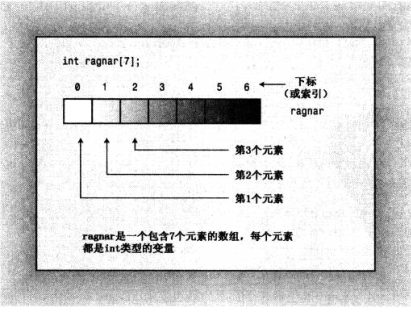
4.1、数组
数组(array)是一种数据格式,能够存储多个同类型的值。
数组声明应该指出以下三点:
存储在每个元素当中的值得类型,
数组名
数组中的的元素数
通用格式:
typename arrayName[arraySize];
表达式arraySize指定元素的数目,它必须是整型常数,或const值。
4.1.2、数组初始化方法;

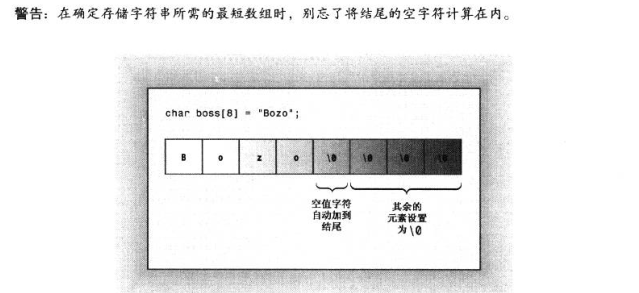
4.2、字符串
字符串是存储在内存的连续字节中的一系类字符,C++处理字符串的方式有两种,第一种来自C语言,常被称为C-风格字符串,另一种给予string类库的方法。
存储在连续字节中的一系类字符意味着可以将字符串存储在插入数组中,其中每个字符都位于自己的数据元素中,字符串提供了一种存储文本信息的快捷方式。

拼接字符串常量:

4.2.3字符串的输入
每次读取一行字符串输入
istream中的类(如cin)提供了一些面向行的类成员函数:getline()和get()。这两个函数都读取一行输入,直到到达换行符。然而,随后getline()将丢弃换行符,而get()将换行符保留在输入序列中。


4.3、C++ string类
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str1 = "hello";
string* str2 = new string("hello");
string str3 = "world";
//获取字符串长度
int length = str1.length();
cout << "调用str.length()函数获取字符串长度:" << length << endl;
cout << endl;
//字符串连接
string str4 = str1 + str3;
cout << "字符串连接结果:" << str4 << endl;
cout << endl;
//字符串比较
if (str1 < str3)
cout << "字符串比较:" << "str1<str2" << endl;
cout << endl;
//获取字符串的第一个字符
string::const_iterator it = str1.begin();
cout << *it << endl;
cout << endl;
//获取字符串的最后一个字符
it = str1.end();//end是指向最后一个字符后面的元素,而且不能输出,所以cout << *it << endl;这样输出会报错
it--;
cout << *it << endl;
cout << endl;
//倒置串
reverse(str1.begin(), str1.end());
cout << "倒置串:" << str1 << endl;
cout << endl;
//字符串转字符数组
//不推荐的用法,但是需要了解
string a = "abc123";
const char *b;//这里必须为const char *,不能用char *,不然下一句会报错
b = a.c_str();
cout << "a:" << a << endl;
cout << "b:" << b << endl;
a = "asd456";
cout << "a:" << a << endl;
cout << "b:" << b << endl;
//推荐用法
string c = "abc123";
char *d = new char[20];
strcpy(d, c.c_str());//因为这里没有直接赋值,所以指针类型可以不用const char *
cout << "c:" << c << endl;
cout << "d:" << d << endl;
c = "asd456";
cout << "c:" << c << endl;
cout << "d:" << d << endl;
cout << endl;
//查找串
//find-从指定位置起向后查找,直到串尾
string st1("babbabab");
cout << st1.find('a') << endl;//1,默认从位置0(即第1个字符)开始查找
cout << st1.find('a', 2) << endl;//4 在st1中,从位置2(b,包括位置2)开始,查找a,返回首次匹配的位置
cout << (st1.find('c', 0) == -1) << endl;//1
cout << (st1.find('c', 0) == 4294967295) << endl;//1 两句均输出1,原因是计算机中-1和4294967295都表示为32个1(二进制)
string st2("aabcbcabcbabcc");
str1 = "abc";
cout << st2.find(str1, 2) << endl;//6,从st2的位置2(b)开始匹配,返回第一次成功匹配时匹配的串(abc)的首字符在st2中的位置,失败返回-1
cout << st2.find("abcdefg", 2, 3) << endl;//6 取abcdefg得前3个字符(abc)参与匹配,相当于st2.find("abc", 2)
//rfind-从指定位置起向前查找,直到串首
cout << st1.rfind('a', 7) << endl;//6
//find_first_of-在源串中从位置pos起往后查找,只要在源串中遇到一个字符,该字符与目标串中任意一个字符相同,就停止查找,返回该字符在源串中的位置;若匹配失败,返回-1
string str6("bcgjhikl");
string str7("kghlj");
cout << str6.find_first_of(str7, 0) << endl;//2,从str1的第0个字符b开始找,g与str2中的g匹配,停止查找,返回g在str1中的位置2
//find_last_of-与find_first_of函数相似,只不过查找顺序是从指定位置向前
string str("abcdecg");
cout << str.find_last_of("hjlywkcipn", 6) << endl;//5,从str的位置6(g)开始向前找,g不匹配,再找c,c匹配,停止查找,返回c在str中的位置5
//find_first_not_of-在源串中从位置pos开始往后查找,只要在源串遇到一个字符,与目标串中的任意字符都不相同,就停止查找,返回该字符在源串中的位置;若遍历完整个源串,都找不到满足条件的字符,则返回-1
cout << str.find_first_not_of("kiajbvehfgmlc", 0) << endl;//3 从源串str的位置0(a)开始查找,目标串中有a,匹配,..,找d,目标串中没有d(不匹配),停止查找,返回d在str中的位置3
//find_last_not_of-与find_first_not_of相似,只不过查找顺序是从指定位置向前
cout << str.find_last_not_of("kiajbvehfgmlc", 6) << endl;//3
system("pause");
return 0;
}