There are n items each belonging to zero or one of m groups where group[i] is the group that the i-th item belongs to and it's equal to -1 if the i-th item belongs to no group. The items and the groups are zero indexed. A group can have no item belonging to it.
Return a sorted list of the items such that:
- The items that belong to the same group are next to each other in the sorted list.
- There are some relations between these items where
beforeItems[i]is a list containing all the items that should come before thei-th item in the sorted array (to the left of thei-th item).
Return any solution if there is more than one solution and return an empty list if there is no solution.
Example 1:
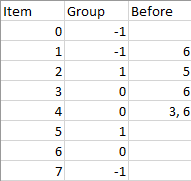
Input: n = 8, m = 2, group = [-1,-1,1,0,0,1,0,-1], beforeItems = [[],[6],[5],[6],[3,6],[],[],[]] Output: [6,3,4,1,5,2,0,7]
Example 2:
Input: n = 8, m = 2, group = [-1,-1,1,0,0,1,0,-1], beforeItems = [[],[6],[5],[6],[3],[],[4],[]] Output: [] Explanation: This is the same as example 1 except that 4 needs to be before 6 in the sorted list.
Constraints:
1 <= m <= n <= 3*10^4group.length == beforeItems.length == n-1 <= group[i] <= m-10 <= beforeItems[i].length <= n-10 <= beforeItems[i][j] <= n-1i != beforeItems[i][j]beforeItems[i]does not contain duplicates elements.
class Solution { public int[] sortItems(int n, int m, int[] group, List<List<Integer>> beforeItems) { // 1.topology sort items // 2.topology sort group // 3.put sorted items to its group with output of 1 and 2 // 4.iterate group inorder and add items in each group to the result array HashMap<Integer, List<Integer>> gGraph = new HashMap(); HashMap<Integer, List<Integer>> iGraph = new HashMap(); //put items belongs no group to its own group for(int i = 0; i < group.length; i++){ if(group[i] == -1) group[i] = m++; } int[] itemInDegree = new int[n]; int[] groupInDegree = new int[m]; //build item graph for(int to = 0; to < beforeItems.size(); to++){ int toGroup = group[to]; for(int from:beforeItems.get(to)){ itemInDegree[to]++; if(!iGraph.containsKey(from)){ iGraph.put(from, new ArrayList<Integer>()); } iGraph.get(from).add(to); } } //build group graph for(int to = 0; to < group.length; to++){ int toGroup = group[to]; for(int from:beforeItems.get(to)){ int fromGroup = group[from]; if(!gGraph.containsKey(fromGroup)) gGraph.put(fromGroup, new ArrayList()); if(fromGroup != toGroup){ groupInDegree[toGroup]++; } gGraph.get(fromGroup).add(toGroup); } } List<Integer> iList = tpSort(iGraph, itemInDegree, n); List<Integer> gList = tpSort(gGraph, groupInDegree, m); if(iList.size() == 0 || gList.size() == 0) return new int[0]; //key:group; val:list of items in this group HashMap<Integer, List<Integer>> groupedList = new HashMap(); for(int item:iList){ int grp = group[item]; if(!groupedList.containsKey(grp)) groupedList.put(grp, new ArrayList()); groupedList.get(grp).add(item); } int i = 0; int[] ans = new int[n]; for(int grp:gList){ if(!groupedList.containsKey(grp)) continue; for(int item: groupedList.get(grp)){ ans[i] = item; i++; } } return ans; } public List<Integer> tpSort(HashMap<Integer, List<Integer>> graph, int[] inDegree, int count){ List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList(); Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList(); for(int i = 0; i < inDegree.length; i++){ if(inDegree[i] == 0) q.offer(i); } while(!q.isEmpty()){ int cur = q.poll(); ans.add(cur); if(!graph.containsKey(cur)) continue; for(int next: graph.get(cur)){ inDegree[next]--; if(inDegree[next] == 0) q.offer(next); } } return count == ans.size()? ans: new ArrayList(); } }
这题也太jb难了
首先得抽象,理解题意,大概意思是有这么多item,item可能属于同一组也可能独立(-1),然后每个item可能有pre node也可能没有。
解法:先对item进行拓扑排序,然后对group进行拓扑排序,然后巴拉巴拉小魔仙,对数重组输出