试题A——组队


直接手算,注意一位球员只能担任一个位置
答案:490
试题B——年号字串

将十进制转换为26进制
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; char str[27] = {0,'A','B','C','D','E','F','G','H','I','J','K','L','M','N','O','P','Q','R','S','T','U','V','W','X','Y','Z'}; int main(){ int num; string ans = ""; scanf("%d",&num); while(num){ ans += str[num%26]; num /= 26; } for(int i = ans.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i){ cout<<ans[i]; } return 0; }
答案:BYQ
试题C——数列求值

斐波那契数列变形题,难点是数据过大,超出了long long ,因此对每一步mod10000.
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; const int mod = 1e4; LL dp[20190325]; int main(){ dp[1] = dp[2] = dp[3] = 1; for(int i = 4;i <= 20190324; ++i){ dp[i] = (dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2] + dp[i - 3]) % mod; } cout<<dp[20190324]<<endl; return 0; }
答案:4659
试题D——数的分解

枚举,结果是一组a,b,c三个数,相同数的不同排列视为同一种,三个数总共有6种排列,因此结果要除以6
时间复杂度为2019^3,,结果要等待一会
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; bool check(int x, int y, int z){ int res = 0; while(x){ res = x % 10; if(res == 2 || res == 4) return false; x /= 10; } while(y){ res = y % 10; if(res == 2 || res == 4) return false; y /= 10; } while(z){ res = z % 10; if(res == 2 || res == 4) return false; z /= 10; } return true; } int main(){ int ans = 0; for(int a = 1; a < 2019; ++a){ for(int b = 1; b < 2019; ++b){ if(b == a) continue; for(int c = 1; c < 2019; ++c){ if(a == c || b == c) continue; if(a + b + c == 2019 && check(a,b,c)) ans++; } } } cout<<ans/6<<endl; return 0; }
答案:40785
试题E——迷宫

01010101001011001001010110010110100100001000101010 00001000100000101010010000100000001001100110100101 01111011010010001000001101001011100011000000010000 01000000001010100011010000101000001010101011001011 00011111000000101000010010100010100000101100000000 11001000110101000010101100011010011010101011110111 00011011010101001001001010000001000101001110000000 10100000101000100110101010111110011000010000111010 00111000001010100001100010000001000101001100001001 11000110100001110010001001010101010101010001101000 00010000100100000101001010101110100010101010000101 11100100101001001000010000010101010100100100010100 00000010000000101011001111010001100000101010100011 10101010011100001000011000010110011110110100001000 10101010100001101010100101000010100000111011101001 10000000101100010000101100101101001011100000000100 10101001000000010100100001000100000100011110101001 00101001010101101001010100011010101101110000110101 11001010000100001100000010100101000001000111000010 00001000110000110101101000000100101001001000011101 10100101000101000000001110110010110101101010100001 00101000010000110101010000100010001001000100010101 10100001000110010001000010101001010101011111010010 00000100101000000110010100101001000001000000000010 11010000001001110111001001000011101001011011101000 00000110100010001000100000001000011101000000110011 10101000101000100010001111100010101001010000001000 10000010100101001010110000000100101010001011101000 00111100001000010000000110111000000001000000001011 10000001100111010111010001000110111010101101111000

这题当时没做出来,参考了博主Acmer-ly的答案。
题目是求最短路径,很容易就想到用BFS,在结构体中添加一个字符串,记录每次前进的方向,
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; char mp[30][50]; bool vis[30][50]; int dir[4][2] = {{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1},{-1,0}};//按照下,左,右,上的顺序走 char dirc[4] = {'D','L','R','U'}; int n,m; struct node{ int x; int y; int step; string str; node(int xx, int yy, int ss,string s){//构造函数 x = xx; y = yy; step = ss; str = s; } }; queue<node> q; //创建队列 bool check(int x, int y){//判断是否越界、是否是墙、是否被访问过了 if(x < 0|| x >= n || y < 0 || y >= m || vis[x][y] ||mp[x][y] == '1'){ return false; } return true; } void bfs(int x, int y){ q.push(node(x, y, 0, "")); vis[x][y] = true; while(!q.empty()){ node now = q.front(); if(now.x == n - 1&&now.y == m - 1){//到达终点了 cout<<now.str<<endl; cout<<now.step<<endl; break; } q.pop(); for(int i = 0;i < 4; i++){ int nx = now.x + dir[i][0]; int ny = now.y + dir[i][1]; if(check(nx, ny)){ q.push(node(nx, ny,now.step + 1, now.str + dirc[i])); vis[nx][ny] = true; } } } } int main(){ scanf("%d%d",&n, &m); for(int i = 0;i < n; i++){ scanf("%s",mp[i]); } bfs(0, 0); return 0; }
试题F——特别数的和

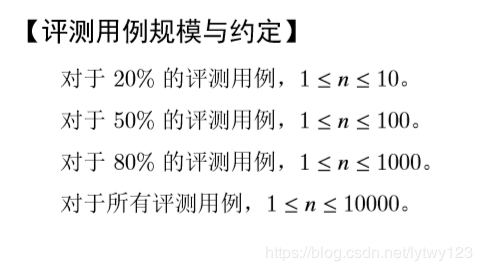
水题,枚举判定即可
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int check(int i){ int k = 0; while(i){ k = i%10; if(k == 2||k == 0||k == 1||k == 9) return true; i/=10; } return false; } int main(){ int n; scanf("%d",&n); int ans = 0; for(int i = 1;i <= n;++i){ if(check(i)){ ans += i; } } cout<<ans<<endl; return 0; }
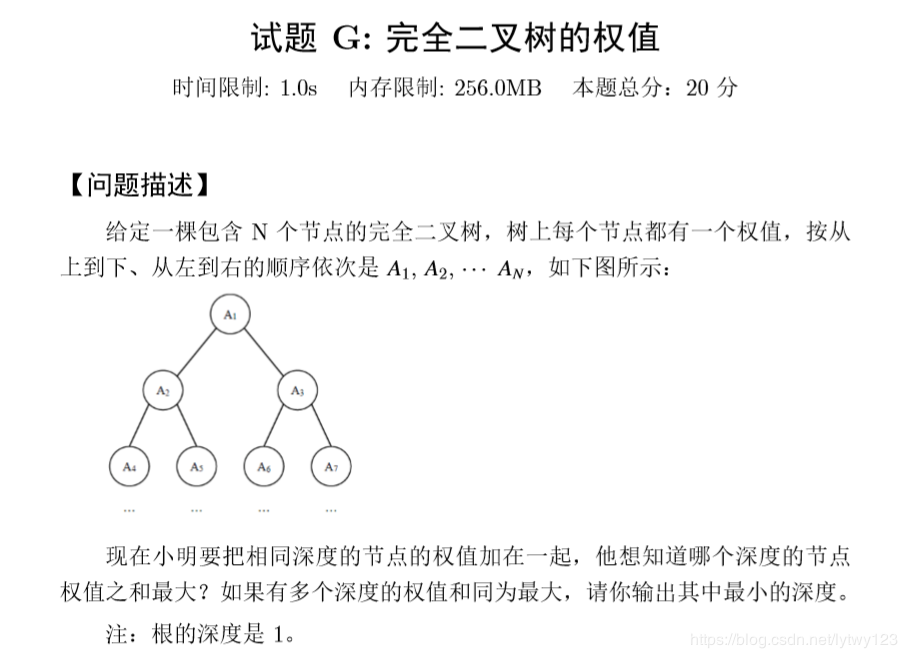
试题G——完全二叉树的权值

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; int main(){ int n; cin>>n; LL maxv = INT_MIN;//最大权值和 LL maxd = 0; for(int i = 0,length = 1,depth = 1;i < n;depth++,length *= 2 ){//逐层计算 LL sum = 0; for(int j = 0; j < length&&i < n; j++,i++){ int x; cin>>x; sum+=x; } if(sum > maxv){ maxv = sum; maxd = depth; } } cout<<maxd<<endl; return 0; }
无需建树,边输入边计算,保留最大权值和的层数,
试题H——等差数列

使用gcd求出最大公约数,再根据公式a[n] - a[1] /d + 1求出等差数列长度。
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; const int maxn = 1e5; LL a[maxn]; int gcd(int a, int b){ return !b ? a : gcd(b, a % b); } int main(){ int n; scanf("%d",&n); for(int i = 1;i <= n; ++i){ scanf("%d",&a[i]); } sort(a+1,a+n+1); for(int i = 2;i <= n; ++i){ a[i] -= a[1]; } int d = a[2]; for(int i = 3; i <= n; ++i){ d = gcd(d, a[i]); } if(d == 0){ cout<<n<<endl; }else{ cout<<a[n] / d + 1<<endl; } return 0; }
试题I——后缀表达式

试题J——灵能传输

