# 日志就是记录一些信息,方便查询或者辅助开发。
分为两种:
1、记录文件
2、显示屏幕。
# 低配
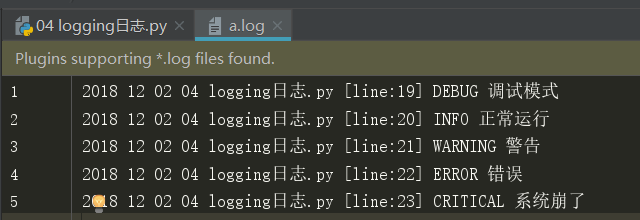
# 低配 import logging # 五种级别,由低到高,默认从warning级别显示。 logging.basicConfig( # level=logging.DEBUG, level=10, # 显示的级别 format='%(asctime)s %(filename)s [line:%(lineno)d] %(levelname)s %(message)s', # 显示格式 datefmt='%Y %m %d', # 日期 # filename='a.log', # 默认是a模式, 就是使用的gbk 编码。 # filemode='w' 一般不用改。 ) logging.debug('调试模式') # 10 logging.info('正常运行') # 20 logging.warning('警告') # 30 logging.error('错误') # 40 logging.critical('系统崩了') # 50
# 低配:只能写入文件或者屏幕输出。
标配:

# 标配 import logging print(logging) # # 1、 创建logging对象 logger = logging.getLogger() # 2、 创建文件对象 fh1 = logging.FileHandler('a1.log', encoding='utf-8') fh2 = logging.FileHandler('a2.log', encoding='utf-8') # ...... # 3、 创建屏幕对象 sh = logging.StreamHandler() # 4、给2个文件对象和1个屏幕对象创建格式化 formater1 = logging.Formatter( fmt='%(asctime)s %(filename)s [line:%(lineno)d] %(levelname)s %(message)s', # 显示格式 datefmt='%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S',) formater2 = logging.Formatter( fmt='%(asctime)s %(levelname)s %(message)s', # 显示格式 datefmt='%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S',) formater3 = logging.Formatter( fmt='%(asctime)s %(filename)s [line:%(lineno)d] %(levelname)s %(message)s', # 显示格式 datefmt='%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S',) # 5、给对象绑定格式(武功) fh1.setFormatter(formater1) fh2.setFormatter(formater2) sh.setFormatter(formater3) # 6、给logger对象添加其他对象(加入天龙八部这本书) logger.addHandler(fh1) logger.addHandler(fh2) logger.addHandler(sh) # 设置logger级别(手动指定级别) logger.setLevel(10) sh.setLevel(50) # 按照logger对象设置的级别显示 fh1.setLevel(30) fh2.setLevel(30) logging.debug('调试模式') # 10 logging.info('正常运行') # 20 logging.warning('警告') # 30 logging.error('错误') # 40 logging.critical('系统崩了') # 50
# 高配。
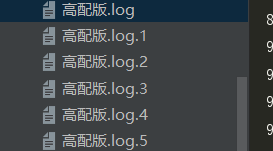
# 通过导入文件(导入字典的方式)写日志 Django。
""" logging配置 """ import os import logging.config # 定义三种日志输出格式 开始 standard_format = '[%(asctime)s][%(threadName)s:%(thread)d][task_id:%(name)s][%(filename)s:%(lineno)d]' '[%(levelname)s][%(message)s]' #其中name为getlogger指定的名字 simple_format = '[%(levelname)s][%(asctime)s][%(filename)s:%(lineno)d]%(message)s' id_simple_format = '[%(levelname)s][%(asctime)s] %(message)s' # 定义日志输出格式 结束 # print(__file__) logfile_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)) # log文件的目录 logfile_name = '高配版.log' # log文件名 # # 如果不存在定义的日志目录就创建一个 # if not os.path.isdir(logfile_dir): # os.mkdir(logfile_dir) # log文件的全路径 logfile_path = os.path.join(logfile_dir, logfile_name) # log配置字典 # 第一层键值对的键固定的关键字不能改变。 LOGGING_DIC = { 'version': 1, # 版本 'disable_existing_loggers': False, # 'formatters': { 'standard': { 'format': standard_format }, 'simple': { 'format': simple_format }, 'id_simple_format':{ 'format': id_simple_format } }, 'filters': {}, 'handlers': { #打印到终端的日志 'console': { 'level': 'DEBUG', 'class': 'logging.StreamHandler', # 打印到屏幕 'formatter': 'simple' }, #打印到文件的日志,收集info及以上的日志 'default': { 'level': 'DEBUG', 'class': 'logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler', # 保存到文件 'formatter': 'standard', 'filename': logfile_path, # 日志文件 'maxBytes': 300, # 日志大小 300bytes 'backupCount': 5, # 最多只有5个文件 'encoding': 'utf-8', # 日志文件的编码,再也不用担心中文log乱码了 }, }, 'loggers': { #logging.getLogger(__name__)拿到的logger配置 '': { 'handlers': ['default', 'console'], # 这里把上面定义的两个handler都加上,即log数据既写入文件又打印到屏幕 'level': 'DEBUG', 'propagate': True, # 向上(更高level的logger)传递 }, }, } logging.config.dictConfig(LOGGING_DIC) # 导入上面定义的logging配置 # # logging.config # 将你写好的logging 字典 在导入logging.config后,传到logging模块中 logger = logging.getLogger() # 生成一个log实例 通过字典自己设置的个性化的log对象 logger.info('正常运行状态') # 记录该文件的运行状态