当代C++库基本上都会使用C++里面的异常特性,依赖于异常特性所创建的库的稳定性是非常好的。因此,我们创建的库也要引入异常类族。本节中,我们就给DTLib添加异常类族。
异常的类型可以是自定义的类类型
对于类类型的异常的匹配依旧是自上而下的严格匹配
赋值兼容性原则在异常匹配中依然适用
一般而言
匹配子类异常的catch放在上部
匹配父类异常的catch放在下部
现代C++库必然包含充要的异常类族,异常类是数据结构类所依赖的“基础设施”,我们的异常类族如下所示:
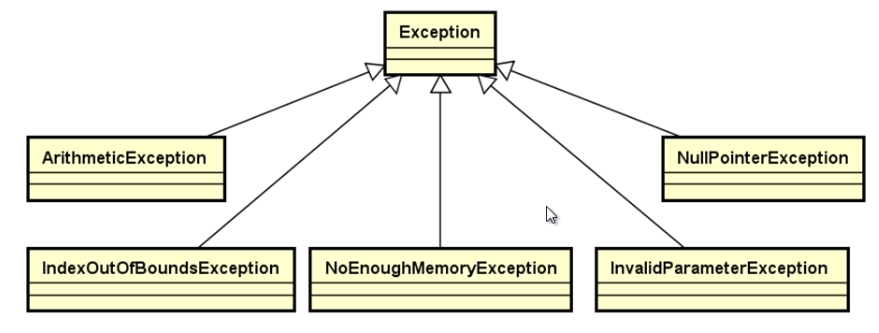
顶层的父类是一个抽象类,不能定义对象,它是用来被继承的。通过继承的方式定义了5个异常类。分别是:
计算异常
越界异常
内存不足异常
参数错误异常
空指针异常
一般而言这几种异常足够了。
具体如下:
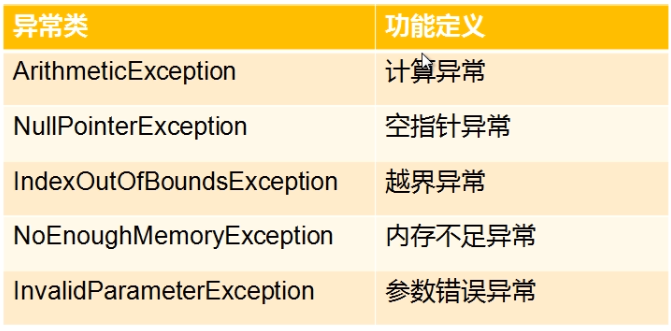
计算异常:例如,1除以0的时候,可以抛出这个异常
空指针异常:如果我们在需要合法的指针时,得到的却是一个空指针,则可以抛出这种异常。
越界异常:访问数组时,有可能越界,越界的情况下就可以抛出这种异常
内存不足异常:动态的申请内存是,内存不足时,就抛出这种异常
参数异常错误:我们编写的算法肯定要接收参数,作为好的习惯,肯定要判断一下参数的合法性,不合法的参数,要抛出这个异常
异常类中的接口定义如下所示:
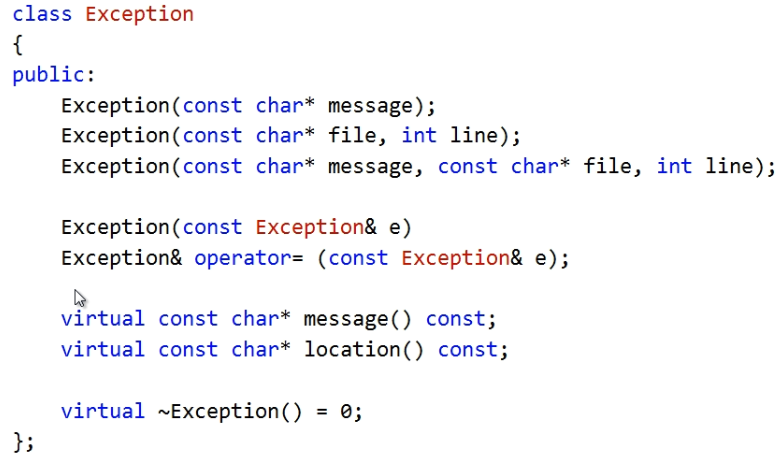
可以看到,析构函数是一个虚函数,而且是一个纯虚的析构函数。纯虚的析构函数仅仅用来说明当前的类是一个抽象类。其它没有任何更多的功能。
异常类的定义如下:
#ifndef EXCEPTION_H #define EXCEPTION_H namespace DTLib { #define THROW_EXCEPTION(e, m) (throw e(m, __FILE__, __LINE__)) class Exception { protected: char *m_message; char *m_location; void init(const char* message, const char* file, int line); public: Exception(const char* message); Exception(const char* file, int line); Exception(const char* message, const char* file, int line); Exception(const Exception& e); Exception& operator= (const Exception& e); virtual const char* message() const; virtual const char* location() const; virtual ~Exception() = 0; }; class ArithmeticException : public Exception { public: ArithmeticException() : Exception(0, 0, 0) {} ArithmeticException(const char* message) : Exception(message) {} ArithmeticException(const char* file, int line) : Exception(file, line) {} ArithmeticException(const char* message, const char* file, int line) : Exception(message, file, line){} ArithmeticException(const ArithmeticException& e) : Exception(e) {} ArithmeticException& operator=(const ArithmeticException& e) { Exception::operator =(e); return *this; } }; } #endif // EXCEPTION_H
Exception.cpp文件如下:
1 #include "Exception.h" 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 namespace DTLib 8 { 9 10 void Exception::init(const char *message, const char *file, int line) 11 { 12 m_message = strdup(message); 13 14 if(file != NULL) 15 { 16 char sl[16] = {0}; 17 18 itoa(line, sl, 10); 19 20 m_location = static_cast<char*>(malloc(strlen(file) + strlen(sl) + 2)); 21 m_location = strcpy(m_location, file); 22 m_location = strcat(m_location, ":"); 23 m_location = strcat(m_location, sl); 24 } 25 else 26 { 27 m_location = NULL; 28 } 29 } 30 31 Exception::Exception(const char *message) 32 { 33 init(message, NULL, 0); 34 } 35 36 Exception::Exception(const char *file, int line) 37 { 38 init(NULL, file, line); 39 } 40 41 Exception::Exception(const char *message, const char *file, int line) 42 { 43 init(message, file, line); 44 } 45 46 Exception::Exception(const Exception &e) 47 { 48 m_message = strdup(e.m_message); 49 m_location = strdup(e.m_location); 50 } 51 52 Exception& Exception::operator =(const Exception& e) 53 { 54 if(this != &e) 55 { 56 free(m_message); 57 free(m_location); 58 59 m_message = strdup(e.m_message); 60 m_message = strdup(e.m_location); 61 } 62 63 return *this; 64 } 65 66 const char* Exception::message() const 67 { 68 return m_message; 69 } 70 71 const char* Exception::location() const 72 { 73 return m_location; 74 } 75 76 Exception::~Exception() 77 { 78 free(m_message); 79 free(m_location); 80 } 81 82 }
根据C++各种教程中的知识,纯虚函数不需要提供实现,纯虚函数等着子类来实现。但是在Exception.cpp中我们提供了纯虚函数(纯虚析构函数)的函数体,也就是给出了实现,这并不是一种错误的做法,这只是一种例外,因为这个纯虚函数是析构函数。C++规定,但凡我们定义了析构函数,不管析构函数是不是纯虚的,一定要提供实现,这是因为在析构一个对象的时候,最终会调用到父类的析构函数,如果父类的析构函数是纯虚的而且没有具体实现,那这一系列的析构是无法完成的。当调用到顶层父类的析构函数时,如果没有实现,这是一种很奇怪的现象。
init函数中,第12行,我们使用了strdup函数将message的内容在堆空间中复制一份。因为,这个函数传入的message的内容可能是在栈上的,所以我们要复制一份。
第18行将整形数转换为字符串,第20行申请内存空间,最后的+2是因为,我们需要写入“:”以及最后的结束符。第21行是字符串复制,第22、23行是字符串拼接。
Exception.h中的THROW_EXCEPTION(e, m) (throw e(m, __FILE__, __LINE__))是一个宏,其中e代表的是异常类的类型,m代表我们自定义的message信息。__FILE__由编译器解析,会将文件名以字符串的形式写到该处。__LINE__也是由编译器处理,会将行号以int型数据写到该处。
测试程序如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "Exception.h" 3 using namespace std; 4 using namespace DTLib; 5 6 7 int main() 8 { 9 try 10 { 11 THROW_EXCEPTION(ArithmeticException, "test"); 12 } 13 catch(Exception& e) 14 { 15 cout << "catch(Exception& e)" << endl; 16 cout << e.message() << endl; 17 cout << e.location() << endl; 18 } 19 20 return 0; 21 }
执行结果如下:
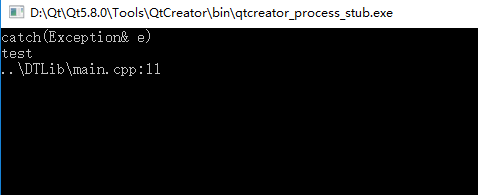
完善Exception.h中的其它异常类,如下所示:
1 #ifndef EXCEPTION_H 2 #define EXCEPTION_H 3 4 namespace DTLib 5 { 6 7 #define THROW_EXCEPTION(e, m) (throw e(m, __FILE__, __LINE__)) 8 9 class Exception 10 { 11 protected: 12 char *m_message; 13 char *m_location; 14 15 void init(const char* message, const char* file, int line); 16 public: 17 Exception(const char* message); 18 Exception(const char* file, int line); 19 Exception(const char* message, const char* file, int line); 20 21 Exception(const Exception& e); 22 Exception& operator= (const Exception& e); 23 24 virtual const char* message() const; 25 virtual const char* location() const; 26 27 virtual ~Exception() = 0; 28 }; 29 30 class ArithmeticException : public Exception 31 { 32 public: 33 ArithmeticException() : Exception(0, 0, 0) {} 34 ArithmeticException(const char* message) : Exception(message) {} 35 ArithmeticException(const char* file, int line) : Exception(file, line) {} 36 ArithmeticException(const char* message, const char* file, int line) : Exception(message, file, line){} 37 38 ArithmeticException(const ArithmeticException& e) : Exception(e) {} 39 40 ArithmeticException& operator=(const ArithmeticException& e) 41 { 42 Exception::operator =(e); 43 44 return *this; 45 } 46 }; 47 48 class NullPointerException : public Exception 49 { 50 public: 51 NullPointerException() : Exception(0, 0, 0) {} 52 NullPointerException(const char* message) : Exception(message) {} 53 NullPointerException(const char* file, int line) : Exception(file, line) {} 54 NullPointerException(const char* message, const char* file, int line) : Exception(message, file, line){} 55 56 NullPointerException(const NullPointerException& e) : Exception(e) {} 57 58 NullPointerException& operator=(const NullPointerException& e) 59 { 60 Exception::operator =(e); 61 62 return *this; 63 } 64 }; 65 66 class IndexOutOfBoundsException : public Exception 67 { 68 public: 69 IndexOutOfBoundsException() : Exception(0, 0, 0) {} 70 IndexOutOfBoundsException(const char* message) : Exception(message) {} 71 IndexOutOfBoundsException(const char* file, int line) : Exception(file, line) {} 72 IndexOutOfBoundsException(const char* message, const char* file, int line) : Exception(message, file, line){} 73 74 IndexOutOfBoundsException(const IndexOutOfBoundsException& e) : Exception(e) {} 75 76 IndexOutOfBoundsException& operator=(const IndexOutOfBoundsException& e) 77 { 78 Exception::operator =(e); 79 80 return *this; 81 } 82 }; 83 84 class NoEnoughMemoryException : public Exception 85 { 86 public: 87 NoEnoughMemoryException() : Exception(0, 0, 0) {} 88 NoEnoughMemoryException(const char* message) : Exception(message) {} 89 NoEnoughMemoryException(const char* file, int line) : Exception(file, line) {} 90 NoEnoughMemoryException(const char* message, const char* file, int line) : Exception(message, file, line){} 91 92 NoEnoughMemoryException(const NoEnoughMemoryException& e) : Exception(e) {} 93 94 NoEnoughMemoryException& operator=(const NoEnoughMemoryException& e) 95 { 96 Exception::operator =(e); 97 98 return *this; 99 } 100 }; 101 102 class InvalidParameterException : public Exception 103 { 104 public: 105 InvalidParameterException() : Exception(0, 0, 0) {} 106 InvalidParameterException(const char* message) : Exception(message) {} 107 InvalidParameterException(const char* file, int line) : Exception(file, line) {} 108 InvalidParameterException(const char* message, const char* file, int line) : Exception(message, file, line){} 109 110 InvalidParameterException(const InvalidParameterException& e) : Exception(e) {} 111 112 InvalidParameterException& operator=(const InvalidParameterException& e) 113 { 114 Exception::operator =(e); 115 116 return *this; 117 } 118 }; 119 120 } 121 122 #endif // EXCEPTION_H
Exception.cpp文件和上面一样,再次贴出如下:
1 #include "Exception.h" 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 namespace DTLib 8 { 9 10 void Exception::init(const char *message, const char *file, int line) 11 { 12 m_message = strdup(message); 13 14 if(file != NULL) 15 { 16 char sl[16] = {0}; 17 18 itoa(line, sl, 10); 19 20 m_location = static_cast<char*>(malloc(strlen(file) + strlen(sl) + 2)); 21 m_location = strcpy(m_location, file); 22 m_location = strcat(m_location, ":"); 23 m_location = strcat(m_location, sl); 24 } 25 else 26 { 27 m_location = NULL; 28 } 29 } 30 31 Exception::Exception(const char *message) 32 { 33 init(message, NULL, 0); 34 } 35 36 Exception::Exception(const char *file, int line) 37 { 38 init(NULL, file, line); 39 } 40 41 Exception::Exception(const char *message, const char *file, int line) 42 { 43 init(message, file, line); 44 } 45 46 Exception::Exception(const Exception &e) 47 { 48 m_message = strdup(e.m_message); 49 m_location = strdup(e.m_location); 50 } 51 52 Exception& Exception::operator =(const Exception& e) 53 { 54 if(this != &e) 55 { 56 free(m_message); 57 free(m_location); 58 59 m_message = strdup(e.m_message); 60 m_message = strdup(e.m_location); 61 } 62 63 return *this; 64 } 65 66 const char* Exception::message() const 67 { 68 return m_message; 69 } 70 71 const char* Exception::location() const 72 { 73 return m_location; 74 } 75 76 Exception::~Exception() 77 { 78 free(m_message); 79 free(m_location); 80 } 81 82 }
主函数测试程序如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "Exception.h" 3 using namespace std; 4 using namespace DTLib; 5 6 7 int main() 8 { 9 try 10 { 11 THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "test"); 12 } 13 catch(NoEnoughMemoryException& e) 14 { 15 cout << "catch(NoEnoughMemoryException& e)" << endl; 16 cout << e.message() << endl; 17 cout << e.location() << endl; 18 } 19 catch(Exception& e) 20 { 21 cout << "catch(Exception& e)" << endl; 22 cout << e.message() << endl; 23 cout << e.location() << endl; 24 } 25 26 return 0; 27 }
执行结果如下:
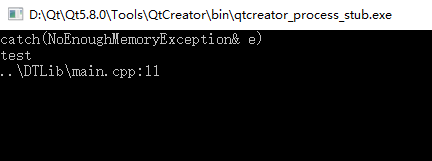
由以上异常类族可以得出以下设计原则:
如果要编写可复用的代码库,尽量使用面向对象技术进行架构,尽量使用异常机制分离正常逻辑和异常逻辑。
小结:
现代C++库必然包含充要的异常类族
所有库中的数据结构类都依赖于异常机制,依赖图如下
异常机制能够分离库中代码的正常逻辑和异常逻辑
