using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Runtime.Remoting;
namespace Marshal
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 获取一个指向应用程序域的引用
AppDomain adCallingThreadDomain = Thread.GetDomain();
// 每一个应用程序域都会被分配一个名字帮助调试 ,以下代码获取引用程序域的名字
String callingDomainName = adCallingThreadDomain.FriendlyName;
// 获取应用程序域的完整名
String exeAssembly = Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().FullName;
AppDomain ad2 = null;
// ************************************************************************************************************
// 使用Marshal-by-Reference的方式跨域通信
Console.WriteLine("{0}Demo #1", Environment.NewLine);
// 建立一个域,安全和配置均使用当前域的设置
ad2 = AppDomain.CreateDomain("AD #2", null, null);
MarshalByRefType mbrt = null;
// 加载Assembly到新的域,new一个对象并且返回到当前域 (实际上返回的是一个引用代理)
mbrt = (MarshalByRefType)ad2.CreateInstanceAndUnwrap(exeAssembly, "Marshal.MarshalByRefType");
Console.WriteLine("Type={0}", mbrt.GetType()); // CLR 对GetType做了一些手脚,返回的是被代理数据的真实类型
// 以下代码证明我们获取的是一个代理对象
Console.WriteLine("Is proxy={0}", RemotingServices.IsTransparentProxy(mbrt));
// 我们调用了代理类的SomeMethod() , 代理类跨域访问真正的对象
mbrt.SomeMethod();
// 卸载新建的那个应用程序域
AppDomain.Unload(ad2);
// mbrt refers to a valid proxy object; the proxy object refers to an invalid AppDomain
try
{
// 再次调用代理类的SomeMethod() , 由于域已经被卸载 抛出一个异常
mbrt.SomeMethod();
Console.WriteLine("Successful call.");
}
catch (AppDomainUnloadedException)
{
Console.WriteLine("Failed call.");
}
// ************************************************************************************************************
// 使用Marshal-by-Value 的方式跨域通信
Console.WriteLine("{0}Demo #2", Environment.NewLine);
// 新建域
ad2 = AppDomain.CreateDomain("AD #2", null, null);
// 加载程序集并创建代理类
mbrt = (MarshalByRefType)ad2.CreateInstanceAndUnwrap(exeAssembly, "Marshal.MarshalByRefType");
// 该方法返回了一个值的拷贝 marshaled by value (not be reference).
MarshalByValType mbvt = mbrt.MethodWithReturn();
// 证明返回值不是一个代理类
Console.WriteLine("Is proxy={0}", RemotingServices.IsTransparentProxy(mbvt));
// 查看返回值是谁创建的
Console.WriteLine("Returned object created " + mbvt.ToString());
// 卸载应用程序域
AppDomain.Unload(ad2);
// 由于是值传递,那么卸载域对函数没有影响 // marshaled by value
try
{
//不会有异常抛出
Console.WriteLine("Returned object created " + mbvt.ToString());
Console.WriteLine("Successful call.");
}
catch (AppDomainUnloadedException)
{
Console.WriteLine("Failed call.");
}
// ************************************************************************************************************
// non-marshalable type 跨域通信
Console.WriteLine("{0}Demo #3", Environment.NewLine);
ad2 = AppDomain.CreateDomain("AD #2", null, null);
mbrt = (MarshalByRefType)ad2.CreateInstanceAndUnwrap(exeAssembly, "TestConsole.MarshalByRefType");
// 没有标记为 Serializable 的类型对象 不能通过marshaled by value 跨域通信
NonMarshalableType nmt = mbrt.MethodArgAndReturn(callingDomainName);
}
}
//即使没有标记为Serializable 也可以通过 marshaled-by-reference 的方式跨域通信
public sealed class MarshalByRefType : MarshalByRefObject
{
public MarshalByRefType()
{
Console.WriteLine("{0} ctor running in {1}",
this.GetType().ToString(), Thread.GetDomain().FriendlyName);
}
public void SomeMethod()
{
Console.WriteLine("Executing in " + Thread.GetDomain().FriendlyName);
}
public MarshalByValType MethodWithReturn()
{
Console.WriteLine("Executing in " + Thread.GetDomain().FriendlyName);
MarshalByValType t = new MarshalByValType();
return t;
}
public NonMarshalableType MethodArgAndReturn(String callingDomainName)
{
// NOTE: callingDomainName is [Serializable]
Console.WriteLine("Calling from ‘{0}’ to ‘{1}’.",
callingDomainName, Thread.GetDomain().FriendlyName);
NonMarshalableType t = new NonMarshalableType();
return t;
}
}
//只有标记为 Serializable 的类型 才能用marshaled by value 的方式跨域通信
[Serializable]
public sealed class MarshalByValType : Object
{
private DateTime m_creationTime = DateTime.Now; // NOTE: DateTime is [Serializable]
public MarshalByValType()
{
Console.WriteLine("{0} ctor running in {1}, Created on {2:D}",
this.GetType().ToString(),
Thread.GetDomain().FriendlyName,
m_creationTime);
}
public override String ToString()
{ return m_creationTime.ToLongDateString();
}
}
// 没有标记为 Serializable 的类型 不能用marshaled by value 的方式跨域通信
// [Serializable]
public sealed class NonMarshalableType : Object
{
public NonMarshalableType()
{
Console.WriteLine("Executing in " + Thread.GetDomain().FriendlyName);
}
}
}
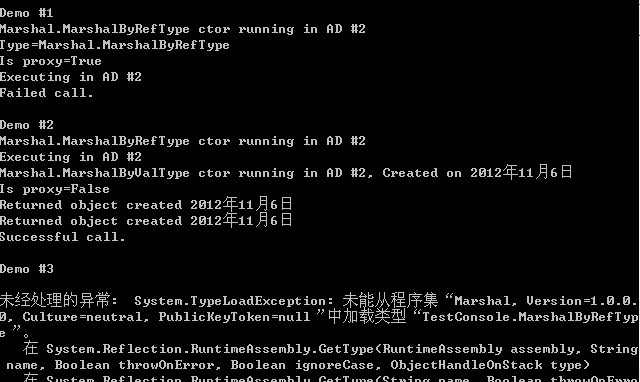
显示结果为: