哈夫曼编码,旨在对信息实现一种高效的编码,这种编码中任何一个都不是其他编码的前缀码。因此,在实际接收时,一旦匹配,就可以立即解码。
具体算法过程可以参加网上的很多教程。
给出一个自己的实现,一方面加强印象,一方面练习一下。能力有限,还请同学们多多帮助。
1 ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// 2 /// 3 /// 代码并没有做仔细的参数验证等异常处理,仅仅做了功能级别的实现 4 /// 5 ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// 6 7 #define __debug 8 using System; 9 using System.Collections.Generic; 10 using System.Linq; 11 12 namespace Algo 13 { 14 public class ChainedNode 15 { 16 public string symbol; 17 public double probab; 18 public ChainedNode parent; 19 public string flag; 20 public bool isLeave; 21 } 22 23 public class Huffman 24 { 25 private List<ChainedNode> nodelist; 26 27 public Huffman(Dictionary<string, double> dic) 28 { 29 nodelist = new List<ChainedNode>(); 30 foreach (var item in dic) 31 { 32 ChainedNode node = new ChainedNode(); 33 node.probab = item.Value; 34 node.symbol = item.Key; 35 node.isLeave = true; 36 nodelist.Add(node); 37 } 38 } 39 40 public List<ChainedNode> BuildHuffman() 41 { 42 List<ChainedNode> res = new List<ChainedNode>(); 43 44 while (nodelist.Count > 1) 45 { 46 nodelist = (from t in nodelist orderby t.probab ascending select t).ToList(); 47 48 ChainedNode first = nodelist[0]; 49 first.flag = "0"; 50 nodelist.RemoveAt(0); 51 ChainedNode second = nodelist[0]; 52 second.flag = "1"; 53 nodelist.RemoveAt(0); 54 55 ChainedNode c = new ChainedNode(); 56 c.probab = first.probab + second.probab; 57 c.symbol = first.symbol + second.symbol; 58 59 first.parent = c; 60 second.parent = c; 61 62 nodelist.Add(c); 63 if (first.isLeave) 64 { 65 res.Add(first); 66 } 67 if (second.isLeave) 68 { 69 res.Add(second); 70 } 71 } 72 return res; 73 } 74 75 public void GenerateCode(List<ChainedNode> head) 76 { 77 for (int i = 0; i < head.Count; i++) 78 { 79 ChainedNode cn = head[i]; 80 string symbol = cn.symbol; 81 string build = string.Empty; 82 double prop = cn.probab; 83 while (cn.parent != null) 84 { 85 build = cn.flag + build; 86 cn = cn.parent; 87 } 88 cn = head[i]; 89 cn.flag = build; 90 #if __debug 91 Console.WriteLine("{0}:{1}:{2}.", cn.symbol, cn.probab, cn.flag); 92 #endif 93 } 94 } 95 } 96 97 class Program 98 { 99 static void Main(string[] args) 100 { 101 Dictionary<string, double> dic = new Dictionary<string, double>(); 102 dic.Add("u1", 0.1); 103 dic.Add("u2", 0.2); 104 dic.Add("u3", 0.4); 105 dic.Add("u4", 0.2); 106 dic.Add("u5", 0.1); 107 108 Huffman hc = new Huffman(dic); 109 var list = hc.BuildHuffman(); 110 hc.GenerateCode(list); 111 112 Console.ReadLine(); 113 } 114 } 115 }
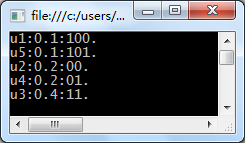
运行结果如下图