如何实现可迭代对象和迭代器对象
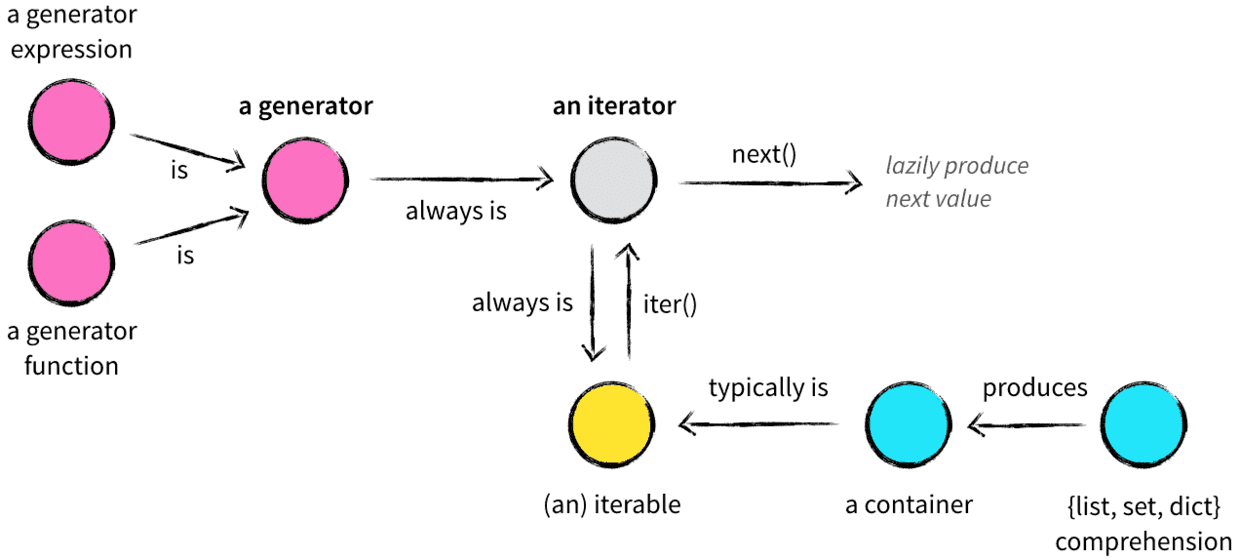
什么是可迭代对象和迭代器对象
区分一下容器的概念
容器是用来储存元素的一种数据结构,它支持隶属测试,容器将所有数据保存在内存中,在Python中典型的容器有:
- list, deque, …
- set,frozesets,…
- dict, defaultdict, OrderedDict, Counter, …
- tuple, namedtuple, …
- str
迭代器
for _ in x: pass
这里x是可迭代对象
迭代器本质上是一个产生值的工厂,每次向迭代器请求下一个值,迭代器都会进行计算出相应的值并返回。
那么什么是迭代器呢?任何具有__next__()方法的对象都是迭代器,对迭代器调用next()方法可以获取下一个值。而至于它使如何产生这个值的,跟它能否成为一个迭代器并没有关系。
使用方法:
# for _ in x 实际调用也是用iter, iter(x) next(iter)
iter1 = iter(x)
print(next(iter1))
print(next(iter1))
print(next(iter1))
from itertools import count
counter = count(start=13)
next(counter)
next(counter)
“用时访问”的策略
“用时访问”的策略也就是说用到的时候,才生成对象,而不是提前生成对象放在内存里
举个例子:
for i in range(100000):
print(i**i)
这个程序先生成了长度为100000的列表,然后再慢慢进行计算,这样不仅生成列表有延迟,也会占有大量内存。解决方法就是可迭代对象
自己实现可迭代对象和迭代器对象
-
自己写的在https://www.tianqi.com/ 获取城市温度的一个爬虫
import requests def getWeather(city): # 根据城市生成url url = 'https://www.tianqi.com/' url += city try: print('try reading from %s' % url) # 增加header 模拟浏览器访问 headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) '} response = requests.get(url, headers = headers, timeout = 30) response.raise_for_status() response.encoding = response.apparent_encoding print('finished reading from web') # 使用美丽汤找到天气数据 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, features='html.parser') weather = soup.find(attrs={'class' : 'weatherbox'}).find('span') return weather.text except: pass # 打印结果 print(getWeather('shanghai')) print(getWeather('beijing'))output
try reading from https://www.tianqi.com/shanghai finished reading from web 小雨转多云6 ~ 10℃ try reading from https://www.tianqi.com/beijing finished reading from web 多云-4 ~ 7℃ -
实现上面爬虫的可迭代
from collections import Iterable, Iterator import requests class WeatherIterator(Iterator): """ 一个迭代器对象, 返回城市的天气, 只有在用的时候才会开始爬虫,不需要先爬虫才能迭代 """ def __init__(self, cities): self.cities = cities self.index = 0 def __next__(self): # 继承Iterator后, 需要实现的方法 if self.index >= len(self.cities): raise StopIteration else: temp_city = self.cities[self.index] self.index += 1 return self.get_weather(temp_city) def get_weather(self, city): url = 'https://www.tianqi.com/' url += city try: headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) '} response = requests.get(url, headers = headers, timeout = 30) response.raise_for_status() response.encoding = response.apparent_encoding from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, features='html.parser') weather = soup.find(attrs={'class' : 'weatherbox'}).find('span') return ('%s: %s' % (city, weather.text)) except: pass class WeatherIterable(Iterable): """ 一个可迭代对象 """ def __init__(self, cities): self.cities = cities def __iter__(self): return WeatherIterator(self.cities)使用效果
>>> cities = ['shanghai', 'beijing', 'nanjing'] >>> for i in WeatherIterable(cities): >>> print(i) shanghai: 多云8 ~ 15℃
beijing: 多云-4 ~ 3℃
nanjing: 大雨4 ~ 8℃
```