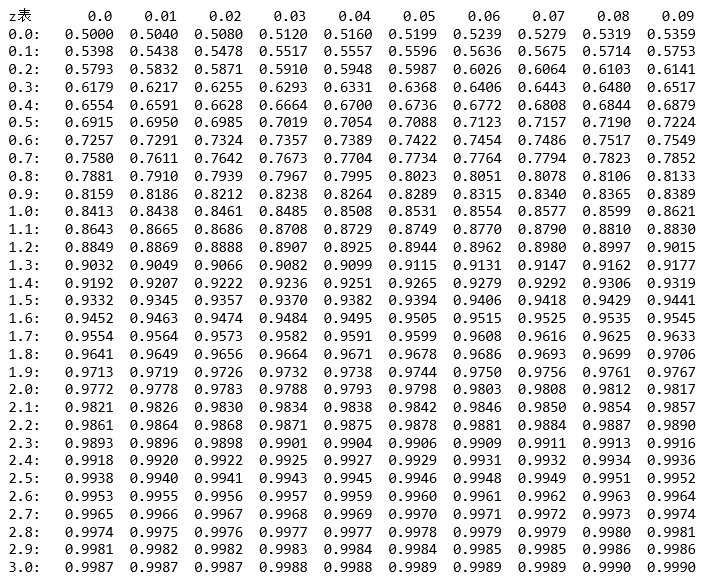
正态分布(Normal Distribution)
1、正态分布是一种连续分布,其函数可以在实线上的任何地方取值。
2、正态分布由两个参数描述:分布的平均值μ和方差σ2 。
3、正态分布的取值可以从负无穷到正无穷。
3、Z-score 是非标准正态分布标准化后的x 即 z = (x−μ) / σ
#显示标准正态分布曲线图

1 import numpy as np 2 import scipy.stats as stats 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 5 mu = 0 # mean 6 sigma = 1 # standart deviation 7 x = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.1) 8 y = stats.norm.pdf(x, 0, 1) 9 print('Chart 1:') 10 plt.plot(x, y) 11 plt.title('Normal: $mu$ = {0:.1f}, $sigma^2$ = {1:0.1f}'.format(mu, sigma)) 12 plt.xlabel('x') 13 plt.ylabel('Probability density') # probobility of observing each of these observations 14 plt.show()
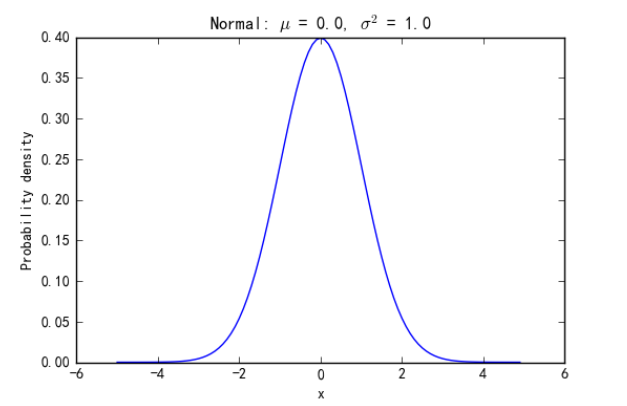
标准正态分布表
表头的横向表示小数点后第二位,表头的纵向则为整数部分以及小数点后第一位;两者联合作为完整的x,坐标轴的横轴
# 显示标准正态分布表格

1 import numpy as np 2 from scipy.stats import norm 3 4 n = 100 5 x = np.arange(0, 0.1, 0.01) 6 y = np.arange(0, 3.1, 0.1) 7 print('z表 ', end = '') 8 for j in x: 9 print( str(j), end=' ') 10 print() 11 for i in y: 12 print( i , end = ': ') 13 for j in x: 14 z = norm.cdf(j+i) 15 print('{0:.4f}'.format(z), end = ' ') 16 print('')