struct的小秘密:空结构体占多大内存呢?

直观的答案有两种:
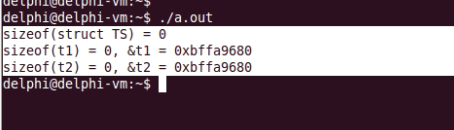
1、空结构体的大小为0
2、结构体本来就是为了将不同的变量集合在一起使用的,定义空结构体会导致编译错误
实例分析:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 struct TS 4 { 5 6 }; 7 8 int main() 9 { 10 struct TS t1; 11 struct TS t2; 12 13 printf("sizeof(struct TS) = %d ", sizeof(struct TS)); 14 printf("sizeof(t1) = %d, &t1 = %p ", sizeof(t1), &t1); 15 printf("sizeof(t2) = %d, &t2 = %p ", sizeof(t2), &t2); 16 17 return 0; 18 }
gcc编译运行如下所示:
用bcc编译器对上述程序进行编译,结果如下:
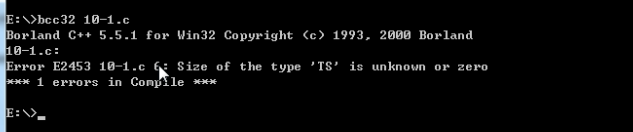
bcc不允许定义空结构体。
用vc编译器编译结果如下:
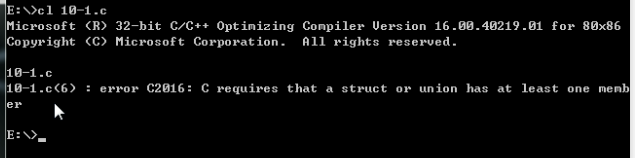
vc编译器也不允许定义空结构体。
结构体与柔性数组:

在C语言中,结构体的最后一个元素可以定义成int array[]的形式。大小待定的数组即为柔性数组。
示例:
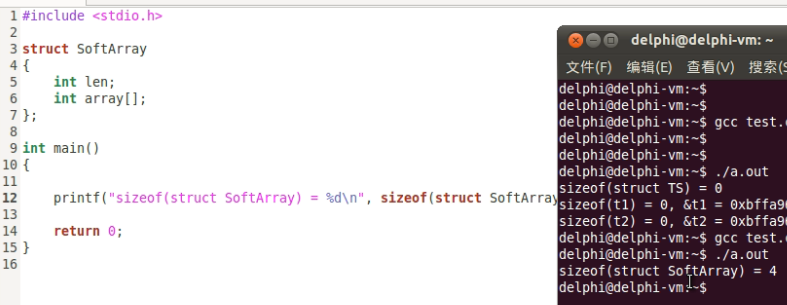
柔性数组的用法:
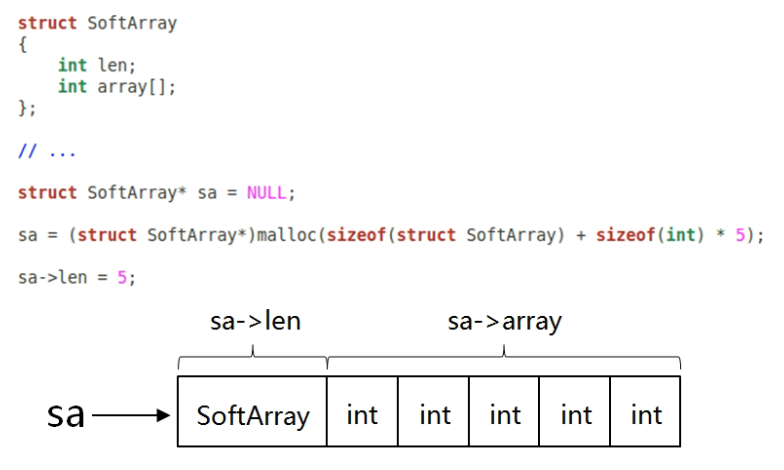
SoftArray的成员只有len。array[]只是一个标识,实际使用时代表的是len之后的动态申请的空间。
示例:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <malloc.h> 3 4 struct SoftArray 5 { 6 int len; 7 int array[]; 8 }; 9 10 struct SoftArray* create_soft_array(int size) 11 { 12 struct SoftArray* ret = NULL; 13 14 if( size > 0 ) 15 { 16 ret = (struct SoftArray*)malloc(sizeof(struct SoftArray) + sizeof(int) * size); 17 18 ret->len = size; 19 } 20 21 return ret; 22 } 23 24 void delete_soft_array(struct SoftArray* sa) 25 { 26 free(sa); 27 } 28 29 void func(struct SoftArray* sa) 30 { 31 int i = 0; 32 33 if( NULL != sa ) 34 { 35 for(i=0; i<sa->len; i++) 36 { 37 sa->array[i] = i + 1; 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 42 int main() 43 { 44 int i = 0; 45 struct SoftArray* sa = create_soft_array(10); 46 47 func(sa); 48 49 for(i=0; i<sa->len; i++) 50 { 51 printf("%d ", sa->array[i]); 52 } 53 54 delete_soft_array(sa); 55 56 return 0; 57 }
运行结果如下:
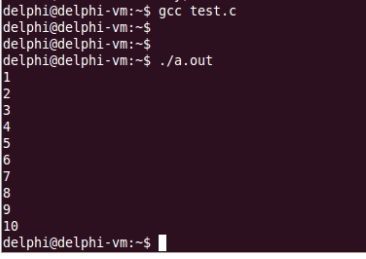
柔性数组的好处在于,我们的func函数只需要一个指向柔性数组的指针就好了,而不需要数组大小的参数。也不用在定义数组的时候就预先指定数组的大小。这样既方便又好用。
C语言中的union:
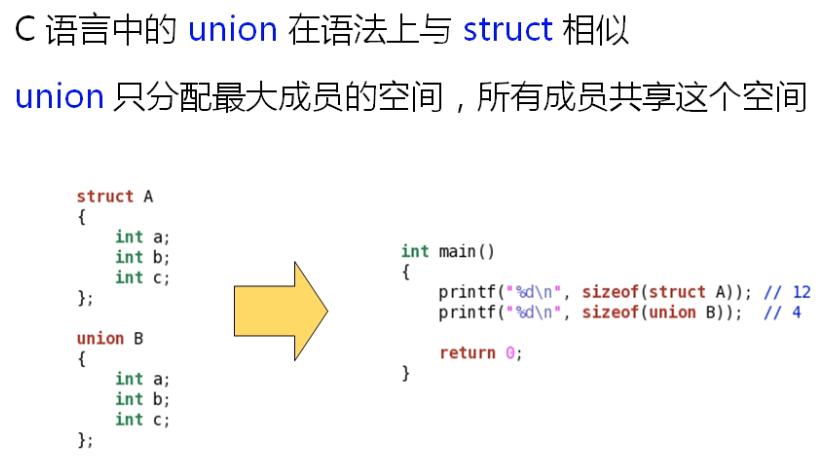
union的注意事项:
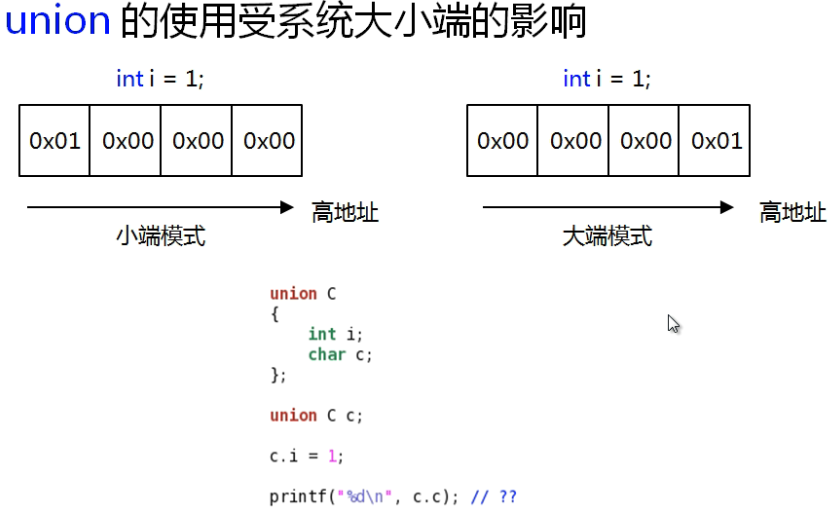
判断系统的大小端:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 int system_mode() 4 { 5 union SM 6 { 7 int i; 8 char c; 9 }; 10 11 union SM sm; 12 13 sm.i = 1; 14 15 return sm.c; 16 } 17 18 19 int main() 20 { 21 printf("System Mode: %d ", system_mode()); 22 return 0; 23 }
运行结果如下:
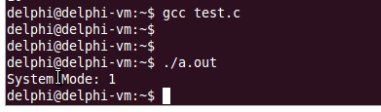
可见当前运行在小端模式系统。
在使用联合体时一定要注意大小端。
小结:
struct中的每个数据成员有独立的存储空间
struct可以通过最后的数组标识符产生柔性数组,柔性数组的好处在于可以在程序运行阶段得到一个数组,并且带长度信息
union中的所有成员共享同一个存储空间
union的使用会受到系统大小端的影响