import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np ''' 初始化运算图,它包含了上节提到的各个运算单元,它将为W,x,b,h构造运算部件,并将它们连接 起来 ''' graph = tf.Graph() #一次tensorflow代码的运行都要初始化一个session session = tf.InteractiveSession(graph=graph) ''' 我们定义三种变量,一种叫placeholder,它对应输入变量,也就是上节计算图所示的圆圈部分, 他们的值在计算开始进行时才确定,这里对应x; 一种叫Variables,他们的值一开始就初始化,在后续运算中可以进行更改,这里对应W,b; 一种叫immutable tensor,这里对应h,它的值不允许我们直接修改 ''' x = tf.placeholder(shape=[1, 10], dtype=tf.float32, name='x') #将W的各个分量初始化到[-0.1, 0.1]之间 W = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform(shape=[10,5], minval=-0.1, maxval=0.1, dtype=tf.float32), name='W') #把b的各个分量初始化为0 b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros(shape=[5], dtype=tf.float32), name='b') h = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.matmul(x, W) + b)
#使用run为各个变量分配内存并执行初始化操作 tf.global_variables_initializer().run() h_eval = session.run(h, feed_dict={x: np.random.rand(1,10)}) #结束时一定要关闭session session.close()
''' 先启动运算图和session ''' graph = tf.Graph() session = tf.InteractiveSession(graph = graph) #将要读入文件名存储在一个队列中 filenames = ['test%d.txt' %i for i in range(1,4)] #下面建立一个输入管道 filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(filenames, capacity = 3, shuffle = True, name = 'string_input_procucer') for f in filenames: if not tf.gfile.Exists(f): raise ValueError('Failed to find file: ' + f) else: print('File %s found.' %f) #构建reader将数据全部读入,tensorflow提供多种reader让我们读入不同格式数据 reader = tf.TextLineReader() ''' 调用reader.read读入数据,它一次读入一行,read返回数据结构(key, value),其中key对应读入数据的 文件名,value对应读入的一行数据 ''' key, value = reader.read(filename_queue, name='text_read_op') ''' 使用decoder将读入数据解码成指定数据结构,这里我们把读入的一行数据分解成多个数据列,由于每行包含 10个数字,因此对应10个数据列,因为一个文本包含5行数据,三个文本总共包含15行,因此一列数据包含 15个数字 ''' record_defaults = [[-1.0],[-1.0],[-1.0],[-1.0],[-1.0],[-1.0], [-1.0],[-1.0],[-1.0],[-1.0],] col1, col2, col3, col4, col5, col6, col7, col8, col9, col10 = tf.decode_csv(value, record_defaults = record_defaults) #把数据列合在一起形成二维向量 features = tf.stack([col1,col2,col3,col4,col5,col6,col7,col8,col9,col10]) ''' 在训练网络时,我们往往需要很多训练数据,当数据量庞大时,一次将数据全部读入内存是不现实的, 因此我们需要开辟一片缓存,然后将数据分批读入,capacity表示缓存最多能读入几条数据, batch_size表示一次将相应条数据进行读取处理, min_after_dequeue表示缓存中至少要读入几条数据,num_threads表示使用几个线程进行操作 ''' x = tf.train.shuffle_batch([features], batch_size=3, capacity=5, name='data_batch', min_after_dequeue=1, num_threads = 1) #启动输入管道的运行流程 ''' 由于数据读入和预处理是一种非常耗时的工作,tensorflow会创建多个线程同时对数据进行读取和处理, coord对应所有处理线程的管理器,start_queue_runners则启动所有处理线程 ''' coord = tf.train.Coordinator() threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(coord=coord, sess=session) W = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform(shape=[10,5], minval=-0.1, maxval=0.1, dtype=tf.float32), name = 'W') b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros(shape=[5], dtype=tf.float32), name='b') h = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.matmul(x, W) + b) tf.global_variables_initializer().run() for step in range(5): x_eval, h_eval = session.run([x, h]) print('====step %d ====' %step) print('Evaluated data (x)') print(x_eval) print('Evaluated data (h)') print(h_eval) print('') #终止数据管道线程 coord.request_stop() coord.join(threads) session.close()
def print_tensor(tensor): init = tf.global_variables_initializer() with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init) v = sess.run(tensor) print(v) # will show you your variable.
ref = tf.Variable(tf.constant([1,9,3,10,5], dtype=tf.float32), name='scatter_value') indices = [1,3] updates = tf.constant([2,4], dtype = tf.float32) tf_scatter_update = tf.scatter_update(ref, indices, updates, use_locking=None, name=None) print_tensor(tf_scatter_update)
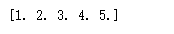
''' 下面代码要构造一个4*3的二维向量,同时指定把updates变量对应的一维向量安置到indices指定位置, 也就是把[1,1,1]作为4*3二维向量的第1行,把[2,2,2]作为4*3向量的第3行,其他行自动初始化为0, ''' indices=[[1], [3]] updates = tf.constant([[1,1,1], [2,2,2]]) shape = [4,3] tf_scatter_nd_1 = tf.scatter_nd(indices, updates, shape, name=None) print_tensor(tf_scatter_nd_1)
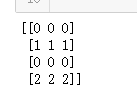
''' 构造一个4*3二维向量,然后把数值2插入到第1行第0列, 把数值1插入到第3行第2列,其他值初始化为0 ''' indices = [[1,0], [3,2]] updates = tf.constant([2,1]) shape = [4,3] tf_scatter_nd_2 = tf.scatter_nd(indices, updates, shape, name=None) print_tensor(tf_scatter_nd_2)
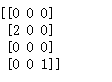
''' 下面代码把向量[1,2,3,4,5]中下标为1,4的分量提取出来,因此得到向量 [2,5] ''' params = tf.constant([1,2,3,4,5], dtype=tf.float32) indices = [1,4] tf_gather = tf.gather(params, indices, validate_indices = True, name = None) print_tensor(tf_gather)

''' 把二维向量中指定行提取出来 ''' params = tf.constant([[0,0,0], [1,1,1], [2,2,2],[3,3,3]]) indices = [[0], [2]] tf_gather_nd = tf.gather_nd(params, indices, name=None) print_tensor(tf_gather_nd)

''' 构造一个4*4二维矩阵模拟图片 ''' x = tf.constant([[ [[1], [2], [3], [4]], [[4], [3], [2], [1]], [[5], [6], [7], [8]], [[8], [7], [6], [5]] ]], dtype=tf.float32) #定义用于做卷积操作的小矩阵 x_filter = tf.constant([ [[[0.5]], [[1]]], [[[0.5]], [[1]]] ], dtype = tf.float32) ''' 把大矩阵切割成2*2小矩阵,然后与上面定义矩阵做乘机, 然后每次向右或向下平移一个单位后再做对应小矩阵的乘机运算 ''' #定义一次平移距离,四个分量分别为batch_stride,height_stride,width_stride,channles_stride] x_strides = [1,1,1,1] x_padding = 'VALID' x_conv = tf.nn.conv2d(input = x, filter = x_filter, strides = x_strides, padding = x_padding) print_tensor(x_conv)

x = tf.constant([[ [[1], [2], [3], [4]], [[4], [3], [2], [1]], [[5], [6], [7], [8]], [[8], [7], [5], [6]] ]], dtype = tf.float32) ''' 把矩阵分割成2*2小矩阵 ''' x_ksize = [1, 2, 2 ,1] #做max pooling 时每次沿水平和竖直方向挪动2个单位 x_stride = [1, 2, 2, 1] x_padding = 'VALID' x_pool = tf.nn.max_pool(value = x, ksize = x_ksize, strides = x_stride, padding = x_padding) print_tensor(x_pool)

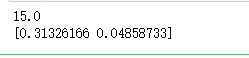
''' 和方差: MSE = (1^2 + 2^2 + 3^2 + 4^2) / 4 = 15 ''' x = tf.constant([[1,2], [3,4]], dtype = tf.float32) mse = tf.nn.l2_loss(x) print_tensor(mse) ''' cross entropy H = -y*log(y') - (1-y)*log(1-y') ''' y = tf.constant([[1,0],[0,1]], dtype = tf.float32) y_hat = tf.constant([[3,2], [2,5]], dtype = tf.float32) H = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2(logits = y_hat, labels = y) print_tensor(H)
''' 使用梯度下降法对函数y=x^2求最小值,设置学习率为0.1 ''' x = tf.Variable(tf.constant(2.0, dtype=tf.float32), name = 'x') y = x ** 2 minimize_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01).minimize(y) init = tf.global_variables_initializer() with tf.Session() as session: session.run(init) for i in range(1000): session.run(minimize_op) print("step: ", i, " x: ", session.run(x), " y: ", session.run(y))
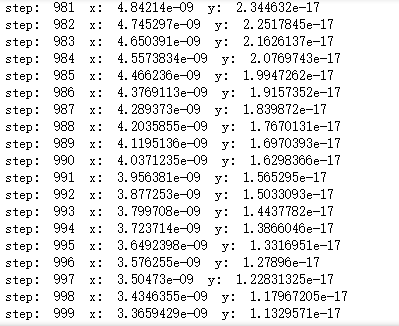
import tensorflow as tf ''' 首先将x 初始化为1,然后有两条语句,第一条作用是实现 x = x + 3, 第二条作用是实现 z = x * 4, 如果是串行执行,那么执行第一句后x变成4,执行第二句后z变成16,但tensorflow并不串行执行, 所以最终得到结果与上面预想不同 ''' x = tf.Variable(tf.constant(1.0), name = 'x') x_assign = tf.assign(x, x+3) z = x*4 init = tf.global_variables_initializer() with tf.Session() as session: session.run(init) print('z = ', session.run(z)) print('x = ', session.run(x))
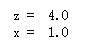
import tensorflow as tf ''' 让x = x + 3 与 z = x * 4串行执行 ''' x = tf.Variable(tf.constant(1.0), name = 'x') init = tf.global_variables_initializer() with tf.Session() as session: session.run(init) with tf.control_dependencies([tf.assign(x, x+4)]): z = x * 4 print('z = ', session.run(z)) print('x = ', session.run(x))

def simple_computation(w): x = tf.Variable(tf.constant(2.0, shape = None, dtype = tf.float32), name = 'simple_computation_x') y = tf.Variable(tf.constant(3.0, shape = None, dtype = tf.float32), name = 'simple_computation_y') z = x * 2 + y**3 return z with tf.Session() as session: z = simple_computation(2) init = tf.global_variables_initializer() session.run(init) res = session.run(z) print('simple computation result : ', res)
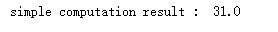
with tf.Session() as session: for i in range(10): z = simple_computation(2) init = tf.global_variables_initializer() session.run(init) res = session.run(z) for n in tf.get_default_graph().as_graph_def().node: if "simple_computation_x" in n.name: print(n.name)

import tensorflow as tf def simple_computation_reuse1(w): #把tf.Variable换成tf.get_variable x = tf.get_variable('x', initializer = tf.constant(1.0, shape = None, dtype = tf.float32)) y = tf.get_variable('y', initializer = tf.constant(2.0, shape = None, dtype = tf.float32)) z = x * w + y**2 return z def simple_computation_reuse2(w): ''' 变量重用时初始化方式必须一致,例如上面变量x初始化值是1.0,重用时它的初始哈值也必须是1.0 ''' x = tf.get_variable('x', initializer = tf.constant(1.0, shape = None, dtype = tf.float32)) y = tf.get_variable('y', initializer = tf.constant(2.0, shape = None, dtype = tf.float32)) z = w*x*y return z
''' 设定一个命名空间,在该空间里给定名字的变量只分配一次内存,我们可以通过变量名多次获取变量内存, 这样可以防止一个变量分配多次内存 ''' with tf.variable_scope('reuse_scope_exampleA', reuse = tf.AUTO_REUSE) as scope: #reuse_scope_exampleA/x,reuse_scope_exampleA/y z1 = simple_computation_reuse1(tf.constant(1.0, dtype = tf.float32)) with tf.variable_scope(scope, reuse = tf.AUTO_REUSE) as scope1: with tf.name_scope(scope1.original_name_scope): #下面调用会重用reuse_scope_exampleA/x,reuse_scope_exampleA/y z2 = simple_computation_reuse2(z1) #再次重用my_reuse_scopeA/x,my_reuse_scopeA/y with tf.variable_scope(scope, reuse = tf.AUTO_REUSE) as scope3: with tf.name_scope(scope3.original_name_scope): zz1 = simple_computation_reuse1(tf.constant(1.0, dtype = tf.float32)) zz2 = simple_computation_reuse2(zz1)
with tf.variable_scope('reuse_scope_exampleB', reuse = tf.AUTO_REUSE): #下面调用创建变量reuse_scope_exampleB/x,reuse_scope_exampleB/y a1 = simple_computation_reuse1(tf.constant(1.0, dtype = tf.float32)) with tf.variable_scope('my_reuse_scopeB/', reuse = tf.AUTO_REUSE): #下面调用重用reuse_scope_exampleB/x, reuse_scope_exampleB/y a2 = simple_computation_reuse2(a1)
with tf.Session() as session: init = tf.global_variables_initializer() session.run(init) res = session.run([z1, z2, z2]) #把含有scope或scopeB的变量打印出,看看他们是否只有一份 for n in tf.get_default_graph().as_graph_def().node: if "reuse_scope_exampleA" in n.name or 'reuse_scope_exampleB' in n.name: print(n.name)

!pip install keras
import tensorflow as tf from keras.datasets import mnist import numpy as np (train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = mnist.load_data() train_num = train_images.shape[0] rows = train_images.shape[1] cols = train_images.shape[2] test_num = test_images.shape[0] train_images = train_images.reshape(train_num, rows * cols) test_images = test_images.reshape(test_num, rows * cols) train_images = (train_images - np.mean(train_images)) / np.std(train_images) test_images = (test_images - np.mean(test_images)) / np.std(test_images)
WEIGHTS = "weights" BIAS = "bias" batch_size = 100 img_width, img_height = 28, 28 input_size = img_width * img_height num_labels = 10 tf.reset_default_graph() #定义接收图片和图片标签的向量 tf_inputs = tf.placeholder(shape=[batch_size, input_size], dtype = tf.float32, name = 'inputs') tf_labels = tf.placeholder(shape=[batch_size, num_labels], dtype = tf.float32, name = 'labels')
''' 我们构建的网络有三层,前两层是全连接层,最后一层含有10个节点,每个节点输出当前图片对应数字的概率 ''' def define_networks(): with tf.variable_scope('layer1'): ''' 第一层网络有500个节点,由于一张图片相当于28*28的二维数组,因此输入层和第一层网络在全连接 情况下,有(28*28 = 784)*500个链路参数,他们对应一个[784, 500]的二维向量 ''' tf.get_variable(WEIGHTS, shape=[input_size, 500], initializer = tf.random_uniform_initializer(0, 0.02)) tf.get_variable(BIAS, shape=[500], initializer = tf.random_uniform_initializer(0, 0.01)) with tf.variable_scope('layer2'): ''' 第二层网络有250个节点,第一层与第二层在全连接情况下有500*250个链路参数,对应[500, 250] 的二维向量 ''' tf.get_variable(WEIGHTS, shape = [500, 250], initializer = tf.random_uniform_initializer(0, 0.02)) tf.get_variable(BIAS, shape = [250], initializer = tf.random_uniform_initializer(0, 0.01)) with tf.variable_scope('layer3'): ''' 第三层只有10个节点,第二层与第三层在全连接情况下有250*10个链路参数,对应[250,10] 的二维向量 ''' tf.get_variable(WEIGHTS, shape = [250, 10], initializer = tf.random_uniform_initializer(0, 0.02)) tf.get_variable(BIAS, shape = [10], initializer = tf.random_uniform_initializer(0, 0.01))
''' 设置网络层的激活函数 ''' def define_activations(x): #第一层使用relu激活函数 with tf.variable_scope('layer1', reuse = tf.AUTO_REUSE): w, b = tf.get_variable(WEIGHTS), tf.get_variable(BIAS) tf_h1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(x, w) + b, name = 'hidden1') with tf.variable_scope('layer2', reuse = tf.AUTO_REUSE): #第二层使用relu激活函数 w, b = tf.get_variable(WEIGHTS), tf.get_variable(BIAS) tf_h2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(tf_h1, w) + b, name = 'hidden2') with tf.variable_scope('layer3', reuse = tf.AUTO_REUSE): #第三层使用先不使用激活,直接把结果输出 w, b = tf.get_variable(WEIGHTS), tf.get_variable(BIAS) tf_logits = tf.nn.bias_add(tf.matmul(tf_h2, w), b, name = 'logits') return tf_logits
define_networks() logits = define_activations(tf_inputs) #定义损失函数 softmax = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2(logits = logits, labels = tf_labels) tf_loss = tf.reduce_mean(softmax) #使用梯度下降法调整网络参数 tf_loss_minimize = tf.train.MomentumOptimizer(momentum=0.9, learning_rate = 0.01).minimize(tf_loss) #定义网络对输入图片的判断结果 tf_predictions = tf.nn.softmax(define_activations(tf_inputs))
#启动训练流程 session = tf.InteractiveSession() tf.global_variables_initializer().run() NUM_EPOCHS = 50 def accuracy(predictions, labels): #统计判断结果的准确率 return np.sum(np.argmax(predictions, axis = 1).flatten() == labels.flatten()) / batch_size test_accuracy_over_time = [] train_loss_over_time = [] for epoch in range(NUM_EPOCHS): train_loss = [] for step in range(train_images.shape[0] // batch_size): #将标签转换为One-hot-vector labels_one_hot = np.zeros((batch_size, num_labels), dtype = np.float32) labels_one_hot[np.arange(batch_size), train_labels[step*batch_size: (step+1)*batch_size]] = 1.0 if epoch == 0 and step == 0: print('one hot labels:') print(labels_one_hot[:10]) print() #执行训练流程 loss, _ = session.run([tf_loss, tf_loss_minimize], feed_dict = { tf_inputs: train_images[step*batch_size : (step+1)*batch_size, :], tf_labels: labels_one_hot }) train_loss.append(loss) test_accuracy = [] #测试网络训练效果 for step in range(test_images.shape[0] // batch_size): test_predictions = session.run(tf_predictions , feed_dict = {tf_inputs: test_images[step*batch_size : (step+1)*batch_size, :]}) batch_test_accuracy = accuracy(test_predictions, test_labels[step*batch_size: (step+1)*batch_size]) test_accuracy.append(batch_test_accuracy) print("Average train loss for the %d epoch: %.3f " % (epoch+1, np.mean(train_loss))) train_loss_over_time.append(np.mean(train_loss)) print(' Average test accuracy for the %d epoch: %.2f ' % (epoch+1, np.mean(test_accuracy) * 100.0)) test_accuracy_over_time.append(np.mean(test_accuracy)*100) session.close()


import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x_axis = np.arange(len(train_loss_over_time)) fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2) fig.set_size_inches(w=25,h=5) ax[0].plot(x_axis, train_loss_over_time) ax[0].set_xlabel('Epochs',fontsize=18) ax[0].set_ylabel('Average train loss',fontsize=18) ax[0].set_title('Training Loss over Time',fontsize=20) ax[1].plot(x_axis, test_accuracy_over_time) ax[1].set_xlabel('Epochs',fontsize=18) ax[1].set_ylabel('Test accuracy',fontsize=18) ax[1].set_title('Test Accuracy over Time',fontsize=20) fig.savefig('mnist_stats.jpg')
