一、if条件语句的知识与实践
1.if条件语句语法(单分支结构)
第一种:
if < 条件表达式 >
then
指令
fi
第二种:
if < 条件表达式 >; then
指令
fi

嵌套:
if < 条件表达式 >
then
if < 条件表达式 >
then
指令
fi
fi
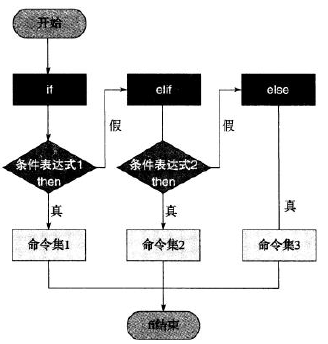
2.多分支结构
if < 条件表达式 >
then
指令
else
指令
fi

if < 条件表达式 >
then
指令
elif < 条件表达式 >
then
指令
else
指令
fi
3.单分支实践
(1)把下面的测试文件中条件表达式语句改成if条件语句
[root@codis-178 ~]# [ -f /etc/hosts ] && echo 1
1
[root@codis-178 ~]# [[ -f /etc/hosts ]] && echo 1
1
[root@codis-178 ~]# test -f /etc/hosts && echo 1
1
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat 7_1.sh
#!/bin/bash
if [ -f /etc/hosts ]
then
echo 1
fi
if [[ -f /etc/hosts ]]
then
echo 1
fi
if test -f /etc/hosts
then
echo 1
fi
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh 7_1.sh
1
1
1
(2)判断系统剩余内存大小,若低于100MB。就邮件报警,并将脚本加入定时任务,每3分钟执行一次检查。
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat 7_2.sh
#!/bin/bash
FreeMem=`free -m|awk 'NR==3 {print $NF}'`
CHARS="Current memory is $FreeMem"
if [ $FreeMem -lt 100 ]
then
echo $CHARS|tee /tmp/messages.txt
mail -s "`date +%F-%T`$CHARS" test@oldboy.com < /tmp/messages.txt
fi
加入crontab中
# monitor sys mem at 20170802 by xiaoda
*/3 * * * * /bin/sh /data/cron/7_2.sh &>/dev/null
(3)实现整数大小的比较
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat 7_3.sh
#!/bin/bash
read -p "pls input two num:" a b
if [ $a -lt $b ];then
echo "$a < $b"
elif [ $a -gt $b ];then
echo "$a > $b"
elif [ $a -eq $b ];then
echo "$a = $b"
else
echo "Input error"
fi
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh 7_3.sh
pls input two num: 5 6
5 < 6
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh 7_3.sh
pls input two num: 8 4
8 > 4
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh 7_3.sh
pls input two num: 5 5
5 = 5
二、企业案例
1.监控Web和数据库之分析问题

2.监控方法
本地端口监控
netstat -lnt|grep 3306|awk -F "[ :]+" '{print $5}'
netstat -lntup|grep 3306 |wc -l
netstat -lntup|grep mysql|wc -l
lsof -i tcp:3306|wc -l
远程端口监控
nmap 127.0.0.1 -p 3306 |grep open |wc -l
nc -w 2 127.0.0.1 3306 &>/dev/null
服务进程或进程数监控
ps -ef|grep mysql|grep -v grep|wc -l
客户端模拟用户访问
[root@codis-178 ~]# wget --spider --timeout=10 --tries=2 www.baidu.com
Spider mode enabled. Check if remote file exists.
--2017-08-02 13:55:10-- http://www.baidu.com/
Resolving www.baidu.com... 61.135.169.125, 61.135.169.121
Connecting to www.baidu.com|61.135.169.125|:80... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 277 [text/html]
Remote file exists and could contain further links,
but recursion is disabled -- not retrieving.
curl -s http://www.baidu.com
3.开发监控MySQL数据库的脚本
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat 7_4.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo method1--------------
if [ `netstat -lnt|grep 3306|awk -F "[ :]+" '{print $5}'` -eq 3306 ]
then
echo "MySQL is Running."
else
echo "MySQL is Stopped."
#/etc/init.d/mysqld start
fi
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh 7_4.sh
method1--------------
MySQL is Running.
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat 7_4_1.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo method2--------------
if [ `netstat -lnt|grep 3306|awk -F "[ :]+" '{print $5}'` = "3306" ]
then
echo "MySQL is Running."
else
echo "MySQL is Stopped."
#/etc/init.d/mysqld start
fi
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh 7_4_1.sh
method2--------------
MySQL is Running.
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat 7_4_2.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo method3--------------
if [ `netstat -lntup|grep mysqld|wc -l` -gt 0 ]
then
echo "MySQL is Running."
else
echo "MySQL is Stopped."
#/etc/init.d/mysqld start
fi
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh 7_4_2.sh
method3--------------
MySQL is Running.
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat 7_4_3.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo method4--------------
if [ `lsof -i tcp:3306|wc -l` -gt 0 ]
then
echo "MySQL is Running."
else
echo "MySQL is Stopped."
#/etc/init.d/mysqld start
fi
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh 7_4_3.sh
method4--------------
MySQL is Running.
4.监控Nginx Web服务异常
[root@codis-178 ~]# netstat -lnt|grep -w 8081|awk -F "[ :]+" '{print $5}'
8081
[root@codis-178 ~]# netstat -lntup|grep -w 8081|wc -l
1
[root@codis-178 ~]# lsof -i tcp:8081|wc -l
4
[root@codis-178 ~]# ps -ef |grep nginx|grep -v grep|wc -l
3
[root@codis-178 ~]# ps -C nginx --no-header
10869 ? 00:00:00 nginx
10870 ? 00:10:55 nginx
10871 ? 00:07:43 nginx
[root@codis-178 ~]# ps -C nginx --no-header|wc -l
3
5.开发监控Nginx Web服务的脚本
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat 7_5.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo http method1---------------
if [ `netstat -lnt|grep 8081|awk -F "[ :]+" '{print $5}'` -eq 8081 ]
then
echo "Nginx is Running."
else
echo "Nginx is Stoped."
fi
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh 7_5.sh
http method1---------------
Nginx is Running.
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat 7_5_1.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo http method1---------------
if [ `netstat -lnt|grep 8081|awk -F "[ :]+" '{print $5}'` = "8081" ]
then
echo "Nginx is Running."
else
echo "Nginx is Stoped."
fi
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh 7_5_1.sh
http method1---------------
Nginx is Running.
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat 7_5_2.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo http method2---------------
if [ `netstat -lntup|grep nginx|wc -l` -gt 0 ]
then
echo "Nginx is Running."
else
echo "Nginx is Stoped."
fi
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh 7_5_2.sh
http method2---------------
Nginx is Running.
三、经典案例
1.比较两个整数
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat 7_6.sh
#!/bin/bash
read -p "pls input two num:" a b
expr $a + 10 &>/dev/null
RETVAL1=$?
expr $b + 10 &>/dev/null
RETVAL2=$?
if [ -z "$a" ] || [ -z "$b" ]
then
echo "Pls input two num agin."
exit 1
elif test $RETVAL1 -ne 0 -o $RETVAL2 -ne 0
then
echo "Pls input two "num" again."
exit 2
elif [ $a -lt $b ]
then
echo "$a < $b"
elif [ $a -eq $b ]
then
echo "$a = $b"
else
echo "$a > $b"
fi
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh 7_6.sh
pls input two num: 6 9
6 < 9
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh 7_6.sh
pls input two num: 8 2
8 > 2
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh 7_6.sh
pls input two num: 7 7
7 = 7
2.判断字符串是否为数字
思路1:删除字符串中的所有数字,看长度是否为0
[root@codis-178 ~]# [ -n "`echo oldboy123|sed 's/[0-9]//g'`" ] && echo char ||echo int
char
[root@codis-178 ~]# [ -n "`echo 123|sed 's/[0-9]//g'`" ] && echo char ||echo int
int
[root@codis-178 ~]# [ -z "`echo 123|sed 's/[0-9]//g'`" ] && echo char ||echo int
char
[root@codis-178 ~]# [ -z "`echo 123|sed 's/[0-9]//g'`" ] && echo int ||echo char
int
[root@codis-178 ~]# [ -z "`echo oldboy123|sed 's/[0-9]//g'`" ] && echo int ||echo char
char
思路2:如果num的长度不为0,并且把num中的非数字部分删除,然后再看结果是不是等于num本身,如果两者都成立,则num是数字
[root@codis-178 ~]# num=521
[root@codis-178 ~]# [ -n "$num" -a "$num" = "${num//[^0-9]/}" ] && echo "it is num"
it is num
[root@codis-178 ~]# num=oldboy521
[root@codis-178 ~]# [ -n "$num" -a "$num" = "${num//[^0-9]/}" ] && echo "it is num"
[root@codis-178 ~]#
思路3:通过expr计算判断
[root@codis-178 ~]# expr pldboy + 1 &>/dev/null
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $?
2
[root@codis-178 ~]# expr 123 + 1 &>/dev/null
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $?
0
[root@codis-178 ~]# expr 0 + 0 &>/dev/null
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $?
1
思路4:利用“=~”符号判断
[root@codis-178 ~]# [[ oldboy123 =~ ^[0-9]+$ ]] && echo int ||echo char
char
[root@codis-178 ~]# [[ 123 =~ ^[0-9]+$ ]] && echo int ||echo char
int
3.判断字符串长度是否为0
思路1:使用-z和-n的语法
[root@codis-178 ~]# [ -z "oldboy" ] && echo 1 ||echo 0
0
[root@codis-178 ~]# [ -n "oldboy" ] && echo 1 ||echo 0
1
思路2:使用变量子串判断
[root@codis-178 ~]# [ ${#char} -eq 0 ] && echo 1 ||echo 0
0
思路3:使用expr length函数判断
[root@codis-178 ~]# [ `expr length "oldboy"` -eq 0 ] && echo 1 || echo 0
0
思路4:使用wc的-L参数统计
[root@codis-178 ~]# [ `echo oldboy|wc -L` -eq 0 ] && echo 1 ||echo 0
0
思路5:使用awk length函数判断
[root@codis-178 ~]# [ `echo oldboy|awk '{print length}'` -eq 0 ] && echo 1 || echo 0
0
4.生产场景案例
(1)监控memcached服务
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat memcached.sh
#!/bin/bash
printf "del key
"|nc 127.0.0.1 11211 &>/dev/null
printf "set key 0 0 10
oldboy1234
"|nc 127.0.0.1 11211 &>/dev/null
McValues=`printf "get key
" |nc 127.0.0.1 11211|grep oldboy1234|wc -l`
if [ $McVaules -eq 1 ]
then
echo "memcached status is ok."
else
echo "memcached status is bad."
fi
思考题:如何监控MC服务、命中率、响应时间三个指标
(2)开发rsync启动脚本
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat rsyncd
#!/bin/bash
# chkconfig: 2345 20 80
# description: Rsyncd Startup script by xiaoda
if [ $# -ne 1 ]
then
echo $"usage:$0 {start|stop|restart}"
exit 1
fi
if [ "$1" = "start" ]
then
rsync --daemon
sleep 2
if [ `netstat -lntip|grep rsync|wc -l` -ge 1 ]
then
echo "rsyncd is started."
exit 0
fi
elif [ "$1" = "stop" ]
then
killall rsync &>/dev/null
sleep 2
if [ `netstat -lntip|grep rsync|wc -l` -eq 0 ]
then
echo "rsyncd is stoped."
exit 0
fi
elif [ "$1" = "restart" ]
then
killall rsync
sleep 1
killpro=`netstat -lntup|grep rsync |wc -l`
rsync --daemon
sleep 1
startpro=`netstat -lntup|grep rsync |wc -l`
if [ $killpro -eq 0 -a $startpro -ge 1 ]
then
echo "rsync is restarted."
exit 0
fi
else
echo $"usage:$0 {start|stop|restart}"
exit 1
fi
运行结果:
[root@codis-178 ~]# /etc/init.d/rsyncd stop
rsyncd is stoped.
[root@codis-178 ~]# netstat -lntup |grep 873
[root@codis-178 ~]# /etc/init.d/rsyncd start
[root@codis-178 ~]# netstat -lntup |grep 873
tcp 0 0 192.168.1.178:873 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 13878/rsync