5 面向对象中

5.1 继承性(inheritance)
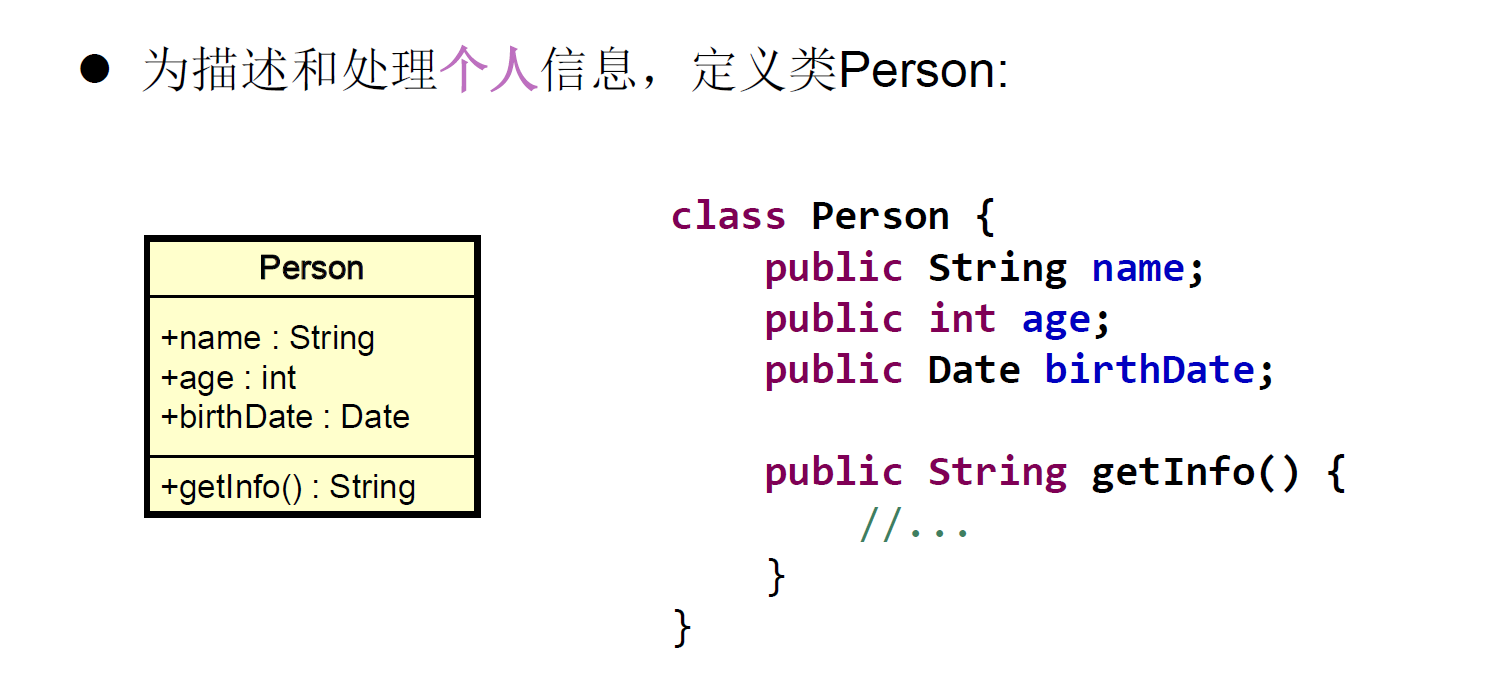
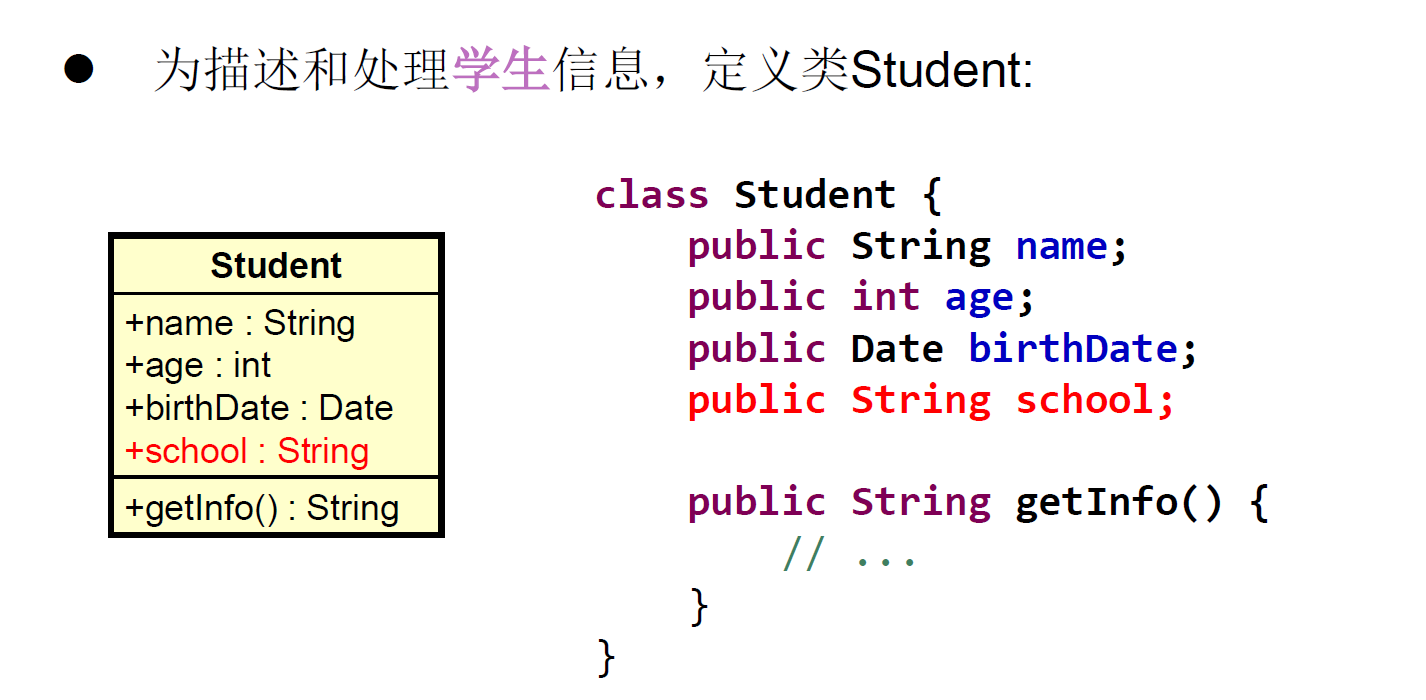
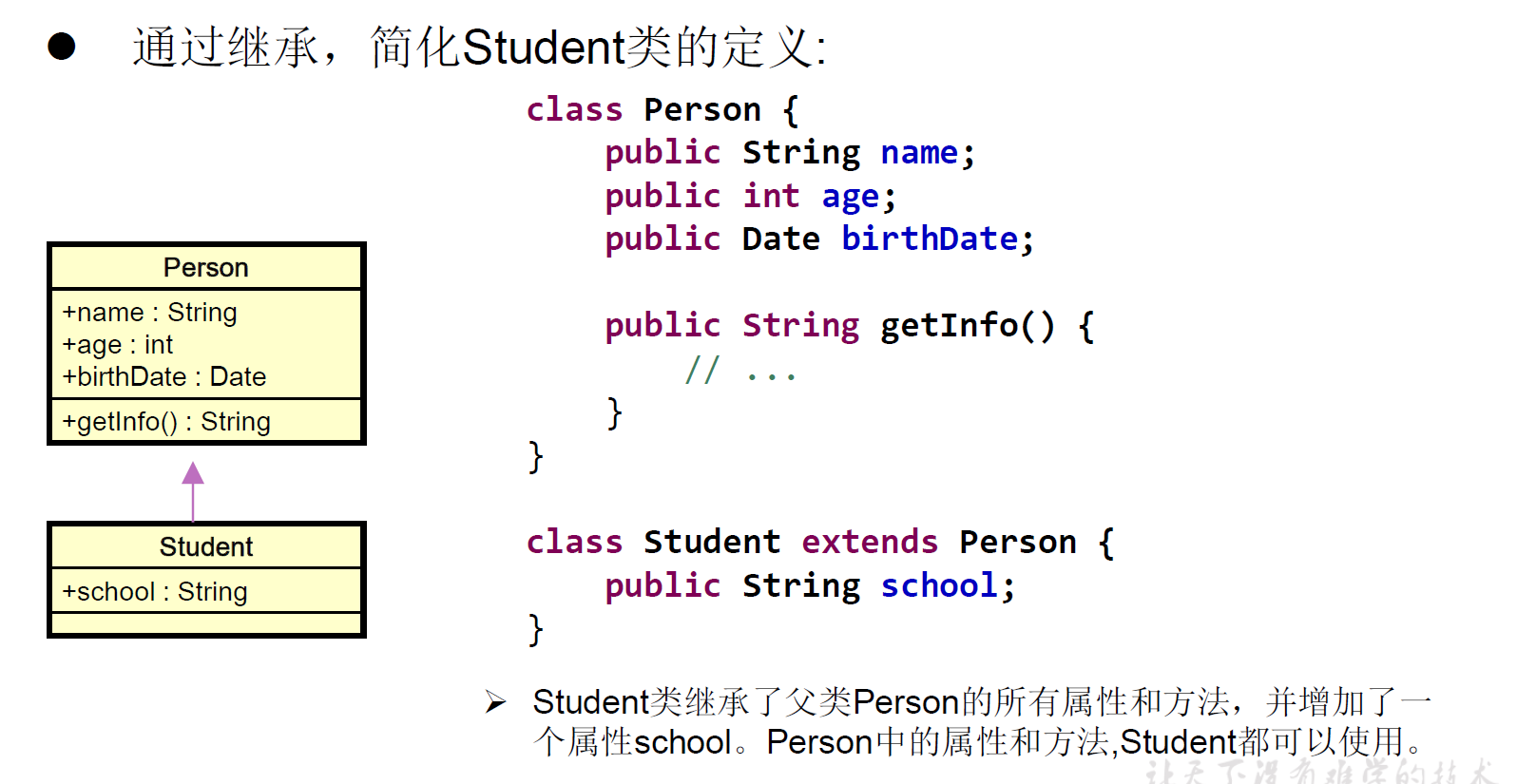
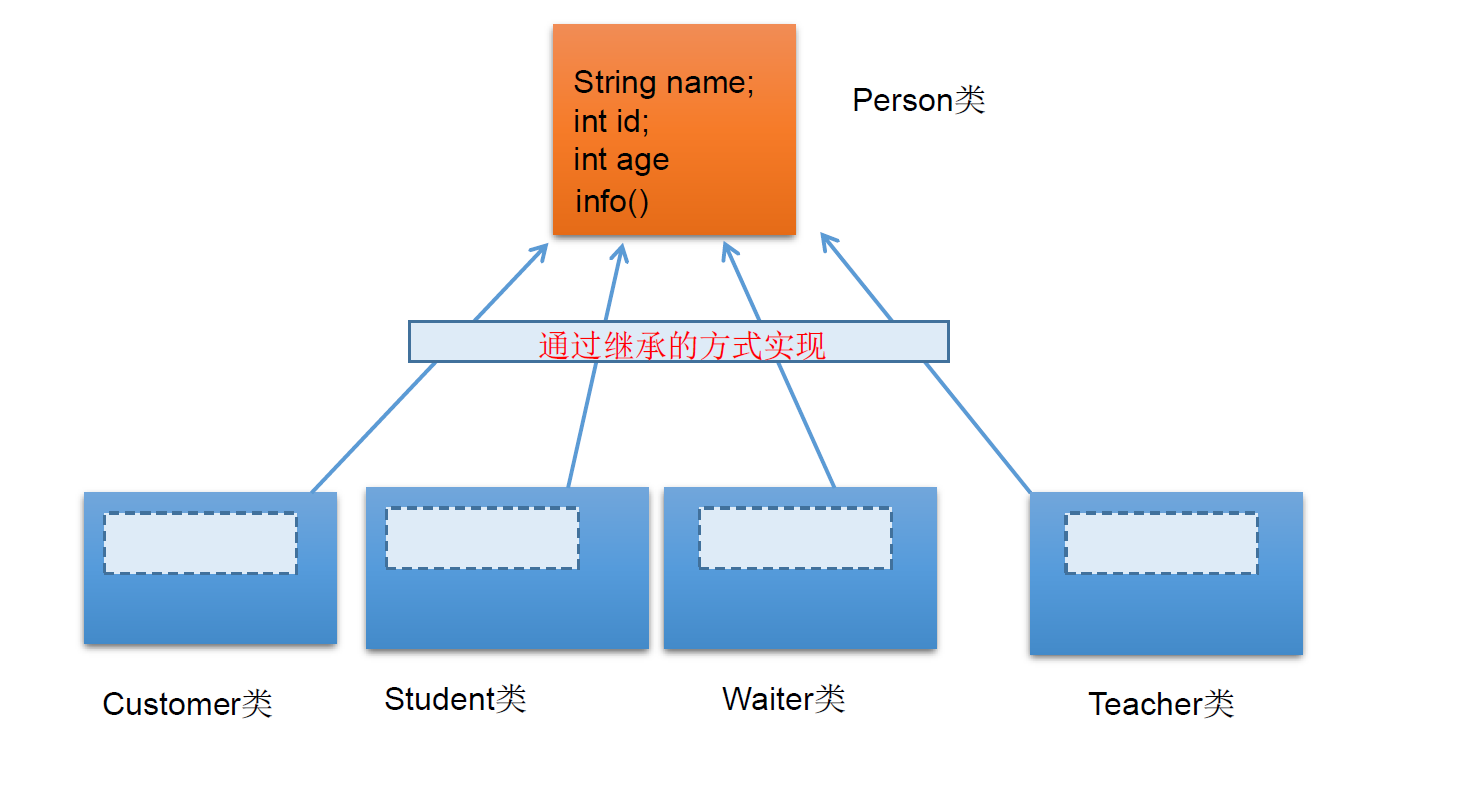

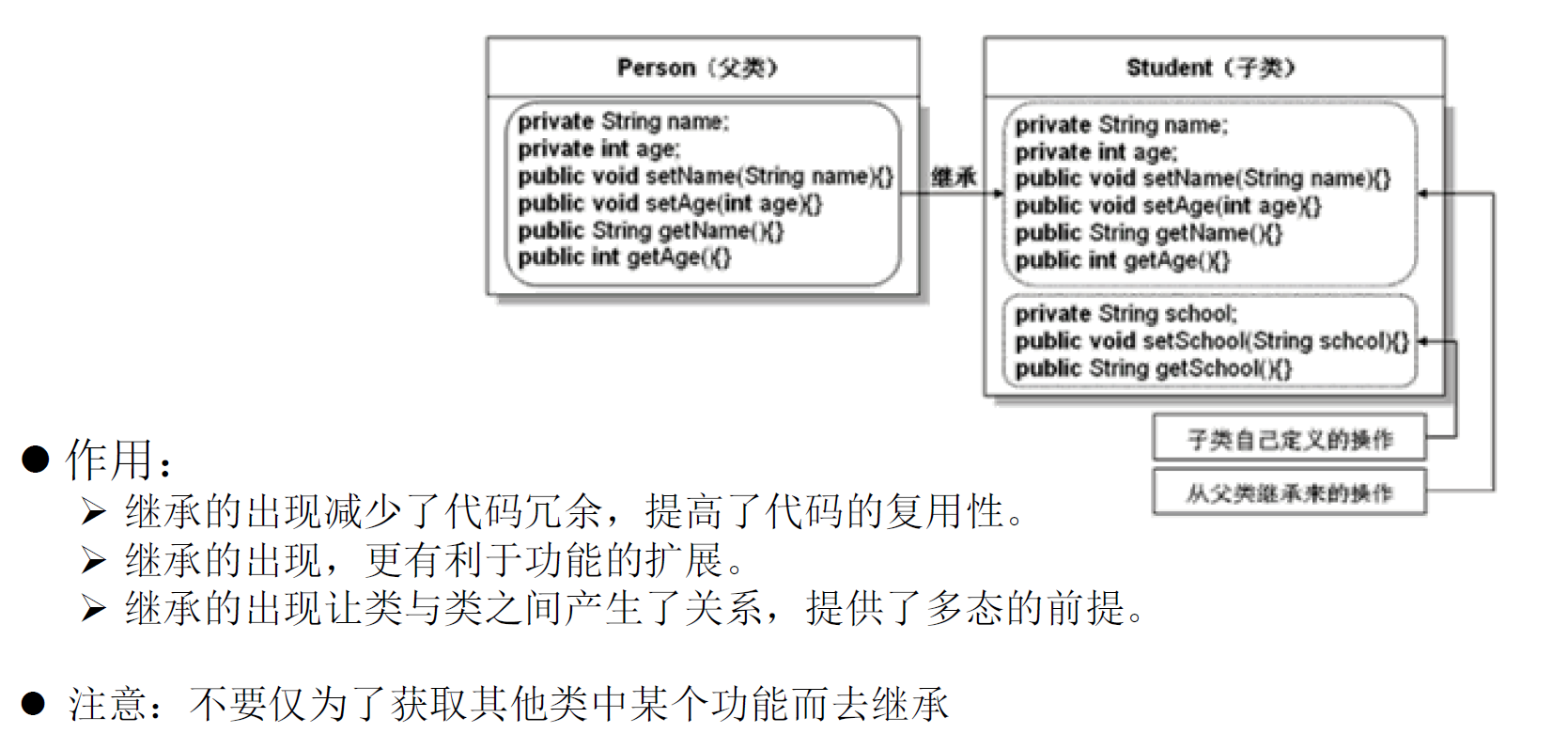

继承的特点
- 一旦子类A继承父类B以后,子类A中就获取了父类B中声明的所有的属性和方法。特别的,父类中声明为private的属性或方法,子类继承父类以后,仍然认为获取了父类中私有的结构。只有因为封装性的影响,使得子类不能直接调用父类的结构而已。
- 子类继承父类以后,还可以声明自己特有的属性或方法:实现功能的拓展。子类和父类的关系,不同于子集和集合的关系。
extends:延展、扩展
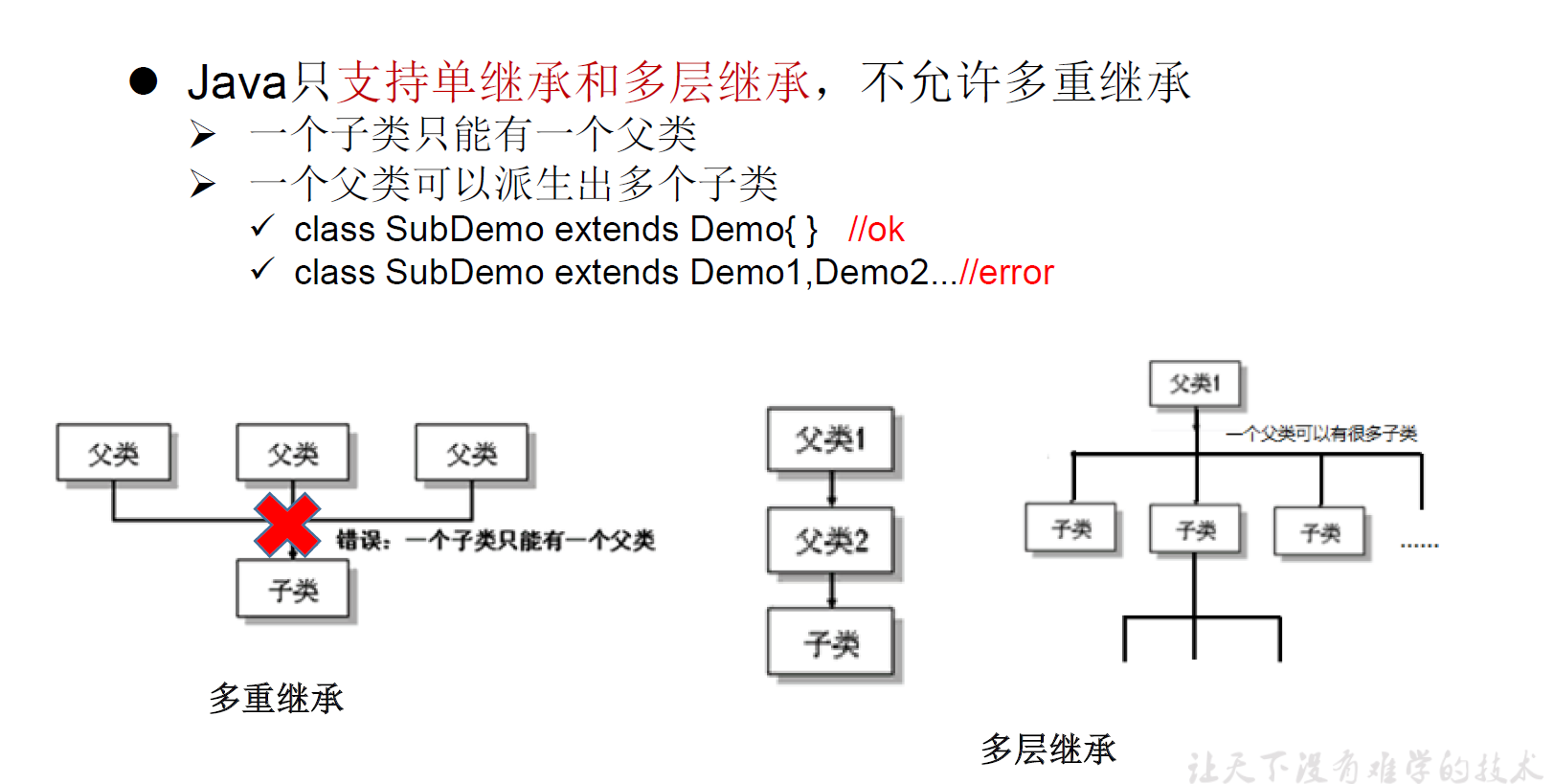
单继承与多层继承
Java中关于继承性的规定:
- 一个类可以被多个子类继承。
- Java中类的单继承性:一个类只能有一个父类。
- 子父类是相对的概念。
- 子类直接继承的父类,称为直接父类。间接继承的父类称为间接父类
- 子类继承父类以后,就获取了直接父类以及所有间接父类中声明的属性和方法|
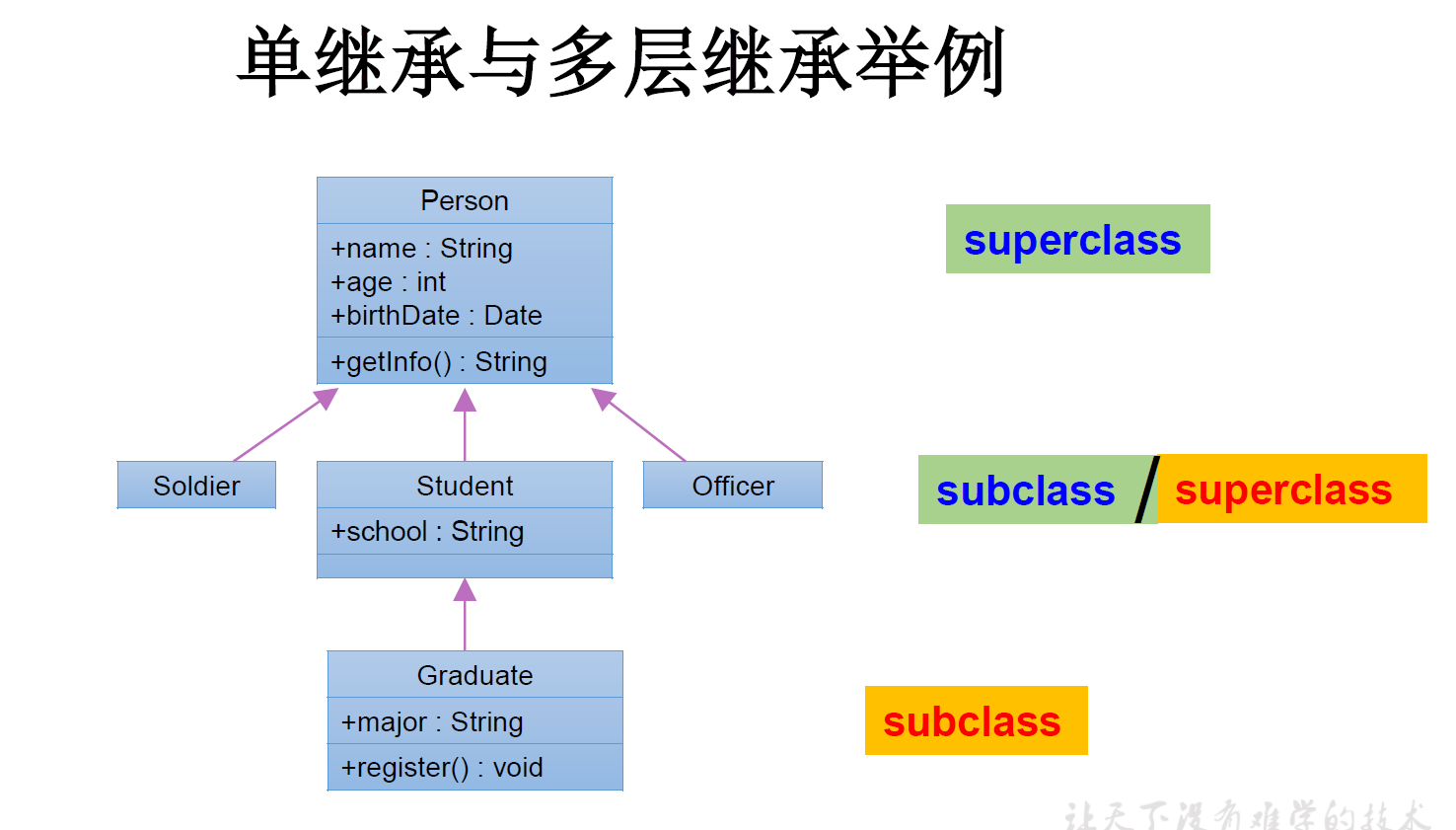
java.lang.object类
- 如果我们没有显式的声明一个类的父类的话,则此类继承于java.lang.object类
- 所有的java类(除java.lang.object类之外)都直接或间接的继承于java.lang.object类
- 意味着,所有的java类具有java. lang.0bject类声明的功能。
5.2 方法的重写


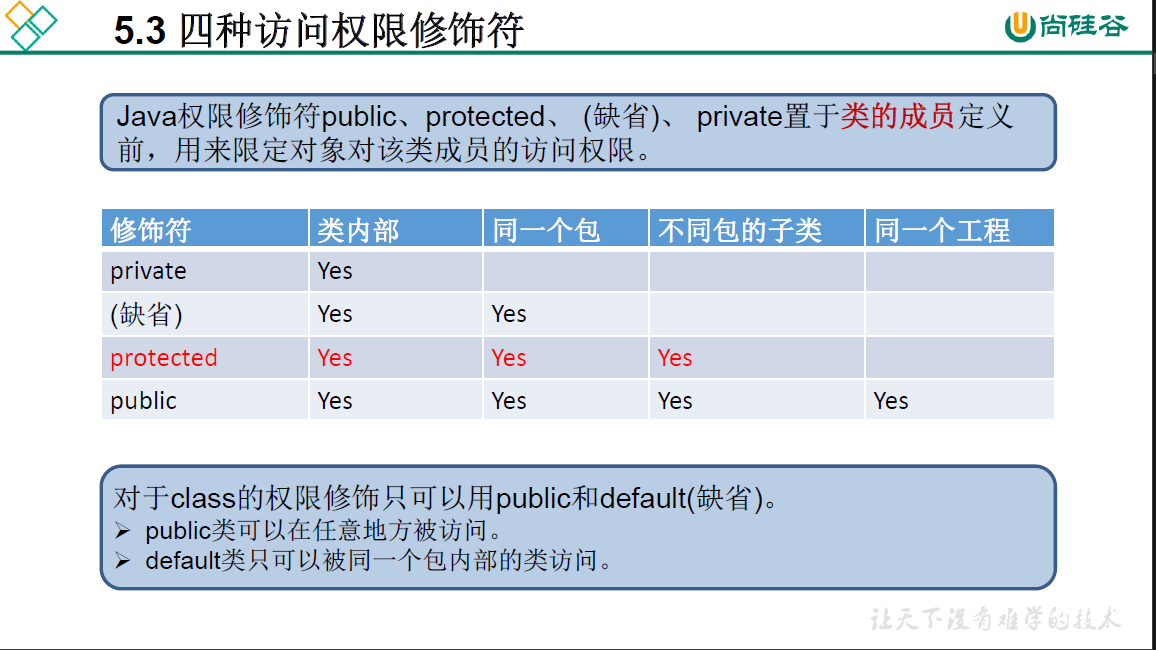
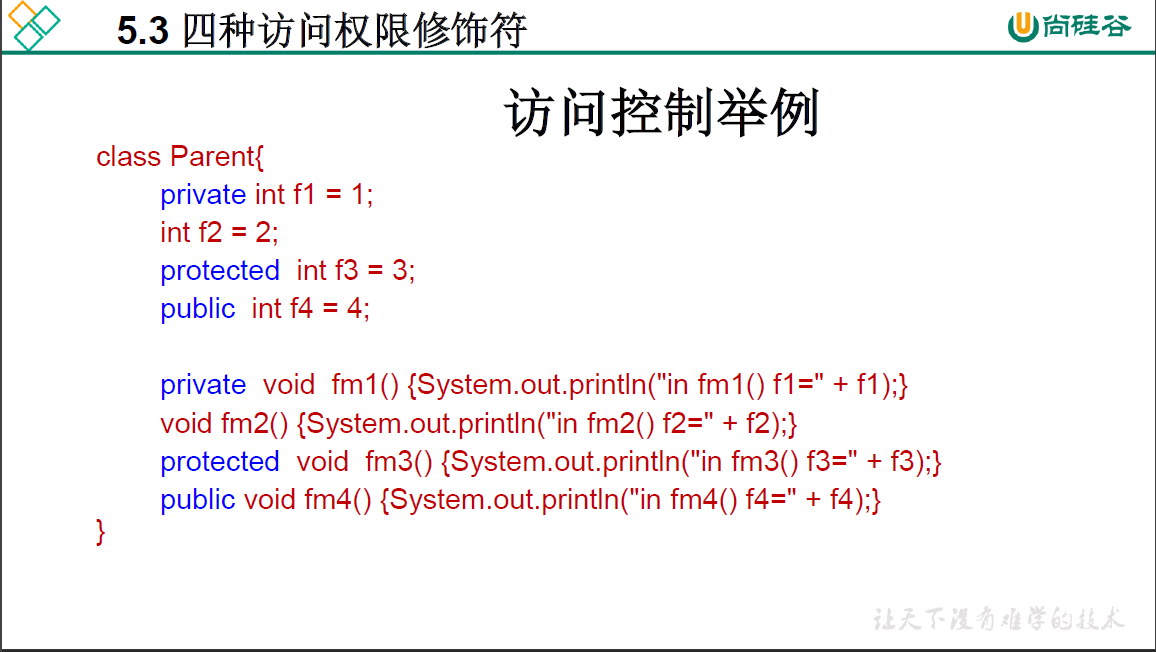
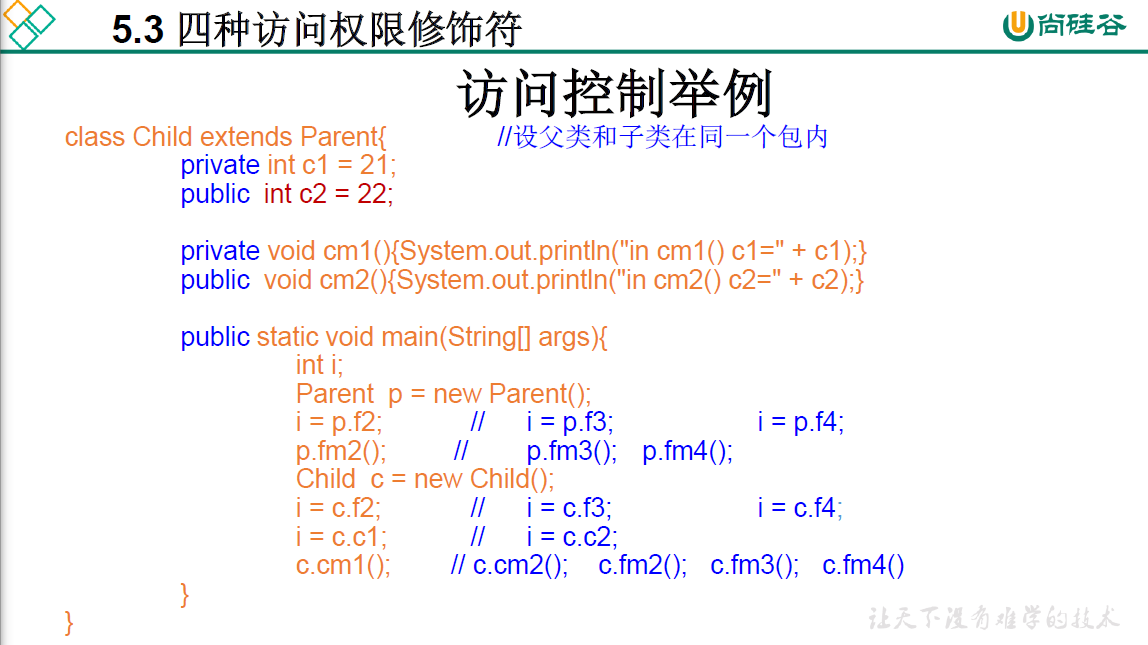
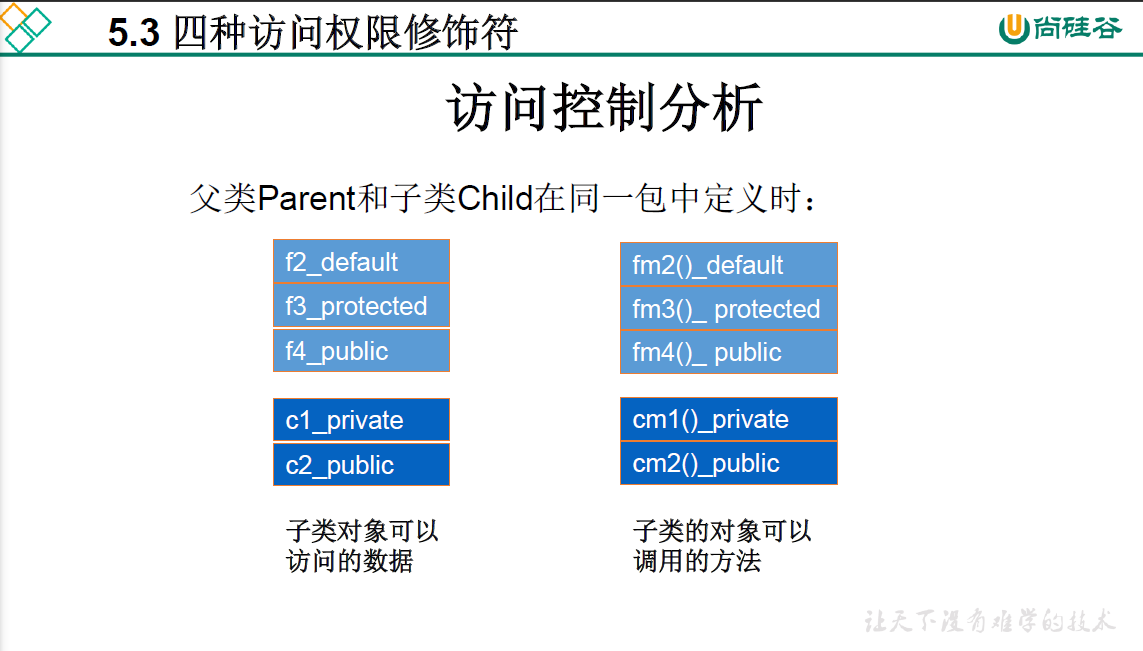
5.3 四种权限修饰符

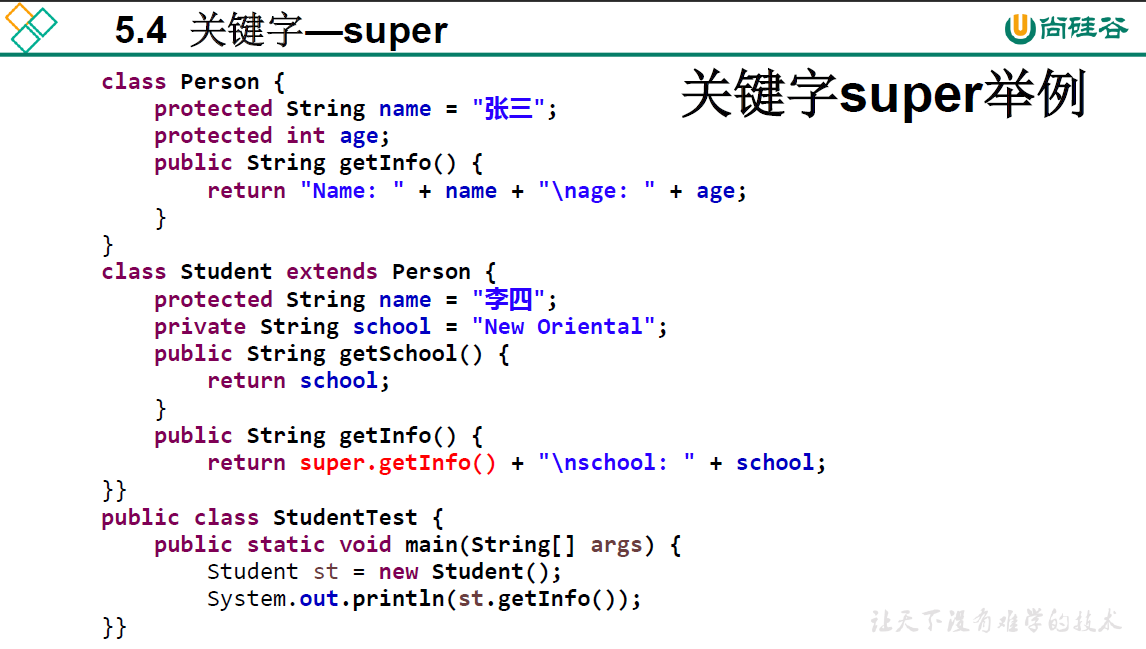
5.4 super关键字


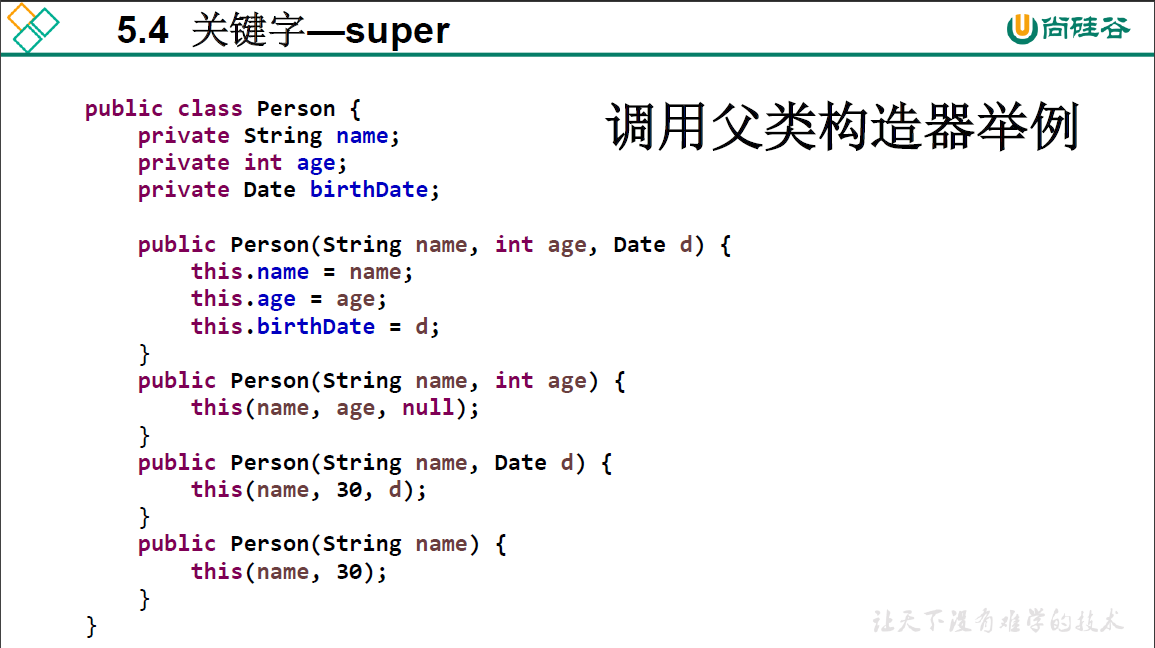
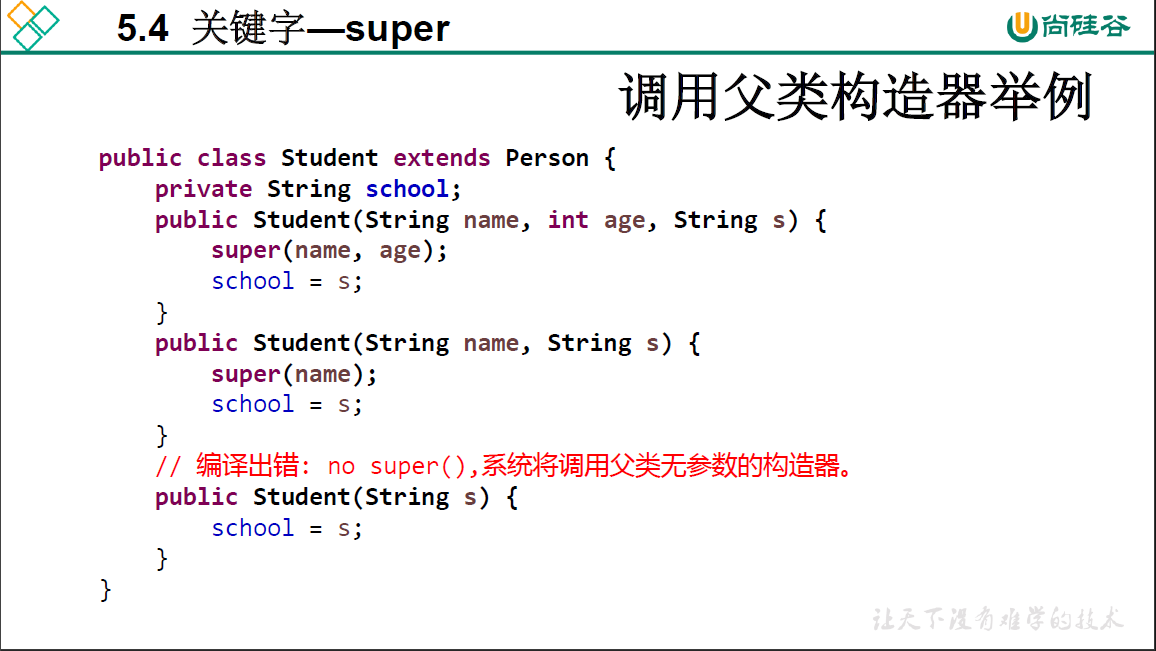
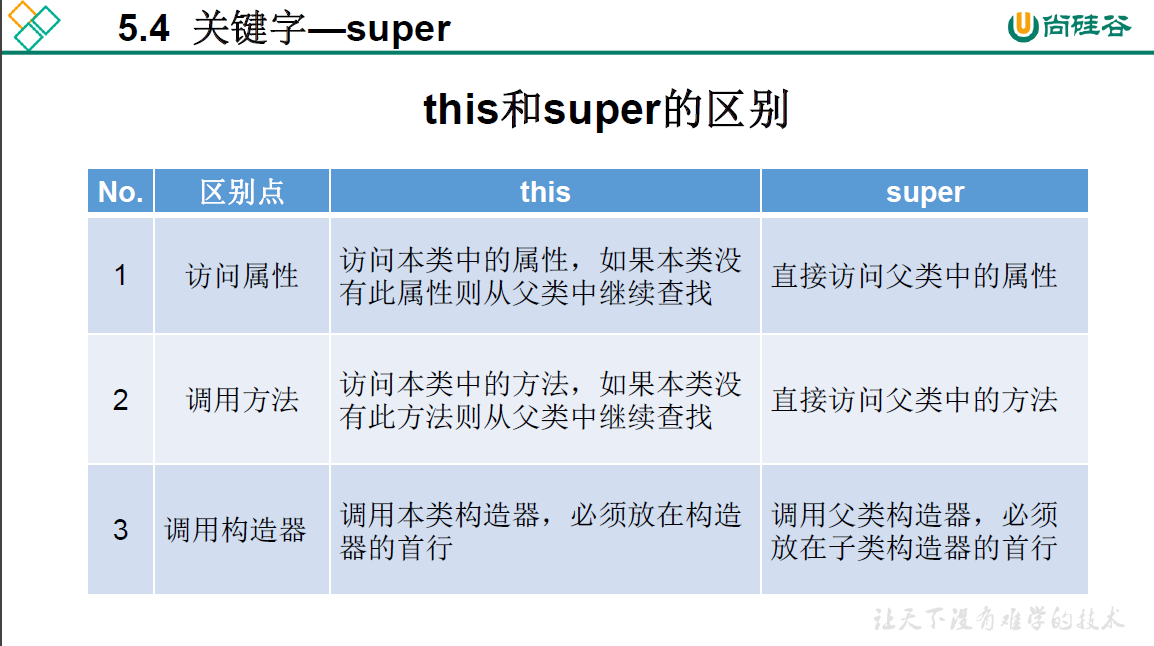

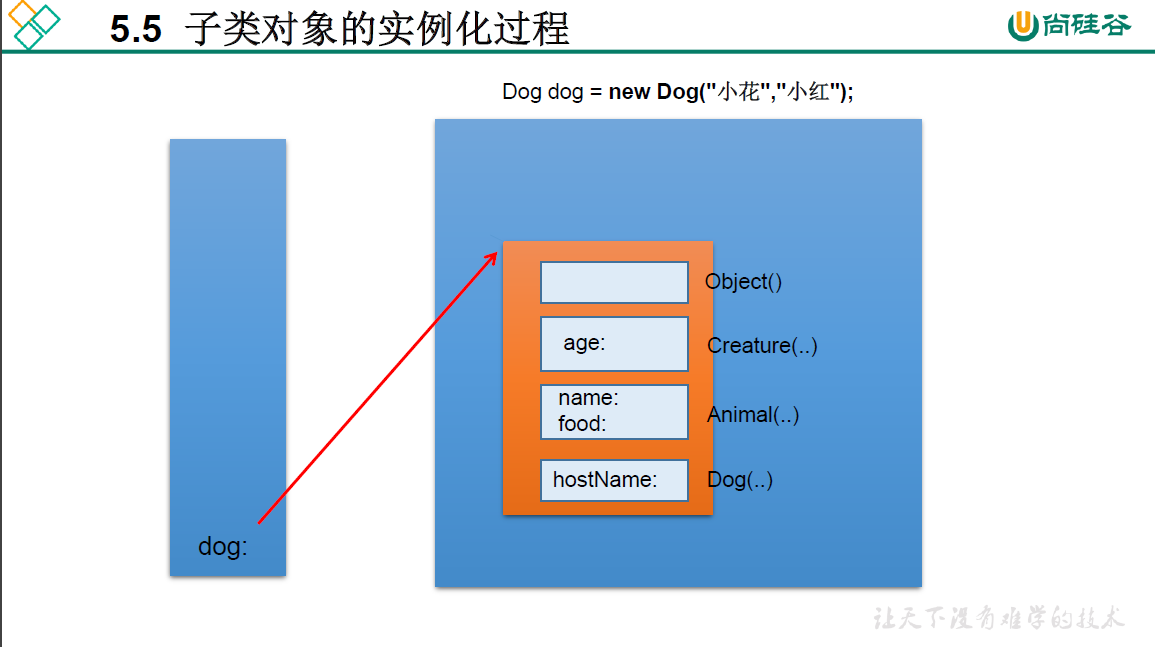
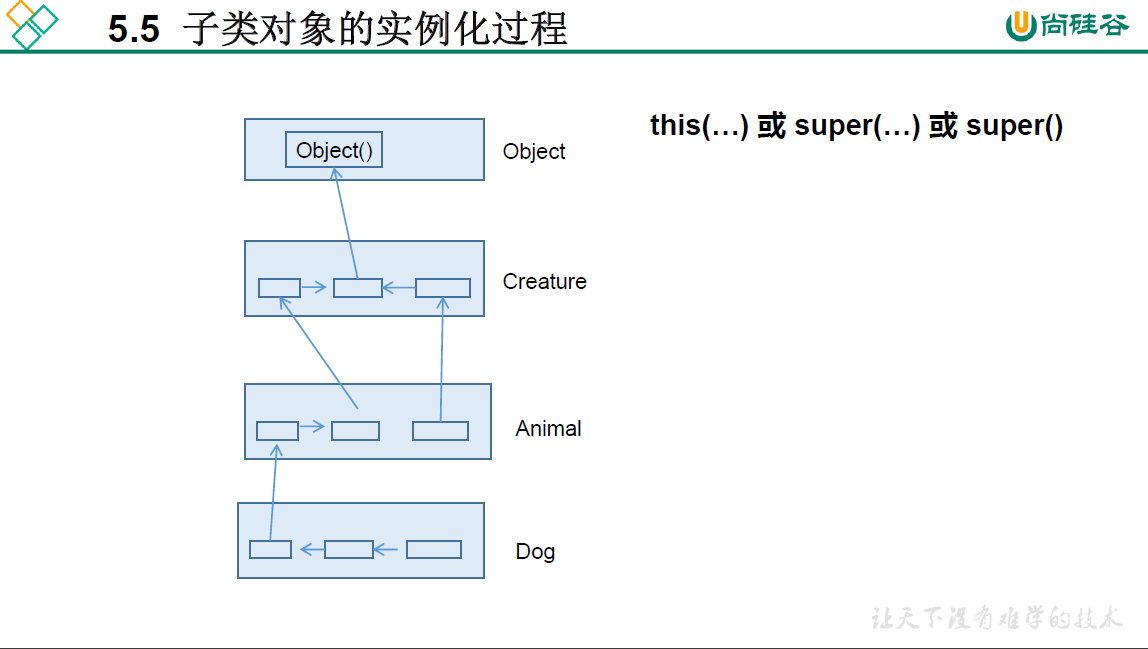
5.5 子类对象实例化过程

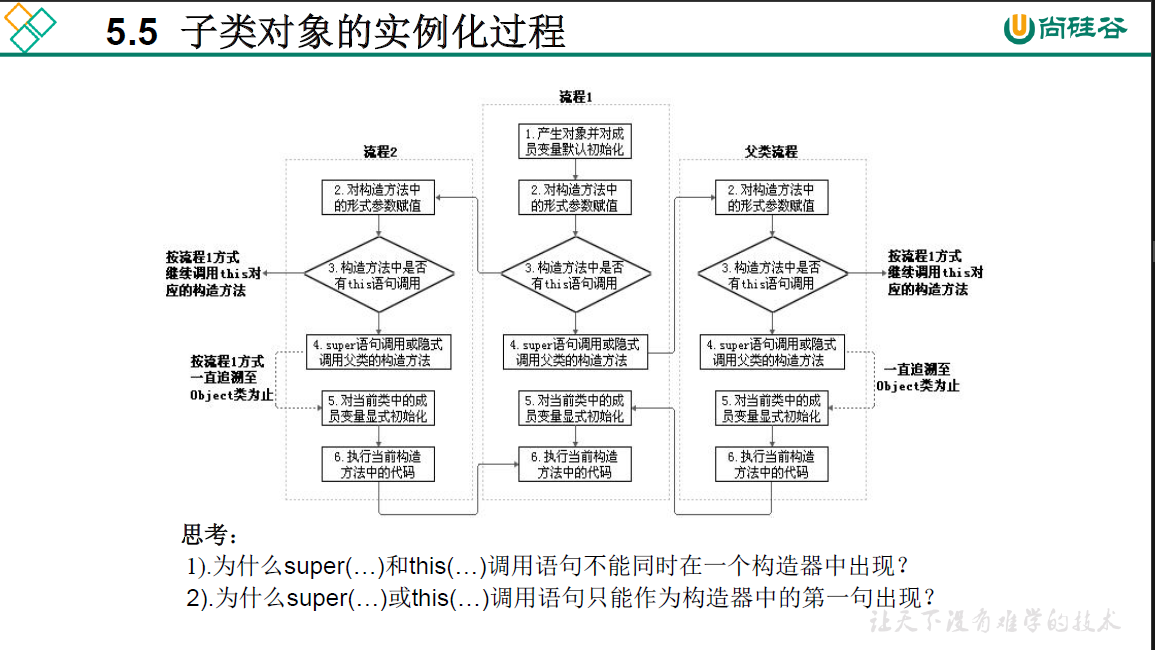
(1)this()和super()都需要出现在构造器的首行;
(2)无论通过哪个构造器创建子类对象,需要保证先初始化父类。目的:当子类继承父类后,"继承"父类中所有的属性和方法,因此子类有必要知道父类如何为对象进行初始化。
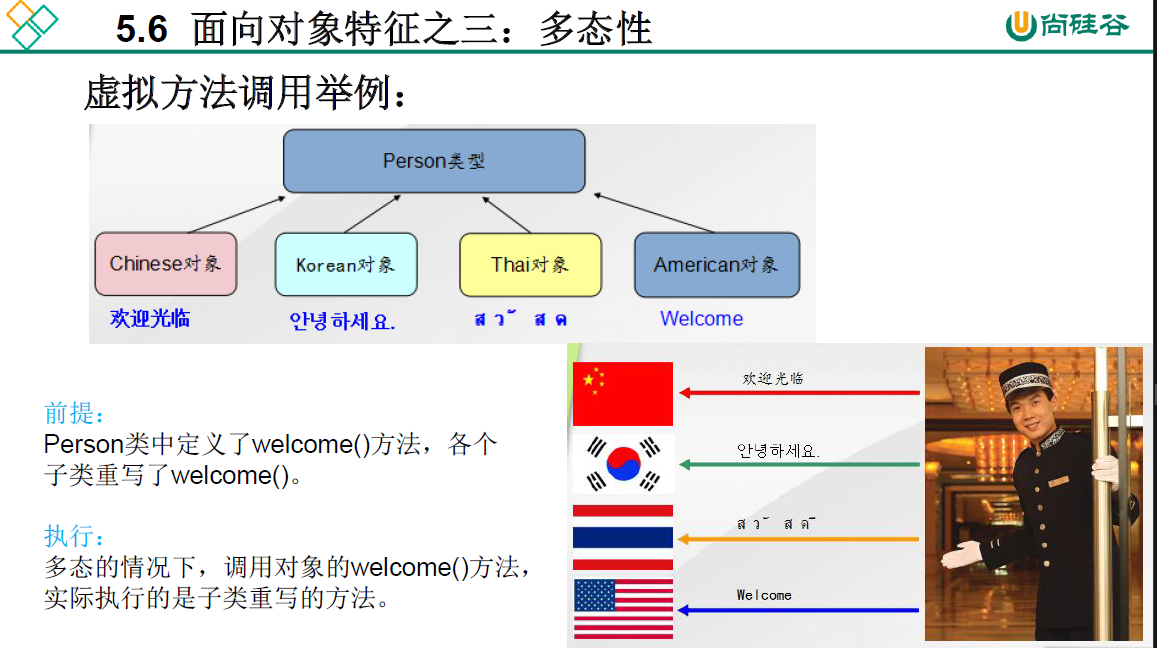
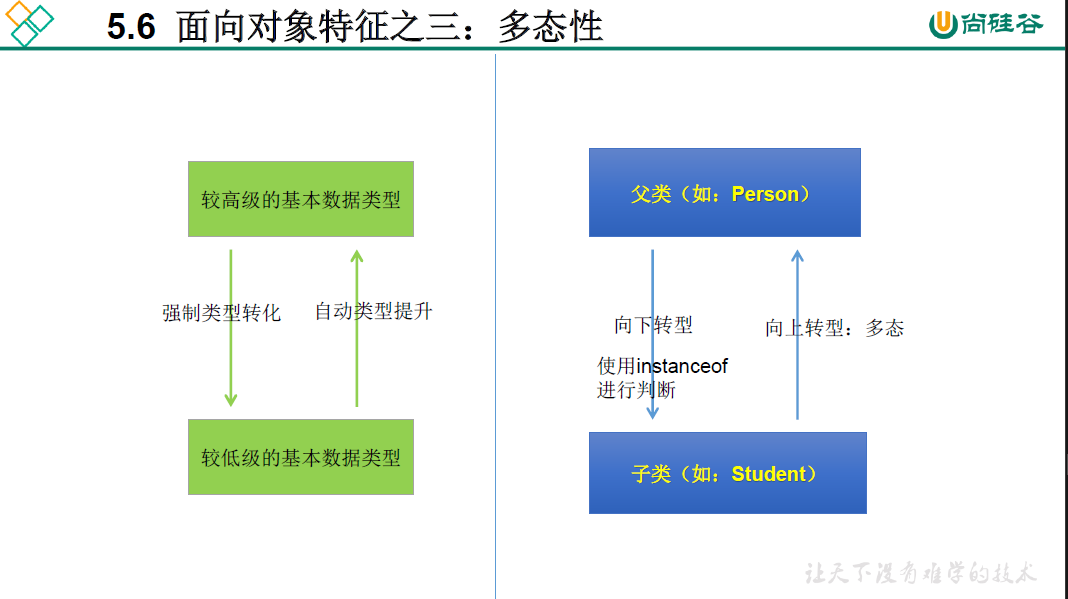
5.6 多态




即属性不具有多态性,只适用于方法




面试题






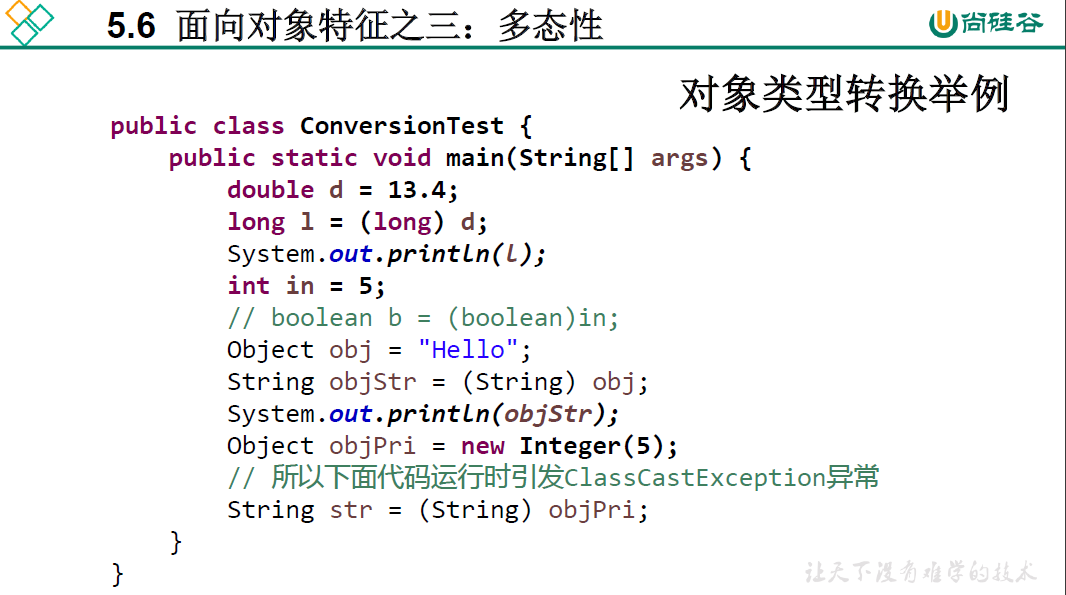

练习:继承成员变量和继承方法的区别
package oop.exercise.exer7;
public class FiledMethodTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sub s = new Sub();
System.out.println(s.count);
s.dispaly();
Base b = s;
System.out.println(b == s); //引用类型比较地址
System.out.println(b.count);
b.dispaly();
}
}
class Base{
int count = 10;
public void dispaly() {
System.out.println(this.count);
}
}
class Sub extends Base{
int count = 20;
public void display() {
System.out.println(this.count);
}
}
//输出结果
20
10
true
10
10

练习5: 多态测试
package oop.exercise.exer7;
/*
* 建立InstanceTest 类,在类中定义方法method(Person e);
在method 中
(1)根据 e 的类型调用相应类的 getInfo 方法。
(2)根据 e 的类型执行:
如果e 为 Person 类的对象, 输出
“a person”
如果e 为 Student 类的对象 输出:
“a student”
“a person ”
如果e 为 Graduate 类的对象,输出:
“a graduated student”
“a student”
“a person”
*/
public class InstanceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InstanceTest t = new InstanceTest();
Graduate g = new Graduate();
t.method(g);
}
public void method(Person e) {
System.out.println(e.getInfo());
if (e instanceof Graduate) {
System.out.println("a graduated student,
a student,
a person");
}else if(e instanceof Student) {
System.out.println("a student,
a person");
}else {
System.out.println("a person");
}
}
}
class Person{
protected String name = "person";
protected int age = 30;
public String getInfo() {
return "name:" + name + '
' + "age:" + age;
}
}
class Student extends Person{
protected String school = "pku";
public String getInfo() {
return "name:" + name + '
' + "age:" + age +
'
' + "school:" + school;
}
}
class Graduate extends Student{
public String major = "IT";
public String getInfo() {
return "name:" + name + '
' + "age:" + age +
'
' + "school:" + school + '
' + "major:" + major;
}
}
练习6
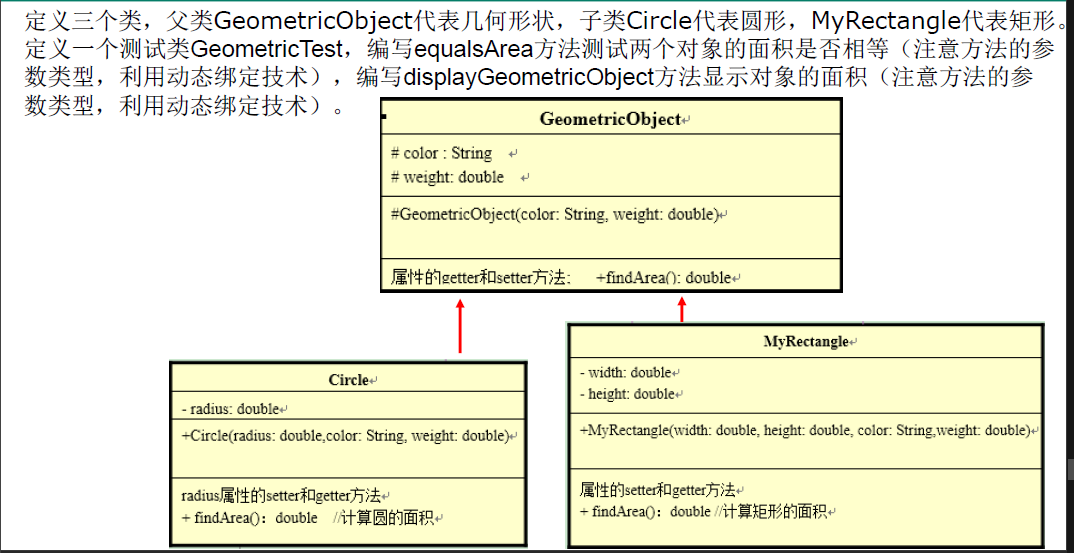
package oop.exercise.exer7;
public class GeometricTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GeometricTest gt = new GeometricTest();
Circle c = new Circle(2, "red", 3);
MyRectangle m = new MyRectangle(2, 3, "blue", 2);
gt.displayGeometricObject(c);
gt.displayGeometricObject(m);
System.out.println(gt.equalsArea(c, m));
}
public boolean equalsArea(GeometricObject g1, GeometricObject g2) {
return g1.findArea() == g2.findArea();
}
public void displayGeometricObject(GeometricObject g) {
System.out.println("the area is:" + g.findArea());
}
}
class GeometricObject{
String color;
double weight;
GeometricObject(String color, double weight){
this.color = color;
this.weight = weight;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public double getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(double weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public double findArea() {
return 0.0; //可以采用抽象方法
}
}
class Circle extends GeometricObject{
private double radius;
Circle(double radius, String color, double weight){
super(color, weight);
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public double findArea() {
return Math.PI * radius * radius;
}
}
class MyRectangle extends GeometricObject{
private double width;
private double height;
MyRectangle(double width, double height, String color, double weight) {
super(color, weight);
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
public double getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(double width) {
this.width = width;
}
public double getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(double height) {
this.height = height;
}
public double findArea() {
return width * height;
}
}
面试题1:多态是编译时行为还是运行时行为?
package study;
import java.util.Random;
//面试题:多态是编译时行为还是运行时行为?
//证明如下:
public class InterviewTest {
public static Animal getInstance(int key) {
switch (key) {
case 0:
return new Cat ();
case 1:
return new Dog ();
default:
return new Sheep ();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int key = new Random().nextInt(3);
System.out.println(key);
Animal animal = getInstance(key);
animal.eat();
}
}
class Animal{
protected void eat(){
System.out.println("animal eat food");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal{
protected void eat() {
System.out.println("cat eat fish");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
public void eat() {
System.out.println("Dog eat bone");
}
}
class Sheep extends Animal{
public void eat() {
System.out.println("Sheep eat grass");
}
}
面试题2:可变形参
package study;
//考查多态的笔试题目:
public class InterviewTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Base base = new Sub();
base.add(1, 2, 3);
Sub s = (Sub)base;
s.add(1,2,3);
}
}
class Base {
public void add(int a, int... arr) {
System.out.println("base");
}
}
class Sub extends Base {
public void add(int a, int[] arr) {
System.out.println("sub_1");
}
public void add(int a, int b, int c) {
System.out.println("sub_2");
}
}
输出结果:
sub_1
sub_2
//可变形参int... arr与int[] arr不能同时存在,如果共存,编译器会认为两个形参相同,在本例中,相当于子类方法重写父类方法,而对于s.add(1,2,3),参数个数确定,优先调用add(int a, int b, int c)方法。
5.7 Object 类的使用


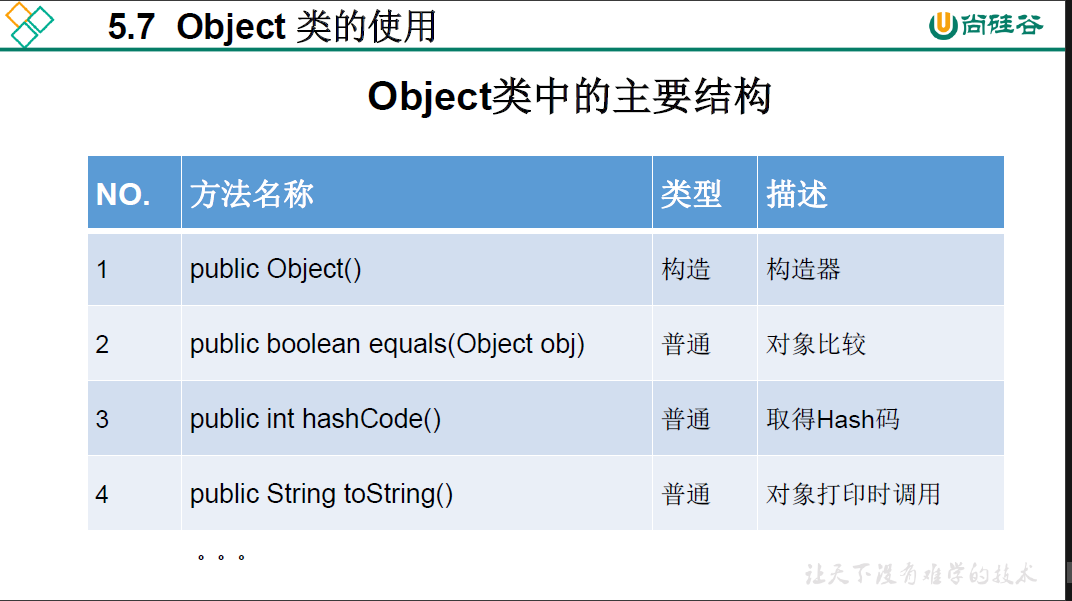



==运算符与equals方法的区别

一、== 运算符
- 可以使用在基本数据类型变量和引用数据类型变量中;
- 如果比较的是基本数据类型变量:比较两个变量保存的数据是否相等。(不一定类型要相同)
- 如果比较的是引用数据类型变量:比较两个对象的地址值是否相同;
二、equals方法
-
是一个方法,而非运算符;
-
只能适用于引用数据类型;
-
Object类中equals()的定义:
public boolean equals(Object obj) { return (this ==obj); }说明:Object类中定义的equals()和==的作用是相同的,即比较两个对象的地址值是否相同。
-
像String、Date、File、包装类等都重写了0bject类中的equals()方法。重写以后,比较的不是
两个引用的地址是否相同,而是比较两个对象的"实体内容"是否相同; -
通常情况下,我们自定义的类如果使用equals()的话,也通常是比较两个对象的"实体内容"是否相同。那么,我们就需要对Object类中的equals(()进行重写;
-
重写的原则:比较两个对象的实体内容是否相同;

package study;
public class ToStringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Iphone a = new Iphone(3670, 190);
System.out.println(a);
}
}
class Iphone{
int price;
double weight;
public Iphone(int price, double weight) {
this.price = price;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override //重写toString方法
public String toString() {
return "Iphone [price=" + price + ", weight=" + weight + "]";
}
}
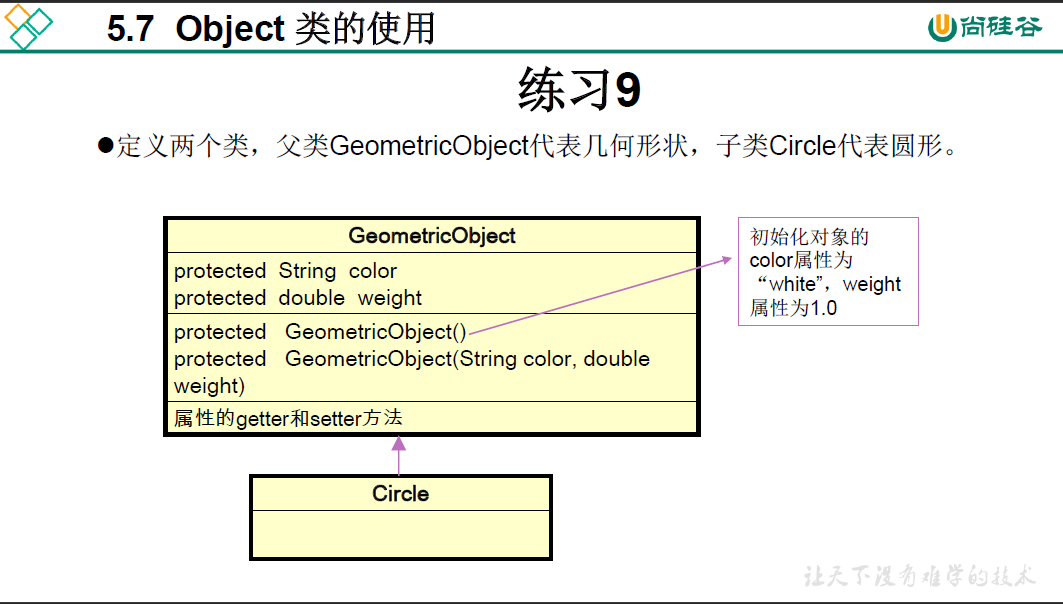
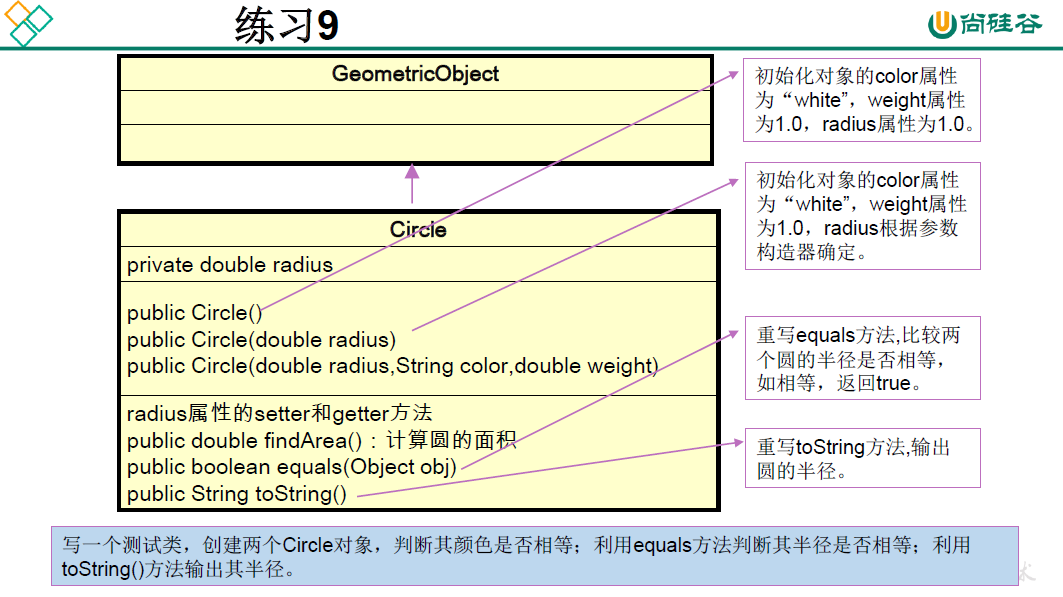
package oop.exercise.exer9;
public class GeometricObjectTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Circle c1 = new Circle(2.0, "red", 3.5);
Circle c2 = new Circle(3.0, "red", 3.5);
System.out.println(c1.getColor().equals(c2.getColor()));
System.out.println(c1.equals(c2));
System.out.println(c1);
}
}
class GeometricObject{
protected String color;
protected double weight;
protected GeometricObject() {
this.color = "white";
this.weight = 1.0;
}
protected GeometricObject(String color, double weight){
this.color = color;
this.weight = weight;
}
public String getColor(){
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public double getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(double weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
}
class Circle extends GeometricObject{
private double radius;
public Circle() {
super("white", 1.0);
this.radius = 1.0;
}
public Circle(double radius) {
super("white", 1.0);
this.radius = radius;
}
public Circle(double radius, String color, double weight) {
super(color, weight);
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public double findArea() {
return Math.PI * radius * radius;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Circle other = (Circle) obj;
if (Double.doubleToLongBits(radius) != Double.doubleToLongBits(other.radius))
return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Circle [radius=" + radius + "]";
}
}
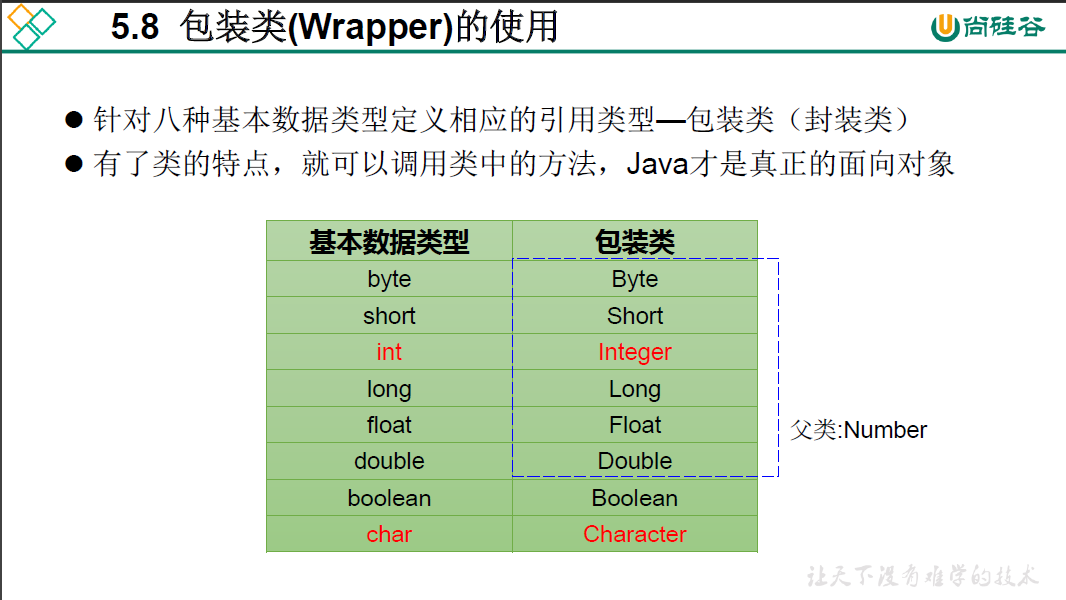
5-8 包装类的使用





package oop.unittest;
import org.junit.Test;
public class WrapperTest {
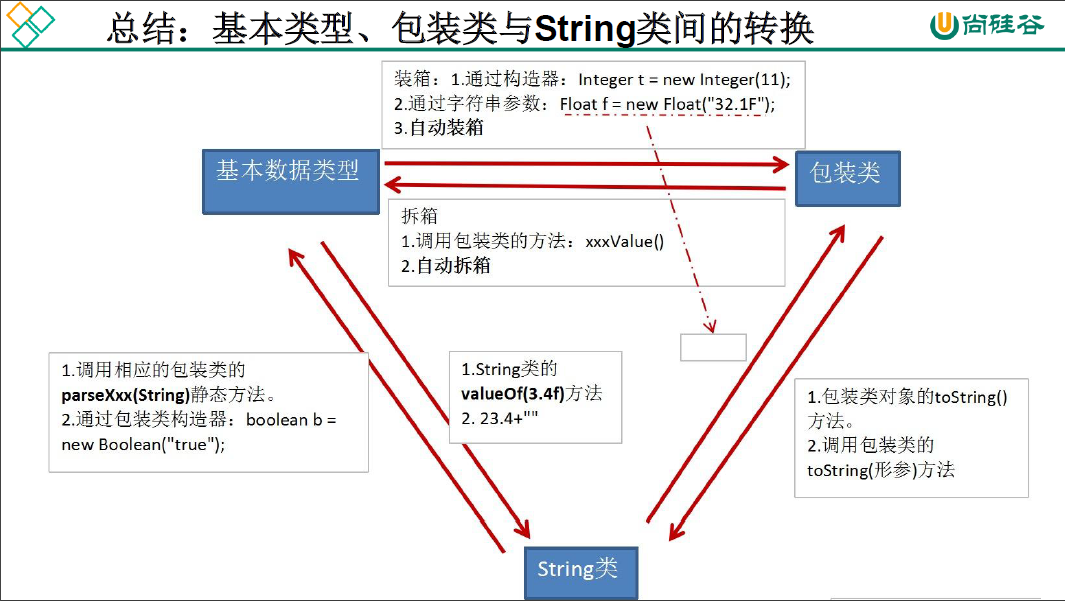
// 基本数据类型————> 包装类:调用包装类的构造器
@Test
public void test1() {
int num1 = 10;
Integer in1 = new Integer(num1);
System.out.println(in1.toString());
Integer in2 = new Integer("123");
System.out.println(in2.toString()); //"123"
// Integer in3 = new Integer("123abc"); // 异常
// System.out.println(in3.toString());
Float f1 = new Float(12.3f);
Float f2 = new Float("12.3");
System.out.println(f1); //"12.3"
System.out.println(f2); //"12.3"
Boolean b1 = new Boolean(true);
Boolean b2 = new Boolean("true");
System.out.println(b1); //true
System.out.println(b2); //true
Boolean b3 = new Boolean("true123"); //只要不为"true",如"true123",则结果为false
System.out.println(b3); //false
Order order = new Order();
System.out.println(order.isMale); // false
System.out.println(order.isFemale); //null
}
// 包装类————> 基本数据类型:调用包装类xxx的xxxValue方法
@Test
public void test2() {
Integer in1 = new Integer(12);
int i1 = in1.intValue();
System.out.println(i1 + 1); //13
Float f1 = new Float(12.3);
float f2 = f1.floatValue();
System.out.println(f2 +1); //13.3
}
// 自动装箱与拆箱,jdk5.0新特性
@Test
public void test3() {
// 自动装箱,基本数据类型-->包装类
int num1 = 10;
Integer in1 = num1;
System.out.println(in1); //"10"
boolean b1 = true;
Boolean b2 = b1;
System.out.println(b2); //true
// 自动拆箱,包装类-->基本数据类型
int num2 = in1;
System.out.println(num2); //10
}
//基本数据类型、包装类--->String类型:调用包装类的parseXxx(String s)方法
@Test
public void test4() {
int num1 = 10;
//方式1:连接运算
String str1 = num1 + "";
System.out.println(str1); //"10"
//方式2:调用String的ValueOf()方法
float f1 = 12.3f;
String str2 = String.valueOf(f1);
System.out.println(str2); //"12.3"
Double d1 = new Double(12.4);
String str3 = String.valueOf(d1);
System.out.println(str3); //"12.4"
}
//String类型--->基本数据类型、包装类:调用包装类的parseXxx(String s)方法
@Test
public void test5() {
String str1 = "123";
//可能会报NumberFormatException
int i1 = Integer.parseInt(str1);
System.out.println(i1 + 1); //124
String str2 = "true";
boolean b1 = Boolean.parseBoolean(str2);
System.out.println(b1); //true
}
}
class Order{
boolean isMale;
Boolean isFemale;
}
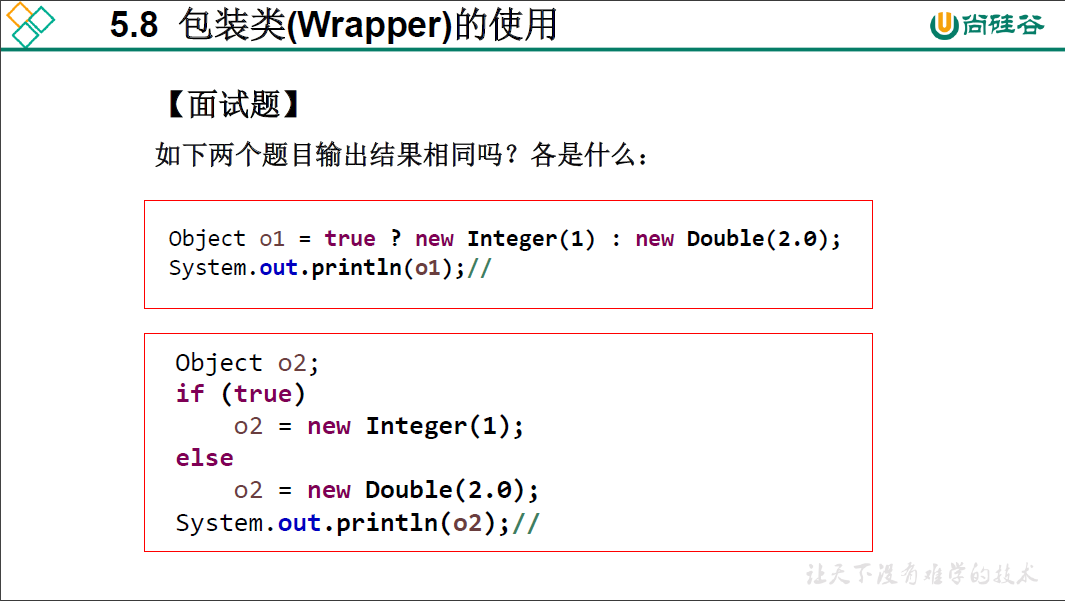
package oop.unittest;
import org.junit.Test;
public class InterviewTest {
@Test
public void test1() {
// 三元运算符后面的表达式编译时会自动统一类型
Object o1 = true ? new Integer(1) : new Double(2.0);
System.out.println(o1); //1.0
}
@Test
public void test2() {
Object o2;
if (true)
o2 = new Integer(1);
else
o2 = new Double(2.0);
System.out.println(o2); //1
}
}
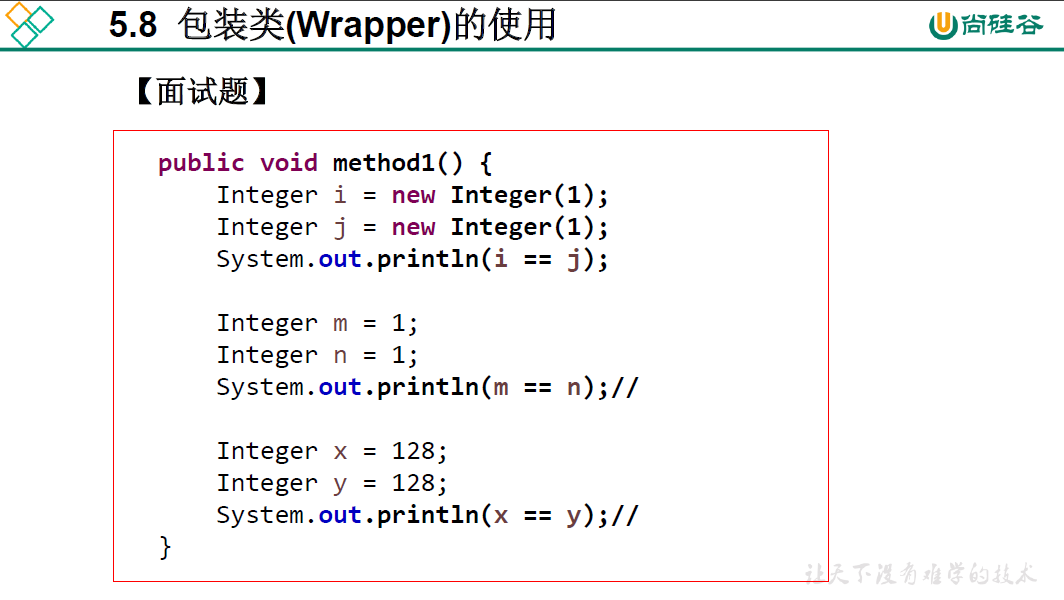
@Test
public void test3( ) {
/*
* Integer内部定义了IntegerCache结构,IntegerCache中定义了Integer[],保存了从-128~127范 围的整数。如果我们使用自动装箱的方式,给Integer赋值的范围在
* -128~127范围内时,可以直接使用数组中的元素,不用再去new新的对象了。目的:提高效率
*/
Integer i = new Integer(1);
Integer j = new Integer(1);
System.out.println(i == j); //false
Integer m = 1;
Integer n = 1;
System.out.println(m == n); //true
Integer x = 128;
Integer y = 128;
System.out.println(x == y); //false
}

@Test
public void test4() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
Vector v = new Vector();
int maxScore = 0;
while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入学生成绩(以负数代表输入结束)");
int score = sc.nextInt();
if (score < 0)
break;
if (score > 100) {
System.out.println("请输入学生成绩(以负数代表输入结束)");
continue;
}
if (maxScore < score)
maxScore = score;
v.addElement(score); //自动装箱
}
char level;
for (int i =0;i < v.size();i++) {
Object obj = v.elementAt(i);
int score = (int)obj; //自动拆箱
if (maxScore - score <= 10)
level = 'A';
else if (maxScore - score <= 20)
level = 'B';
else if (maxScore - score <= 30)
level = 'C';
else
level = 'D';
System.out.println("student-" + i + " score is " + score + ", level is " + level);
}
}