,concat就是行对齐,然后将不同列名称的两张表合并
In [9]: result = pd.concat([df1, df4], axis=1)- 1
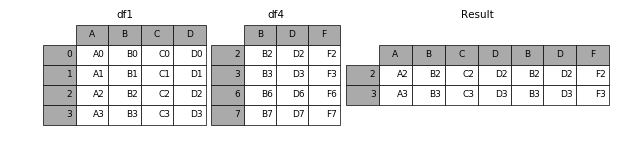
1.2.2 join
加上join参数的属性,如果为’inner’得到的是两表的交集,如果是outer,得到的是两表的并集。
In [10]: result = pd.concat([df1, df4], axis=1, join='inner')- 1
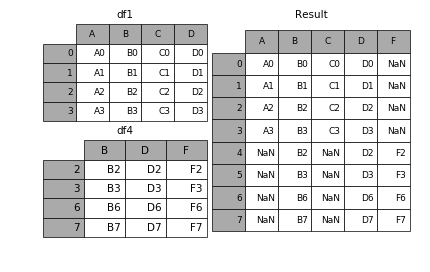
1.2.3 join_axes
如果有join_axes的参数传入,可以指定根据那个轴来对齐数据
例如根据df1表对齐数据,就会保留指定的df1表的轴,然后将df4的表与之拼接
In [11]: result = pd.concat([df1, df4], axis=1, join_axes=[df1.index])- 1
1.3 append
append是series和dataframe的方法,使用它就是默认沿着列进行凭借(axis = 0,列对齐)
- 1
In [12]: result = df1.append(df2)- 1
1.4 无视index的concat
如果两个表的index都没有实际含义,使用ignore_index参数,置true,合并的两个表就睡根据列字段对齐,然后合并。最后再重新整理一个新的index。
1.5 合并的同时增加区分数据组的键
前面提到的keys参数可以用来给合并后的表增加key来区分不同的表数据来源
1.5.1 可以直接用key参数实现
In [27]: result = pd.concat(frames, keys=['x', 'y', 'z'])- 1
1.5.2 传入字典来增加分组键
In [28]: pieces = {'x': df1, 'y': df2, 'z': df3}
In [29]: result = pd.concat(pieces)- 1
- 2
- 3
1.6 在dataframe中加入新的行
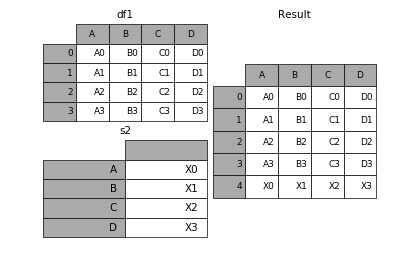
append方法可以将 series 和 字典就够的数据作为dataframe的新一行插入。
In [34]: s2 = pd.Series(['X0', 'X1', 'X2', 'X3'], index=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'])
In [35]: result = df1.append(s2, ignore_index=True)- 1
- 2
- 3
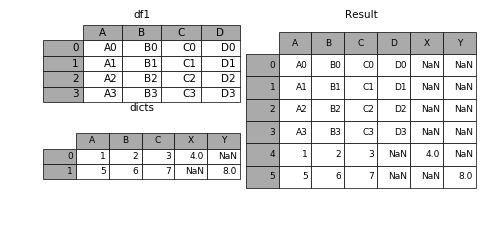
表格列字段不同的表合并
如果遇到两张表的列字段本来就不一样,但又想将两个表合并,其中无效的值用nan来表示。那么可以使用ignore_index来实现。
- 1
In [36]: dicts = [{'A': 1, 'B': 2, 'C': 3, 'X': 4},
....: {'A': 5, 'B': 6, 'C': 7, 'Y': 8}]
....:
In [37]: result = df1.append(dicts, ignore_index=True)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
下一章,我们将继续介绍pandas中其他进行数据合并和重塑的方法模块——join & merging
<div class="person-messagebox">
<div class="left-message"><a href="https://blog.csdn.net/stevenkwong">
<img src="https://profile.csdnimg.cn/4/8/A/3_stevenkwong" class="avatar_pic" username="stevenkwong">
</a></div>
<div class="middle-message">
<div class="title"><span class="tit "><a href="https://blog.csdn.net/stevenkwong" data-report-click="{"mod":"popu_379","ab":"new"}" target="_blank">正版RX-0</a></span>
<!-- 等级,level -->
<img class="identity-icon" src="https://csdnimg.cn/identity/blog4.png"> </div>
</div>
</div>
</article>