实验任务详情:
完成火车站售票程序的模拟。
要求:
(1)总票数1000张;
(2)10个窗口同时开始卖票;
(3)卖票过程延时1秒钟;
(4)不能出现一票多卖或卖出负数号票的情况。
实验代码:
class MyThread implements Runnable{ private int ticket=1000; public void run() { for(int i=0;i<1;i++) { synchronized(this) { if(ticket>0) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch(InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"售票,余票:"+--ticket); } } } } }; public class sf{ public static void main(String[] args) { MyThread mt=new MyThread(); for(int i=1;i<=10;i++) { new Thread(mt,"窗口"+i).start(); } } }
运行结果:
实验总结: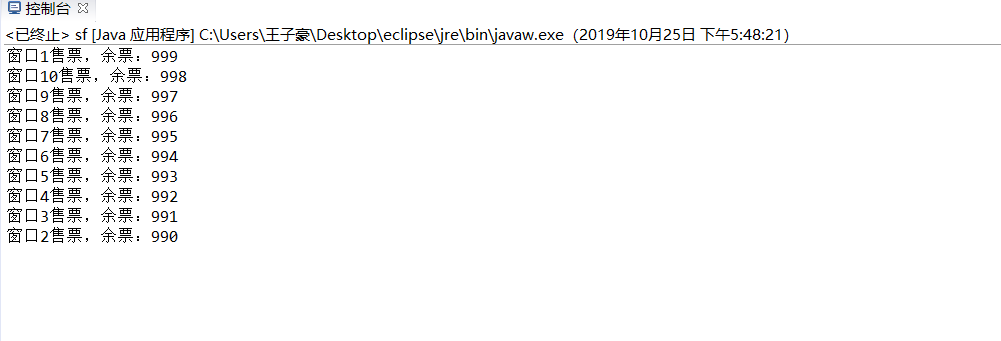
实现多线程的方法
1、 一种是继承Thread类;
继承Thread类多线程的定义语法
2、一种是实现Runnable接口。
使用Runnable接口实现多线程的话,不像继承Thread类那样可以直接使用Thread类中的name属性,需要在类中单独定义一个name属性以保存名称。
通过Runnable接口实现多线程