终于……看到了……代理模式……
我觉得……
这个模式……
真的……
好难啊……
首先是远程代理
Java RMI 概观
↑都是这个东西好难
代理模式:为另一个对象提供一个替身或占位符以控制对这个对象的访问。
使用代理模式创建代表(representative)对象,让代表对象控制某对象的访问,被代理的对象可以是远程的对象,创建开销大的对象或者需要安全控制的对象
类图:
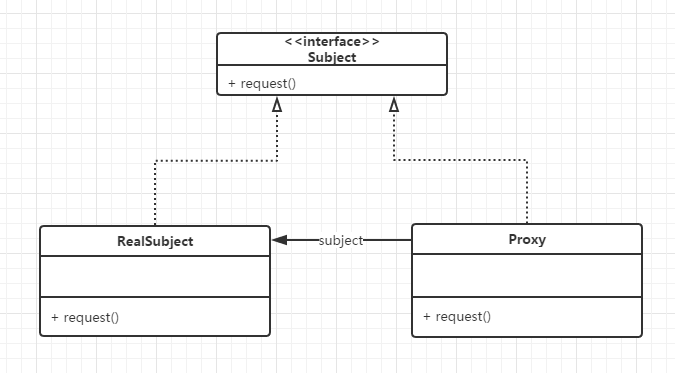
RealSubject是真正做事的对象,它是被Proxy代理和控制访问的对象。客户与RealSubject的交互都必须通过Proxy。
远程代理:远程代理可以作为;另一个JVM上的对象的本地代表。调用代理方法,会代理利用网络转发到远程执行,并将结果通过网络返回给代理,再由代理将结果转给客户。
虚拟代理:虚拟代理作为创建开销大的对象的代表。虚拟代理经常直到我们真正需要一个对象的时候才创建它。当对象在创建前和创建中时,由虚拟代理来扮演对象的替身。对象创建后,代理就会将请求直接委托给对象。
栗子:
写一个程序展示CD封面,当封面没有加载好的时候,就显示“加载中。。。”
创建一个代理类,当照片没有加载好的时候,就显示加载中,但加载好之后,就好所有方法委托给真正的照片类。
为什么要虚拟代理呢?因为没加载好的时候,还没有图片,这个代理就是一个虚拟的图片,,,
import java.awt.Component; import java.awt.Graphics; import java.net.URL; import javax.swing.Icon; import javax.swing.ImageIcon; // 代理Icon也要实现Icon接口 public class ImageProxy implements Icon { ImageIcon imageIcon; URL imageURL; Thread retrievalThread; boolean retrieving = false; // URL是图片资源位置 public ImageProxy(URL url) { imageURL = url; } // 在图像加载完毕前 返回默认的宽和高 public int getIconWidth() { if (imageIcon != null) { return imageIcon.getIconWidth(); } else { return 800; } } public int getIconHeight() { if (imageIcon != null) { return imageIcon.getIconHeight(); } else { return 600; } } public void paintIcon(final Component c, Graphics g, int x, int y) { if (imageIcon != null) { // 如果已经有Icon 就告诉它画出自己 imageIcon.paintIcon(c, g, x, y); } else { // 否则就显示加载中 g.drawString("Loading CD cover, please wait...", x+300, y+190); if (!retrieving) { // 如果我们还有试着取出图像 那么就开始取图像 retrieving = true; retrievalThread = new Thread(new Runnable() { public void run() { try { // 要在这里加载真正的Icon图像 // 请注意 加载图像和ImageIcon是同步的 也就是说 只有在加载完成之后 ImageIcon构造器才会返回 // 这样 我们的程序就会耗在这里 动弹不得 也没办法显示消息 // 我们不希望挂起整个用户界面 所以用另一个线程取出图像 // 在线程中 我们实例化此Icon对象 其构造器会在图像加载完成后才返回 // 当图像准备好时 我们告诉Swing要重绘 imageIcon = new ImageIcon(imageURL, "CD cover"); c.repaint(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); retrievalThread.start(); } } } }
然后是显示图片的ImageComponent类
import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; class ImageComponent extends JComponent { private Icon icon; public ImageComponent(Icon icon) { this.icon = icon; } public void setIcon(Icon icon) { this.icon = icon; } public void paintComponent(Graphics g) { super.paintComponent(g); int w = icon.getIconWidth(); int h = icon.getIconHeight(); int x = (800 - w)/2; int y = (600 - h)/2; icon.paintIcon(this, g, x, y); } }
测试类:
import java.net.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; import java.util.*; import java.util.Map.Entry; public class ImageProxyTestDrive { ImageComponent imageComponent; JFrame frame = new JFrame("CD封面加载器"); JMenuBar menuBar; // 菜单栏 JMenu menu; // 菜单 Map<String, String> cds = new HashMap<>(); public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { new ImageProxyTestDrive(); } public ImageProxyTestDrive() throws Exception{ // 构造菜单项用的, key=CD名, value=URL cds.put("轨迹","http://images.cnblogs.com/cnblogs_com/wenruo/873448/o_%E8%BD%A8%E8%BF%B9.png"); cds.put("分我一半的眼泪","http://images.cnblogs.com/cnblogs_com/wenruo/873448/o_%E5%88%86%E6%88%91%E4%B8%80%E5%8D%8A%E7%9A%84%E7%9C%BC%E6%B3%AA.jpg"); cds.put("光荣","http://images.cnblogs.com/cnblogs_com/wenruo/873448/o_%E5%85%89%E8%8D%A3.png"); cds.put("画中仙","http://images.cnblogs.com/cnblogs_com/wenruo/873448/o_%E7%94%BB%E4%B8%AD%E4%BB%99.jpg"); // 设置初始的CD封面 URL initialURL = new URL(cds.get("轨迹")); // 建立菜单栏 menuBar = new JMenuBar(); menu = new JMenu("Favorite CDs"); menuBar.add(menu); frame.setJMenuBar(menuBar); for(Entry<String, String> e : cds.entrySet()) { String name = e.getKey(); String url = e.getValue(); JMenuItem menuItem = new JMenuItem(name); menu.add(menuItem); menuItem.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { try { imageComponent.setIcon(new ImageProxy(new URL(url))); } catch (MalformedURLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } frame.repaint(); } }); } // set up frame and menus Icon icon = new ImageProxy(initialURL); imageComponent = new ImageComponent(icon); frame.getContentPane().add(imageComponent); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setSize(800,600); frame.setVisible(true); } }
一个虚拟代理就完成了。。。
加载前: 加载后:
加载后: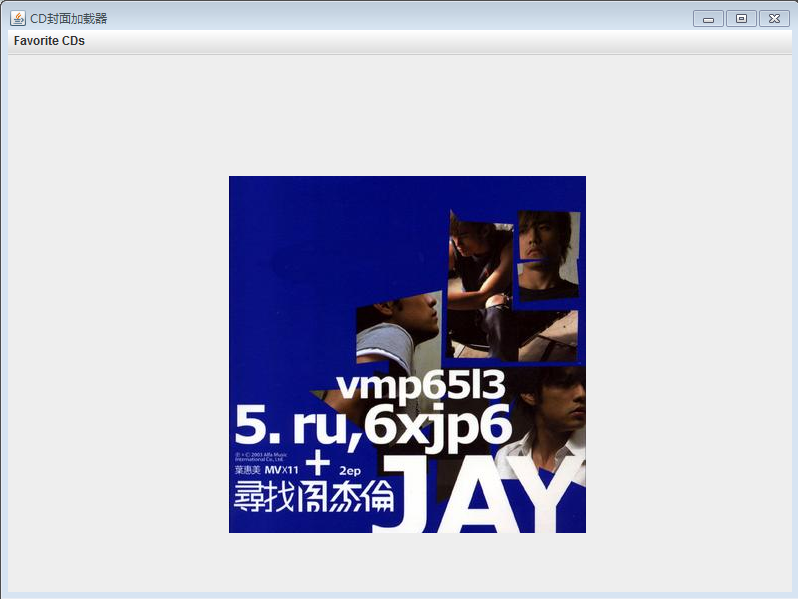
在上面的例子中,每一次都是创建新的ImageProxy来取得对象,即使图像已经被取出来过,可以把已加载的图片放入缓存中,这就是缓存代理。
缓存代理(Caching Proxy)会维护之前创建的对象,当收到请求时,在可能的情况下返回缓存对象。
动态代理:Java在java.lang.reflect包中有自己的代理支持,利用这个包你可以在运行时动态地创建一个代理类,实现一个或多个接口,并将方法的调用转发到你所指定的类。因为实际的代理类是在运行时被创建的,我们称这个技术为:动态代理。
动态代理类图:
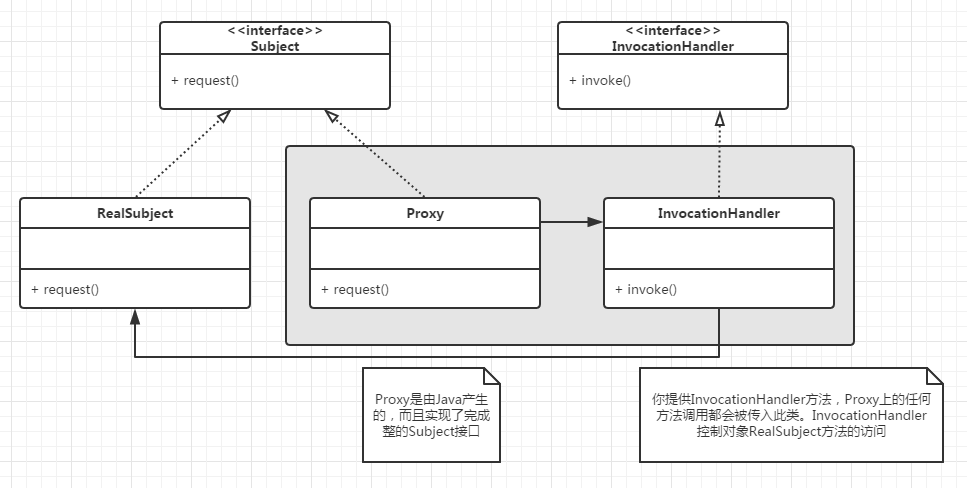
动态代理的实现
有一个系统,存有每个人的信息,和每个人的评分。现在希望每个人不能给自己评分,而更改个人信息只有自己能做到。
于是设计两个代理,一个控制访问自己的类,一个控制访问其他人。
首先是个人信息的接口:
public interface PersonBean { String getName(); String getGender(); String getInterests(); int getHotOrNotRating(); void setName(String name); void setGender(String gender); void setInterests(String interests); void setHotOrNotRating(int rating); }
具体实现类
public class PersonBeanImpl implements PersonBean { String name; String gender; String interests; int rating; int ratingCount = 0; public PersonBeanImpl(String name, String gender, String interests) { super(); this.name = name; this.gender = gender; this.interests = interests; } public String getName() { return name; } public String getGender() { return gender; } public String getInterests() { return interests; } public int getHotOrNotRating() { if (ratingCount == 0) return 0; return (rating / ratingCount); } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public void setGender(String gender) { this.gender = gender; } public void setInterests(String interests) { this.interests = interests; } public void setHotOrNotRating(int rating) { this.rating += rating; ratingCount++; } }
创建两个InvocationHandler,一个给拥有者使用
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class OwnerInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler { PersonBean person; public OwnerInvocationHandler(PersonBean person) { this.person = person; } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { try { if (method.getName().startsWith("get")) { return method.invoke(person, args); } else if (method.getName().equals("setHotOrNotRating")) { throw new IllegalAccessException(); } else if (method.getName().startsWith("set")) { return method.invoke(person, args); } } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } }
一个给非拥有者使用
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class NotOwnerInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler { PersonBean person; public NotOwnerInvocationHandler(PersonBean person) { this.person = person; } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws IllegalAccessException { try { if (method.getName().startsWith("get")) { return method.invoke(person, args); } else if (method.getName().equals("setHotOrNotRating")) { return method.invoke(person, args); } else if (method.getName().startsWith("set")) { throw new IllegalAccessException(); } } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } }
测试类:
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import java.util.ArrayList; public class MatchMakingTestDrive { public static void main(String[] args) { MatchMakingTestDrive test = new MatchMakingTestDrive(); test.drive(); } public MatchMakingTestDrive() { initializeDatabsae(); } public void drive() { PersonBean joe = getPersonFromDatabase("Joe JavaBean"); PersonBean ownerProxy = getOwnerProxy(joe); System.out.println("Name is " + ownerProxy.getName()); ownerProxy.setInterests("bowling, Go"); System.out.println("Interests set from owner proxy"); try { ownerProxy.setHotOrNotRating(10);//不能给自己平分 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Can't set rating from owner proxy"); } System.out.println("Rating is " + ownerProxy.getHotOrNotRating()); PersonBean nonOwnerProxy = getNonOwnerProxy(joe); System.out.println("Name is " + nonOwnerProxy.getName()); try { nonOwnerProxy.setInterests("bowling, Go"); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Can't set interests from non owner proxy"); } nonOwnerProxy.setHotOrNotRating(3); System.out.println("Rating set from non owner proxy"); System.out.println("Rating is " + nonOwnerProxy.getHotOrNotRating()); } PersonBean getOwnerProxy(PersonBean person) { return (PersonBean) Proxy.newProxyInstance( person.getClass().getClassLoader(), person.getClass().getInterfaces(), new OwnerInvocationHandler(person)); } PersonBean getNonOwnerProxy(PersonBean person) { return (PersonBean) Proxy.newProxyInstance( person.getClass().getClassLoader(), person.getClass().getInterfaces(), new NotOwnerInvocationHandler(person)); } /************假装这是数据库实现**************/ ArrayList<PersonBean> beans; void initializeDatabsae() { beans = new ArrayList<>(); beans.add(new PersonBeanImpl("Joe JavaBean", "男", "学习")); } PersonBean getPersonFromDatabase(String name) { for (int i = 0; i < beans.size(); ++i) { PersonBean person = beans.get(i); if (person.getName().equals(name)) return person; } return null; } }
一些其他的代理模式:
防火墙代理:控制网络资源的访问,保护主题免于“坏客户”的侵害。
智能引用代理:当主题被引用时,进行额外的动作,例如计算一个对象呗引用的次数。
缓存代理:为开销大的运算结果提供暂时的存储,它也允许多个客户共享结果,以减少计算或网络延迟。
同步代理:在多线程的情况下为主题提供安全的访问。
复杂隐藏代理:用来隐藏一个类的复杂集合的复杂度,并进行访问控制。
写入时复制代理:用来控制对象的复制,方法是延迟对象的复制,直到客户真的需要为止。这是虚拟代理的变体。