1、JdbcTemplate的基本介绍
JdbcTemplate是Spring对JDBC的封装,目的是使JDBC更加易于使用。JdbcTemplate是Spring的一部分。JdbcTemplate处理了资源的建立和释放。他帮助我们避免一些常见的错误,比如忘了总要关闭连接。他运行核心的JDBC工作流,如Statement的建立和执行,而我们只需要提供SQL语句和提取结果。
Spring为了简化数据库访问,主要做了以下几点工作:
- 提供了简化的访问JDBC的模板类,不必手动释放资源;
- 提供了一个统一的DAO类以实现Data Access Object模式;
- 把
SQLException封装为DataAccessException,这个异常是一个RuntimeException,并且让我们能区分SQL异常的原因,例如,DuplicateKeyException表示违反了一个唯一约束; - 能方便地集成Hibernate、JPA和MyBatis这些数据库访问框架。
2、JdbcTemplate的基本使用
2.1、新增数据(jdbcTemplate.update)
先导入以下依赖包。Spring框架的JdbcTemplate在spring-jdbc的jar包中,,除了要导入这个 jar 包外,还需要导入一个 spring-tx的jar包(它是和事务相关的)。当然连接池的jar包也不能忘记,这里使用的是 druid。
然后在 spring 的 xml 配置文件中配置数据库连接池和 JdbcTemplate,同时我们也开启组件扫描。另外我们可以通过一个 jdbc.properties 配置文件来维护数据库的连接配置。
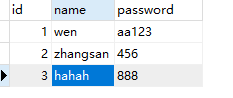
下面假设我们操作的是 test 数据库里面的 user 表,表结构如下:
jdbc.properties 配置文件内容:
prop.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
prop.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
prop.username=root
prop.password=123456
spring 的 xml 配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!--开启组件扫描--> <context:component-scan base-package="test, service, dao"></context:component-scan> <!--引入外部配置文件--> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/> <!--配置数据库连接池--> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="${prop.driverClass}"></property> <!--通过${}使用外部配置文件的值--> <property name="url" value="${prop.url}"></property> <property name="username" value="${prop.username}"></property> <property name="password" value="${prop.password}"></property> </bean> <!-- 配置JdbcTmplate --> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <!-- 注入dataSource --> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> <!-- <constructor-arg name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg>--> <!-- 也可以用构造函数写法 --> </bean> </beans>
新建一个实体类 User :
package entity; public class User { private int id; private String name; private String password; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } }
新建一个 UserServiceImpl 类:
package service; import dao.UserDao; import entity.User; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ @Autowired private UserDao userDao; @Override public void addUser(User user) { userDao.addUser(user); } }
新建一个 UserDaoImpl 类:
package dao; import entity.User; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; @Repository public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{ //注入JdbcTemplate @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; @Override public void addUser(User user) { //创建SQL语句 String sql = "insert into user values(?, ?, ?)"; //调用方法执行SQL int updateRow = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, user.getId(), user.getName(), user.getPassword()); System.out.println(updateRow); } }
验证代码:
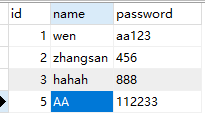
package test; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import entity.User; import service.UserService; import service.UserServiceImpl; public class Test01 { ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean01.xml"); //JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate= ioc.getBean(JdbcTemplate.class); //我们也可以直接通过获取到的jdbctemplate进行SQL操作,上面使用UserServiceImpl和UserDaoImpl只是为了更符合MVC分层的规范 @Test public void test1() { User user = new User(); user.setId(5); user.setName("AA"); user.setPassword("112233"); UserService userService = ioc.getBean(UserServiceImpl.class); userService.addUser(user); //执行增加方法 } }
执行上面 test1 方法,可以看到输出如下:

即对一行数据起了作用,可以看到表数据发生了更改:
2.1.1、批量增加(batchUpdate)
批量增加可以使用 jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate() 方法,示例如下:
UserServiceImpl 增加批量增加方法:
package service; import dao.UserDao; import entity.User; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.util.List; @Service public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ @Autowired private UserDao userDao; @Override public void addBath(List<Object[]> userList) { userDao.addBath(userList); } }
UserDaoImpl 增加批量增加方法:
package dao; import entity.User; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; @Repository public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao { //注入JdbcTemplate @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; @Override public void addBath(List<Object[]> userList) { String sql = "insert into user values(?, ?, ?)"; int[] ints = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, userList); //batchUpdate方法第二个参数是集合,该集合元素是数组,数组里面的每个值对应着添加到数据库表里面的字段值。该方法返回影响行数数组 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints)); } }
验证:
package test; import entity.User; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import service.UserService; import service.UserServiceImpl; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class TestMain { ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean01.xml"); @Test public void test2() { List<Object[]> userList = new ArrayList<>(); Object[] arr1 = {1, "name1", "password1"}; Object[] arr2 = {2, "name2", "password2"}; Object[] arr3 = {3, "name3", "password3"}; userList.add(arr1); userList.add(arr2); userList.add(arr3); UserService userService = ioc.getBean(UserServiceImpl.class); userService.addBath(userList); } }
2.2、修改和删除数据(jdbcTemplate.update)
修改和删除跟上面的新增操作一样,只是SQL语句不同而已。
UserServiceImpl 增加修改和删除方法:
package service; import dao.UserDao; import entity.User; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ @Autowired private UserDao userDao; @Override public void updateUser(User user) { userDao.updateUser(user); } @Override public void deleteUser(int userId) { userDao.deleteUser(userId); } }
UserDaoImpl 增加修改删除方法:
package dao; import entity.User; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; @Repository public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{ //注入JdbcTemplate @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; @Override public void updateUser(User user) { String sql = "update user set name=?, password=? where id=?"; int updateRow = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, user.getName(), user.getPassword(), user.getId()); System.out.println(updateRow); } @Override public void deleteUser(int userId) { String sql = "delete from user where id=?"; int updateRow = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, userId); System.out.println(updateRow); } }
验证代码:
package test; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;import entity.User; import service.UserService; import service.UserServiceImpl;public class Test01 { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean01.xml"); //修改操作 @Test public void test1() { User user = new User(); user.setId(2); user.setName("AA"); user.setPassword("112233"); UserService userService = applicationContext.getBean(UserServiceImpl.class); userService.updateUser(user); } //删除操作 @Test public void test2() { UserService userService = applicationContext.getBean(UserServiceImpl.class); userService.deleteUser(5); } }
2.2.1、批量修改和删除(batchUpdate)
批量修改和批量删除都可以使用 jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate() 方法,示例如下:
UserServiceImpl 增加批量修改和删除方法:
package service; import dao.UserDao; import entity.User; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.util.List; @Service public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ @Autowired private UserDao userDao; //批量修改 @Override public void updateBatch(List<Object[]> listArg) { userDao.updateBatch(listArg); } //批量删除 @Override public void deleteBath(List<Object[]> listArg) { userDao.deleteBath(listArg); } }
UserDaoImpl 增加批量修改和删除方法:
package dao; import entity.User; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; @Repository public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao { //注入JdbcTemplate @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; //批量修改 @Override public void updateBatch(List<Object[]> listArg) { String sql = "update user set name=?, password=? where id=?"; int[] ints = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, listArg); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints)); } //批量删除 @Override public void deleteBath(List<Object[]> listArg) { String sql = "delete from user where id=?"; int[] ints = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, listArg); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints)); } }
验证:
package test; import entity.User; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import service.UserService; import service.UserServiceImpl; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class TestMain { ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean01.xml"); //批量修改 @Test public void test3() { List<Object[]> userList = new ArrayList<>(); Object[] arr1 = {"name1changed", "password1", 1}; Object[] arr2 = {"name2changed", "password2", 2}; Object[] arr3 = {"name3changed", "password3", 3}; userList.add(arr1); userList.add(arr2); userList.add(arr3); UserService userService = ioc.getBean(UserServiceImpl.class); userService.updateBatch(userList); } //批量删除 @Test public void test4() { List<Object[]> userList = new ArrayList<>(); Object[] arr1 = {6}; Object[] arr2 = {7}; userList.add(arr1); userList.add(arr2); UserService userService = ioc.getBean(UserServiceImpl.class); userService.deleteBath(userList); } }
2.3、查询数据
2.3.1、查询返回某个值(queryForObject)
比如查询 user 表内数据总数:
package service; import dao.UserDao; import entity.User; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ @Autowired private UserDao userDao; @Override public int getUserCount() { return userDao.getUserCount(); } }
UserDaoImpl 代码:
package dao; import entity.User; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; @Repository public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{ //注入JdbcTemplate @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; @Override public int getUserCount() { String sql = "select count(*) from user"; int userCount = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, int.class); //第二个参数是返回类型的class return userCount; } }
验证:
package test; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import entity.User; import service.UserService; import service.UserServiceImpl; public class Test01 { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean01.xml"); //查询数量 @Test public void test4() { UserService userService = applicationContext.getBean(UserServiceImpl.class); int userCount = userService.getUserCount(); System.out.println(userCount); //将输出user表内数据总数 } }
2.3.2、查询返回对象(queryForObject)
比如查询 user 表内某一条数据,然后我们可以将该数据封装成一个 User 对象:
package service; import dao.UserDao; import entity.User; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ @Autowired private UserDao userDao; @Override public User getUserInfo(int userId) { return userDao.getUserInfo(userId); } }
UserDaoImpl 代码:
package dao; import entity.User; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; @Repository public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{ //注入JdbcTemplate @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; @Override public User getUserInfo(int userId) { String sql = "select * from user where id=?"; // rowMapper 是一个接口,可以使用这个接口里面的实现类完成数据的封装,规定每一行记录和JavaBean的属性如何映射 User user = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(User.class), userId); return user; } }
验证:
package test; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import entity.User; import service.UserService; import service.UserServiceImpl; public class Test01 { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean01.xml"); @Test public void test3() { UserService userService = applicationContext.getBean(UserServiceImpl.class); User user = userService.getUserInfo(2); System.out.println(user.getName()); } }
2.3.2、查询返回集合(query)
比如查询 user 表内的所有数据,并且将数据都封装成 User 对象:
package service; import dao.UserDao; import entity.User; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.util.List; @Service public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ @Autowired private UserDao userDao; @Override public List<User> getAllUser() { return userDao.getAllUser(); } }
UserDaoImpl 代码:
package dao; import entity.User; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import java.util.List; @Repository public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{ //注入JdbcTemplate @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; @Override public List<User> getAllUser() { String sql = "select * from user"; List<User> userList = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(User.class)); return userList; } }
验证:
package test; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import entity.User; import service.UserService; import service.UserServiceImpl; import java.util.List; public class Test01 { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean01.xml"); //查询全部数据 @Test public void test5() { UserService userService = applicationContext.getBean(UserServiceImpl.class); List<User> userList = userService.getAllUser(); for (User user: userList) { System.out.println(user.getName()); } } }