Mobile IP
Mobile IP
- Proliferation(增生) of mobile devices: PDAs, laptops, smart phones, …
- As user moves, point-of-attachment(辅助箱) to network necessarily changes
- Problem: IP address specifies point-of-attachment to Internet
- Changing IP address involves terminating all connections & sessions
- Mobile IP (RFC 2002): device can change point-of-attachment while retaining(保持) IP address and maintaining communications
Routing in Mobile IP

- Home Agent (HA) keeps track of location of each Mobile Host (MH) in its network; HA periodically(定期) announces its presence
- If an MH is in home network, e.g. MH#1, HA forwards packets directly to MH
- When an MH moves to a Foreign network, e.g. MH#2, MH obtains a care-of-address(转交地址) from foreign agent (FA) and registers this new address with its HA
Routing in Mobile IP
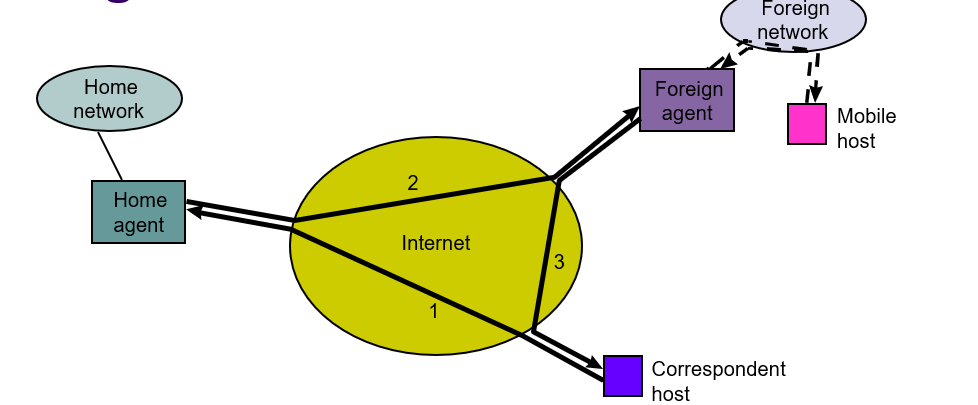
- Correspondent Host (CH) sends packets as usual (1)
- Packets are intercepted by HA which then forwards to Foreign Agent (FA) (2)
- FA forwards packets to the MH
- MH sends packet to CH as usual (3)
- How does HA send packets to MH in foreign network?
IP-to-IP Encapsulation
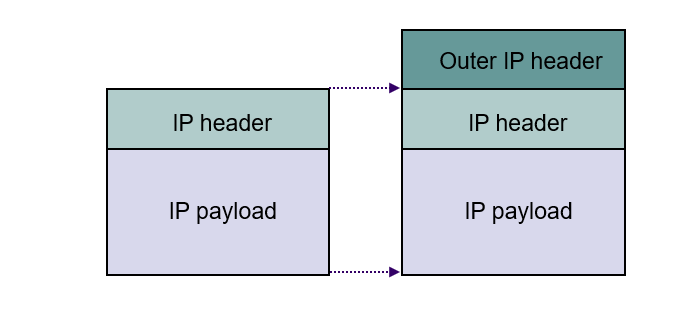
- HA uses IP-to-IP encapsulation
- IP packet has MH IP address
- Outer IP header has HA’s address as source address and care-of-address as destination address
- FA recovers IP packet and delivers to MH
Route Optimization

- Going to HA inefficient if CH and MH are in same foreign network
- When HA receives pkt from CH (1), it tunnels using care-of-address (2a); HA also sends care-of-address to CH (2b)
- CH can then send packets directly to care-of-address (4)
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/vancasola/p/7745465.html



