Network Security
- Combination of low-cost powerful computing and high-performance networks is a two-edged sword:
- Many powerful new services and applications are enabled
- But computer systems and networks become highly susceptible(敏感) to a wide variety of security threats
- Openness vs Security
- Network security involves countermeasures(对策) to protect computer systems from intruders(入侵者)
- Firewalls, security protocols, security practices, etc.
Eavesdropping
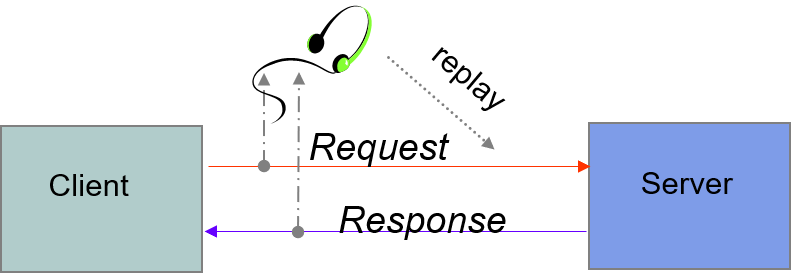
- Information transmitted over network can be observed and recorded by eavesdroppers (using a packet sniffer)
- Information can be replayed(重播) in attempts to access server
- Requirements: privacy, authentication(认证), non-repudiation(否认)
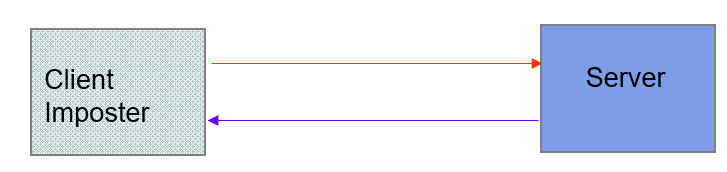
Client Imposter
-
client imposter(冒名顶替者)
-
Imposters attempt to gain unauthorized(未经授权的) access to server
- Ex. bank account or database of personal records
- For example, in IP spoofing(戏弄) imposter sends packets with false source IP address
-
Requirements: privacy, authentication
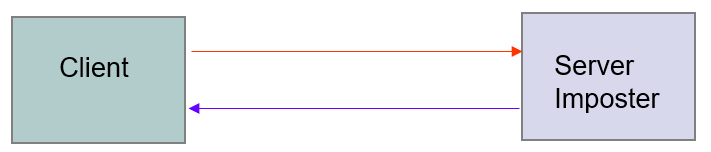
Server Imposter

- An imposter impersonates(模拟) a legitimate(合法的) server to gain sensitive information from a client
- E.g. bank account number and associated user password
- Requirements: privacy, authentication, non-repudiation
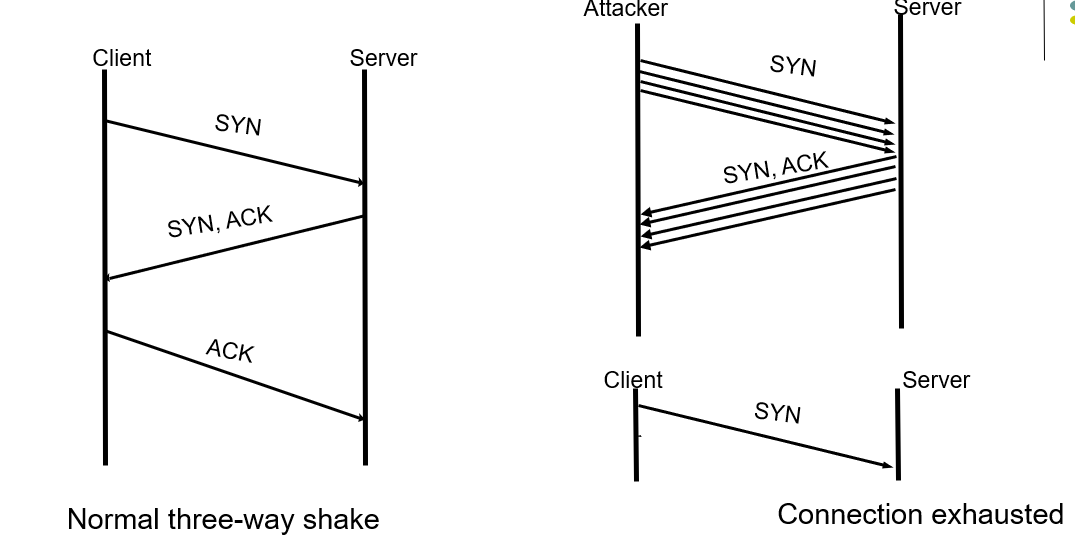
Denial of Service (DoS) Attack
- Attacker can flood a server with requests, overloading the server resources (er. TCP Three-way handshake)
- Results in denial of service to legitimate clients
- Distributed denial of service attack on a server involves coordinated attack from multiple (usually hijacked) computers
- Requirement: availability
TCP SYN Flood
- The attacker sends a repeated same packet, to every port on the target server over using a fake IP address.
- The server will send back ack continunously, prevents other client sending syn.
Man-in-the-Middle Attack

- An imposter manages to place itself as man in the middle
- convincing the server that it is legitimate client
- convincing legitimate client that it is legitimate server
- gathering sensitive information and possibly hijacking(劫持) session
- Requirements: integrity, authentication
Malicious Code
- A client becomes infected with malicious code
- Virus: code that when executed, inserts itself in other programs
- Worms: code that installs copies of itself in other machines attached to a network
- Requirements: privacy, integrity, availability
Security Requirements
Security threats motivate requirements:
- Privacy: information should be readable only by intended recipient(接受者)
- Integrity: recipient can confirm that a message has not been altered during transmission
- Authentication: it is possible to verify that sender or receiver is who he claims to be
- Non-repudiation*(不可抵赖性): sender cannot deny having sent a given message.
- Availability: of information and services
Countermeasures
- Secure communication channels
- Encryption
- Cryptographic checksums and hashes (加密校验和和散列)
- Authentication
- Digital Signatures
- Secure borders
- Firewalls
- Virus checking
- Intrusion detection(入侵检测)
- Authentication
- Access Control (访问控制)