1、具有继承基类的类创建实例时构造和析构的顺序:父类构造->子类构造->子类析构->父类析构
2、继承方式:
- 公有继承:class A:public B
- 保护继承:class A:protected B
- 私有继承:class A:private B
3、覆盖和隐藏
隐藏:
- 子类通过重写父类的同名函数,以达到隐藏父类同名函数的效果;当然,我们继承父类,父类中同名函数仍旧被继承过来的,可以通过super.XXX来访问父类中被隐藏的同函数;三个关键字:父子关系、同名函数、隐藏
- 子类的实例对象调用父类被隐藏的同名函数:实例对象名.父类名::同名函数
- 当子类中有同名不同参数的函数时,子类的实例对象是不能够直接调用父类中的同名函数的,只能够进行隐藏
- 当子类有同名数据成员,同样是做隐藏,要想在子类中访问到父类的同名数据成员,我们需要使用父类名::数据成员名
is-a:
- 基类和派生类的一种关系(车是基类,自行车是派生类,此时自行车is-a车,即自行车是车的一种)
- 可以将一个派生类的对象赋给一个基类对象,但是不能够反过来

1 int main(){
2 Soldier s1;
3 Person p1 = s1;
4 Person *p2 = &s1;
5
6 s1 = p1;//非法的
7 Soldier *s2 = &p1;//非法的
8 return 0;
9 }
- 一个被调用函数的参数可以传入对于的基类或子类对象,很灵活

1 fun1(Person &p){
2 ...
3 }
4
5 fun2(Person *p){
6 ...
7 }
8 int main(){
9 Person p1;
10 Soldier s1;
11 fun1(p1),fun2(&p1);
12 fun1(s1),fun2(&s1);
13 return 0;
14 }
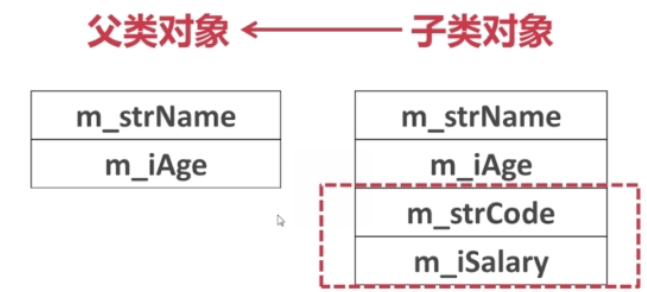
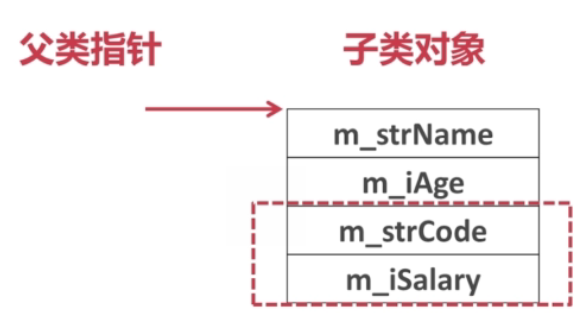
- 存储结构:用子类对象初始化父类对象的情况,此时子类对象会退化,父类对象是不能够访问到子类对象特有的成员的;当用子类对象初始化父类指针时,也是一样的
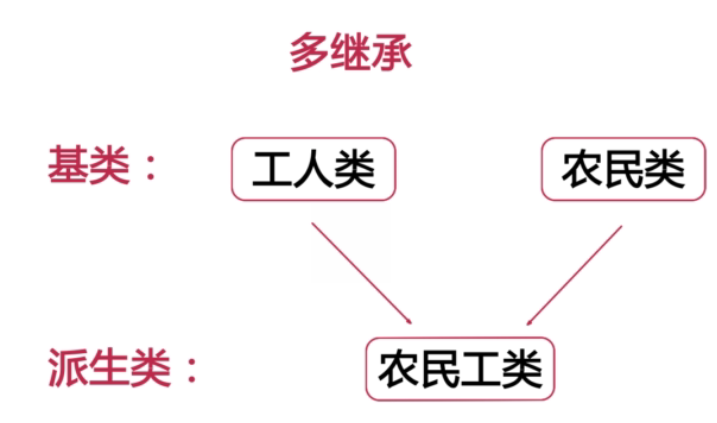
4.多继承和多重继承
- 多重继承:子类和直接父类或间接父类保持is-a的关系

- 多继承:

#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
/**
* 定义工人类: Worker
* 数据成员: m_strName
* 成员函数: work()
*/
class Worker
{
public:
Worker(string name)
{
m_strName = name;
cout << "Worker" << endl;
}
~Worker()
{
cout << "~Worker" << endl;
}
void work()
{
cout << m_strName << endl;
cout << "work" << endl;
}
protected:
string m_strName;
};
/**
* 定义儿童类: Children
* 数据成员: m_iAge
* 成员函数: play()
*/
class Children
{
public:
Children(int age)
{
m_iAge = age;
cout << "Children" << endl;
}
~Children()
{
cout << "~Children" << endl;
}
void play()
{
cout << m_iAge << endl;
cout << "play" << endl;
}
protected:
int m_iAge;
};
/**
* 定义童工类: ChildLabourer
* 公有继承工人类和儿童类
*/
class ChildLabourer : public Worker,public Children
{
public:
ChildLabourer(string name, int age):Worker(name),Children(age)
{
cout << "ChildLabourer" << endl;
}
~ChildLabourer()
{
cout << "~ChildLabourer" << endl;
}
};
int main(void)
{
// 使用new关键字创建童工类对象
ChildLabourer *childLabourer = new ChildLabourer("haha",8);
// 通过童工对象调用父类的work()和play()方法
childLabourer->work();
childLabourer->play();
// 释放
delete childLabourer;
childLabourer=NULL;
return 0;
}
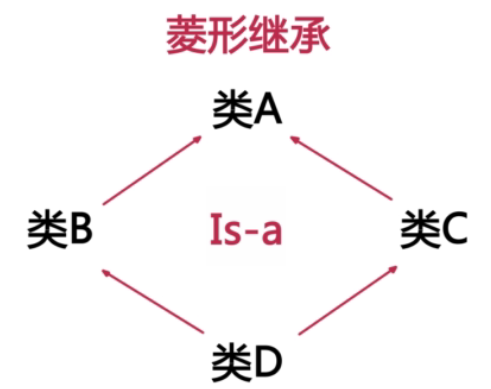
5.虚继承
- 问题引入:菱形继承的困扰,导致A类被构造出多个,系统产生了必要的开销;如何解决这种问题,我们需要用到虚拟继承,保证基类中的数据只保留一份,基类无法保存从子类传入的数据,只是使用默认的参数
- 关键字:virtual

1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <stdlib.h>
3 #include <string>
4 using namespace std;
5
6 /**
7 * 定义人类: Person
8 */
9 class Person
10 {
11 public:
12 Person()
13 {
14 cout << "Person" << endl;
15 }
16 ~Person()
17 {
18 cout << "~Person" << endl;
19 }
20 void eat()
21 {
22 cout << "eat" << endl;
23 }
24
25 };
26
27 /**
28 * 定义工人类: Worker
29 * 虚继承人类
30 */
31 class Worker : virtual public Person
32 {
33 public:
34 Worker(string name)
35 {
36 m_strName = name;
37 cout << "Worker" << endl;
38 }
39 ~Worker()
40 {
41 cout << "~Worker" << endl;
42 }
43 void work()
44 {
45 cout << m_strName << endl;
46 cout << "work" << endl;
47 }
48 protected:
49 string m_strName;
50 };
51
52 /**
53 * 定义儿童类:Children
54 * 虚继承人类
55 */
56 class Children : virtual public Person
57 {
58 public:
59 Children(int age)
60 {
61 m_iAge = age;
62 cout << "Children" << endl;
63 }
64 ~Children()
65 {
66 cout << "~Children" << endl;
67 }
68 void play()
69 {
70 cout << m_iAge << endl;
71 cout << "play" << endl;
72 }
73 protected:
74 int m_iAge;
75 };
76
77 /**
78 * 定义童工类:ChildLabourer
79 * 公有继承工人类和儿童类
80 */
81 class ChildLabourer:public Worker,public Children
82 {
83 public:
84 ChildLabourer(string name, int age):Worker(name),Children(age)
85 {
86 cout << "ChildLabourer" << endl;
87 }
88
89 ~ChildLabourer()
90 {
91 cout << "~ChildLabourer" << endl;
92 }
93 };
94
95 int main(void)
96 {
97 // 用new关键字实例化童工类对象
98 ChildLabourer *p = new ChildLabourer("haha",8);
99 // 调用童工类对象各方法。
100 p->eat();
101 p->work();
102 p->play();
103 delete p;
104 p = NULL;
105
106 return 0;
107 }
108 /*结果:Person
109 Worker
110 Children
111 ChildLabourer
112 eat
113 haha
114 work
115 8
116 play
117 ~ChildLabourer
118 ~Children
119 ~Worker
120 ~Person*/
