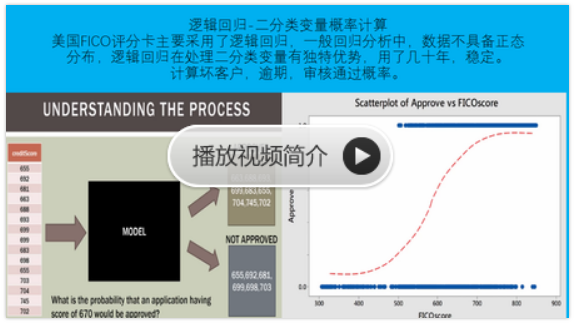
python信用评分卡(附代码,博主录制)
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression as LR from sklearn.linear_model import RandomizedLogisticRegression as RLR rlr=RLR() #建立随机逻辑回归模型,筛选变量 rlr.fit(x,y) #训练模型 rlr.get_support() #获取特征筛选结果 print(u'有效特征为:%s'%','.join(np.array(data.iloc[:,:8].columns)[rlr.get_support()])) x=data[np.array(data.iloc[:,:8].columns)[rlr.get_support()]].as_matrix() #筛选好特征 lr=LR() #建立逻辑回归模型 lr.fit(x,y) #用筛选后的特征数据来训练模型 print(u'逻辑回归模型训练结束') print(u'模型的平均正确率为:%s'%lr.score(x,y)) #给出模型的平均正确率
Scikit_Learn API :
sklearn.linear_model 广义线性模型
sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRegression Logistic 回归分类器
Methods:
score(X, y[, sample_weight]) Returns the mean accuracy on the given test data and labels
Parameters:
:x:array-like, Test samples; y: array-like, True labels for X.
sample_weight:可选项,样本权重
Returns:
score: float, Mean accuracy of self.predict(X) wrt. y 获取各个特征的分数
sklearn.linear_model.RandomizedLogisticRegression 随机逻辑回归
官网对于随机逻辑回归的解释:
Randomized Logistic Regression works by subsampling the training data and fitting a L1-penalized LogisticRegression model where the penalty of a random subset of coefficients has been scaled. By performing this double randomization several times, the method assigns high scores to features that are repeatedly selected across randomizations. This is known as stability selection. In short, features selected more often are considered good features.
解读:对训练数据进行多次采样拟合回归模型,即在不同的数据子集和特征子集上运行特征算法,不断重复,最终选择得分高的重要特征。这是稳定性选择方法。得分高的重要特征可能是由于被认为是重要特征的频率高(被选为重要特征的次数除以它所在的子集被测试的次数)