hCache 是一个纯Java的进程内缓存框架,具有快速、精干等特点,是Hibernate中默认的CacheProvider。
下图是 Ehcache 在应用程序中的位置:
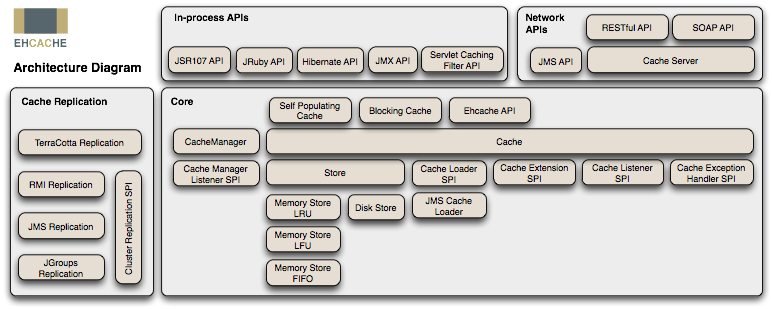
ehcache部署起来很简单,主要分两步:
1.首先要给他写个核心配置XML文件
<ehcache> <diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir"/> <defaultCache maxElementsInMemory="10000" eternal="false" timeToIdleSeconds="120" timeToLiveSeconds="120" overflowToDisk="true" diskPersistent="false" diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU" /> <cache name="cache1" maxElementsInMemory="10000" eternal="false" maxElementsOnDisk="1000" overflowToDisk="true" timeToIdleSeconds="300" timeToLiveSeconds="600" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LFU" /> </ehcache>
属性解释:
简单配置,在ehcache.xml文件中有此配置,在使用Ehcache前最好将其删除掉,自己配置。
缓存名cache1,内存中最多可缓存10000个Element,其中的element会在闲置5分钟或是存活10分钟之后失效。
超过10000element时,element将会输出到磁盘中,输出路径是java.io.tmpdir。
从其他文章找到其详细解释:
· Cache配置
· name:Cache的唯一标识
· maxElementsInMemory:内存中最大缓存对象数。
· maxElementsOnDisk:磁盘中最大缓存对象数,若是0表示无穷大。
· eternal:Element是否永久有效,一但设置了,timeout将不起作用。
· overflowToDisk:配置此属性,当内存中Element数量达到maxElementsInMemory时,Ehcache将会Element写到磁盘中。
· timeToIdleSeconds:设置Element在失效前的允许闲置时间。仅当element不是永久有效时使用,可选属性,默认值是0,也就是可闲置时间无穷大。
· timeToLiveSeconds:设置Element在失效前允许存活时间。最大时间介于创建时间和失效时间之间。仅当element不是永久有效时使用,默认是0.,也就是element存活时间无穷大。
· diskPersistent:是否缓存虚拟机重启期数据。(这个虚拟机是指什么虚拟机一直没看明白是什么,有高人还希望能指点一二)。
· diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds:磁盘失效线程运行时间间隔,默认是120秒。
· diskSpoolBufferSizeMB:这个参数设置DiskStore(磁盘缓存)的缓存区大小。默认是30MB。每个Cache都应该有自己的一个缓冲区。
· memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:当达到maxElementsInMemory限制时,Ehcache将会根据指定的策略去清理内存。默认策略是LRU(最近最少使用)。你可以设置为FIFO(先进先出)或是LFU(较少使用)。这里比较遗憾,Ehcache并没有提供一个用户定制策略的接口,仅仅支持三种指定策略,感觉做的不够理想。
2.实际要缓存的类调用
写一个实例类,这样大家就明白差不多了:
import java.io.Serializable; import net.sf.ehcache.Cache; import net.sf.ehcache.CacheManager; import net.sf.ehcache.Element; public class Demo { static CacheManager manager= new CacheManager(); /** *############################################################################## * * @DESCRIBE * @param args * @throws InterruptedException * *############################################################################## */ public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { String[] cacheNames = manager.getCacheNames(); System.out.println("读取的缓存列表为:"); for(int i=0;i<cacheNames.length;i++){ System.out.println("-- "+(i+1)+" "+cacheNames[i]); } Cache cache = manager.getCache("cache1"); Element element = new Element("key1", "value1"); cache.put(element); element = cache.get("key1"); Serializable value = element.getValue(); System.out.println("序列化后的值为:"+value.toString()); element = cache.get("key1"); Object value1 = element.getObjectValue(); System.out.println("未序列化的值为:"+value1.toString()); int elementsInMemory = cache.getSize(); System.out.println("得到缓存的对象数量:"+elementsInMemory); long elementsInMemory1 = cache.getMemoryStoreSize(); System.out.println("得到缓存对象占用内存的数量:"+elementsInMemory1); long elementsInMemory2 = cache.getDiskStoreSize(); System.out.println("得到缓存对对象占用磁盘的数量:"+elementsInMemory2); int hits = cache.getHitCount(); System.out.println("得到缓存读取的命中次数:"+hits); int hits1 = cache.getMemoryStoreHitCount(); System.out.println("得到内存中缓存读取的命中次数:"+hits1); int hits2 =cache.getDiskStoreHitCount(); System.out.println("得到磁盘中缓存读取的命中次数:"+hits2); int hits3 = cache.getMissCountNotFound(); System.out.println("得到缓存读取的丢失次数:"+hits3); int hits4 = cache.getMissCountExpired(); System.out.println("得到缓存读取的已经被销毁的对象丢失次数:"+hits4); } }