Bean的生命周期
Spring Bean 的生命周期在整个 Spring 中占有很重要的位置,掌握这些可以加深对 Spring 的理解。
首先看下生命周期图:
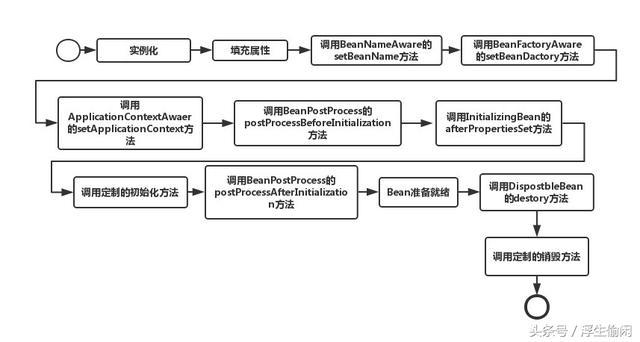
再谈生命周期之前有一点需要先明确:
Spring 只帮我们管理单例模式 Bean 的完整生命周期,对于 prototype 的 bean ,Spring 在创建好交给使用者之后则不会再管理后续的生命周期。
Bean的初始化和销毁方法
/**
* Bean的生命周期
* ---由容器管理bean的创建,初始化,销毁
*
* 构造,创建对象
* 单实例:在容器启动的时候创建对象
* 多实例:在每次获取的时候创建对象
*
* 初始化:
* 对象创建完成,并赋值好,然后调用初始化方法...
* 销毁:
* 单实例:容器关闭时,进行销毁
* 多实例:容器不会管理这个bean,bean不会销毁
* 1).使用自定义的初始化和销毁方法
* 指定init-methdo和destroy-method
*
* 2)使用InitializingBean和DisposableBean初始化和销毁方法
*
* 3)使用@PostConstruct&@PreDestroy
* @PostConstruct 在bean创建完成并属性赋值完成,执行初始化方法
* @PreDestroy 在容器销毁前通知我们清理
*
* 4)BeanPostProcessor,bean的后置处理器
* ---1.postProcessBeforeInitialization 在bean的初始化方法之前进行一些处理工作
* ---2.执行初始化方法
* ---3.postProcessAfterInitialization 在bean的初始化方法调用之后进行调用
*
* Spring底层对BeanPostProcessor的使用:
* bean赋值,注入其他组件,@Autowired,生命周期注解功能,@Asybc等都是通过BeanPostProcessor完成的
*
* */
1.@Bean指定初始化和销毁方法
在bean初始化的时执行init方法,销毁时执行destroy方法
实体类:
package com.wang.bean; public class Car { public Car(){ System.out.println("car cons..."); } public void init(){ System.out.println("car init..."); } public void destroy(){ System.out.println("car destroy..."); } }
xml方式:
<bean id="car" class="com.wang.bean.Car" scope="prototype" lazy-init="true" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy"> </bean>
注解方式:
@Configuration public class LifeCycleConfig { //@Scope("prototype") @Bean(initMethod = "init",destroyMethod = "destroy") public Car car(){ return new Car(); } }
Test:
@Test public void test(){ AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(LifeCycleConfig.class); System.out.println("容器创建完成"); annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean("car");//多实例,获取bean时调用创建对象,容器关闭不会销毁bean annotationConfigApplicationContext.close();//关闭容器,执行销毁方法 }
2.InitializingBean和DisposableBean初始化和销毁方法
在实体类中实现InitializingBean和DisposableBean接口:
public class Car implements InitializingBean,DisposableBean { public Car(){ System.out.println("car cons..."); } @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { System.out.println("afterPropertiesSet...在properties设置之后调用(初始化方法)"); } @Override public void destroy() throws Exception { System.out.println("destroy方法"); } }
在配置类中注册该实体类bean:
@Bean public Car car(){ return new Car(); }
3.@PostConstruct&@PreDestroy
@PostConstruct 在bean创建完成并属性赋值完成,执行初始化方法,@PreDestroy 在容器销毁前通知我们清理
实体类:
public class Dog { public Dog(){ System.out.println("Dog Cons..."); } @PostConstruct public void init(){ System.out.println("Dog PostConstruct..."); } @PreDestroy public void destroy(){ System.out.println("Dog PreDestroy..."); } }
在配置类中注册该实体类bean:
@Bean public Dog dog(){ return new Dog(); }
4.BeanPostProcessor
执行顺序为:
1.postProcessBeforeInitialization 在bean的初始化方法之前进行一些处理工作
2.执行初始化方法
3.postProcessAfterInitialization 在bean的初始化方法调用之后进行调用
@Component //将后置处理器加入容器中 public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("postProcessBeforeInitialization is run ...."+"bean:"+bean+"=>beanName:"+beanName); //返回要用的bean对象 return bean; } @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("postProcessAfterInitialization is run ...."+"bean:"+bean+"=>beanName:"+beanName); return bean; } }