我们在编写脚本的过程中,可能涉及一些敏感信息,例如:用户信息、数据库信息、测试数据等,如果这些数据暴露在脚本中,无疑是不安全的。
将这些信息封装到配置文件,不仅测试时修改方便快捷,不用在脚本中检索要修改的数据,同时也从某种程度上保障了数据的安全。
下面我们介绍一种Python种常用的配置文件封装方法,使用Python自带的configparser模块来完成配置文件的信息读取。下面我们就来详细介绍它的用法。
1 配置文件格式
在使用之前,我们先来了解一下,配置文件.ini的格式。
.ini文件由节(section)、键(option)、值(value)三部分组成,其中item表示键值对。
节:[section];参数(items):键(option)=值(value);注解-使用分号;表示。
在配置文件中,所有的item(键值对),都以section为单位组合。可以理解为一个section就是若干组item。一般来说,一个[section]声明开始到下一个[section]之前,都为该section中的item,特殊情况时也可以使用section嵌套。
示例如下:
1 ;comments of configparaser testing
2 [section1]
3 option1_1 = value1_1
4 option1_2 = value1_2
5
6 [section2]
7 option2_1 = 123456
2 configparser模块
python使用自带的configparser模块用来读取配置文件,配置文件的形式类似windows中的ini文件,pip直接安装,然后就可以import来使用了。
安装configparser:
pip install configparser
3 读取配置文件
3.1 关于配置文件路径
绝对路径:从硬盘根目录为起点到当前所在目录;
相对路径:从某个目录为起点到当前所在目录。
我们都知道,如果使用绝对路径,那么代码放在自己的电脑中,一切正常,当放在其他电脑的任意路径位置时,文件的读取就会出现异常。因此,如果我们使用相对路径,就会比较灵活。我们一般使用“../”来表示上一级目录,“../../”表示上上级的目录,以此类推。
例如:

我们看file.py文件的路径:
绝对路径:D:Folderfile.py
相对路径:.Folderfile.py
3.2 实例
工程目录结构如下:
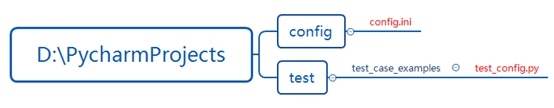
config.ini:
1 ;comments of configparaser testing
2 [section1]
3 option1_1 = value1_1
4 option1_2 = value1_2
5
6 [section2]
7 option2_1 = 123456
read_config_parser.py,封装读取配置文件方法:
1 import configparser
2 import os
3
4
5 class ReadConfigParser(object):
6 """
7 读取配置文件方法
8 configparser模块
9 一个配置文件可以有多个section,例如:数据库相关配置,系统用户配置,邮箱配置等,每个section由[]包裹,即[section1]/[section2]...,以列表形式返回
10 每个section中以键值对的形式存在
11 """
12
13 def get_config(self, cnf_type='', section='', option=''):
14 """
15 获取配置文件中的内容
16 :param cnf_type:操作类型,(1) sections-获取所有section;(2) items-获取某个section中所有键值对;(3) options-获取某个section中所有键;(4) value-获取某个指定section中某个键的值 ;(5) value_int-获取某个指定section中某个键的值,返回类型为int
17 :param section:section名称
18 :param option:某个section中的某个键名称
19 :return:sections/items/options/value/value_int
20 """
21 # 创建实例
22 cf = configparser.ConfigParser()
23 # # 读取配置文件-绝对路径,使用绝对路径,不需要os
24 # cf.read(self.config_abs_path)
25 # 获取config.ini所在目录的上一级目录,根据工程结构,也就是当前路径的上一级路径,这个根据自己的工程目录结构来获取
26 root_path = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath('..'))
27 # 使用相对路径,拼接获得
28 config_path = os.path.join(root_path + 'configconfig.ini')
29 # 读取配置文件
30 cf.read(config_path)
31 # 获取配置文件中所有section,无入参
32 if cnf_type == "sections":
33 sections = cf.sections()
34 return sections
35 # 获取某个section中所有键值对,入参section
36 elif cnf_type == "items":
37 items = cf.items(section)
38 return items
39 # 获取某个section中的所有键,入参section
40 elif cnf_type == "options":
41 options = cf.options(section)
42 return options
43 # 获取某个section中某个键的值,入参section/option
44 elif cnf_type == "value":
45 value = cf.get(section, option)
46 return value
47 elif cnf_type == "value_int":
48 # 获取某个section中某个键的值,入参section/option,返回int
49 value_int = cf.getint(section, option)
50 return value_int
51 else:
52 print(
53 "===>>> WARNING <<<=== Please check your initialation operation. You can select the following options: value/name/section/params")
test_config_parser_demo.py,测试读取配置文件脚本:
1 from public_methods.common.read_config_parser import ReadConfigParser
2
3
4 class TestConfigparser(ReadConfigParser):
5 """
6 本示例Demo,主要用于测试configparser模块,配置文件读取有效性验证
7 """
8
9 def test_config_parser(self):
10 # 获取配置文件中所有的section
11 sections = self.get_config(cnf_type='sections')
12 print('1--配置文件中所有节(sections):')
13 print(sections)
14 print('----------------------------------------')
15 # 获取配置文件[section1]中所有键值对
16 params = self.get_config(cnf_type='items', section='section1')
17 print('3--[section1]中所有的键值对(items):')
18 print(params)
19 print('----------------------------------------')
20 # 获取配置文件[section1]中所有键
21 names = self.get_config(cnf_type='options', section='section1')
22 print('2--[section1]中所有的键(options):')
23 print(names)
24 print('----------------------------------------')
25 # 获取配置文件[section1]中option1_1的值
26 value1_1 = self.get_config(cnf_type='value', section='section1', option='option1_1')
27 print('4--[section1]中option1_1的值:')
28 print(type(value1_1))
29 print(value1_1)
30 print('----------------------------------------')
31 # 获取配置文件[section2]中option1的值,int
32 value2_1 = self.get_config(cnf_type='value_int', section='section2', option='option2_1')
33 print('5--[section2]中option2_1的值:')
34 print(type(value2_1))
35 print(value2_1)
36
37
38 c = TestConfigparser()
39 c.test_config_parser()
控制台结果: