1、域属性注入
创建实体类Student
package com.spring.entity; public class Student { //普通属性 private Integer id; private String name; //域属性 private Car car; public Car getCar() { return car; } public void setCar(Car car) { this.car = car; } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
创建实体类Car类
package com.spring.entity; public class Car { private String type;//汽车的类型 private String color;//汽车的颜色 public String getType() { return type; } public void setType(String type) { this.type = type; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } }
(1)byType
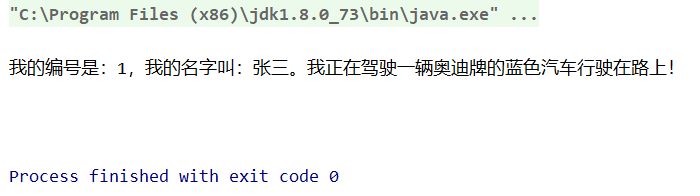
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--使用域属性注入,byType方式--> <bean id="car" class="com.spring.entity.Car"> <property name="color" value="蓝色"></property> <property name="type" value="奥迪"></property> </bean> <!--在Student中装配 autowire:所对应的方式--> <bean id="student" class="com.spring.entity.Student" autowire="byType"> <property name="name" value="张三"></property> <property name="id" value="1"></property> </bean> </beans>
运行结果如下
(2)byName
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--byName方式:要求Car类的id和Student类中的域属性Car对象的对象名一致--> <bean id="car" class="com.spring.entity.Car"> <property name="color" value="红色"></property> <property name="type" value="奔驰"></property> </bean> <bean id="student" class="com.spring.entity.Student" autowire="byName"> <property name="name" value="李四"></property> <property name="id" value="2"></property> </bean> </beans>
运行结果如下

2、数组属性
定义实体类DITest
package com.spring.entity; import java.util.*; public class DITest { //定义String类型数组 private String[] arrays; //定义一个List集合 private List<Integer> lists; //定义一个Set集合 private Set<String> sets; //定义一个Map集合 private Map<String,Object> maps; //配置 private Properties properties; @Override public String toString() { return "DITest{" + "arrays=" + Arrays.toString(arrays) + ", lists=" + lists + ", sets=" + sets + ", maps=" + maps + ", properties=" + properties + '}'; } public String[] getArrays() { return arrays; } public void setArrays(String[] arrays) { this.arrays = arrays; } public List<Integer> getLists() { return lists; } public void setLists(List<Integer> lists) { this.lists = lists; } public Set<String> getSets() { return sets; } public void setSets(Set<String> sets) { this.sets = sets; } public Map<String, Object> getMaps() { return maps; } public void setMaps(Map<String, Object> maps) { this.maps = maps; } public Properties getProperties() { return properties; } public void setProperties(Properties properties) { this.properties = properties; } }
定义相对应的applicationContextDITest.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <bean id="dITest" class="com.spring.entity.DITest"> <!--数组属性--> <property name="arrays"> <!--String集合--> <array> <value>王楠</value> <value>郑楠</value> <value>史志慧</value> </array> </property> <!--list数组--> <property name="lists"> <list> <value>16</value> <value>19</value> <value>18</value> </list> </property> <!--set数组--> <property name="sets"> <set> <value>吃饭</value> <value>睡觉</value> <value>打豆豆</value> </set> </property> <!--map集合--> <property name="maps"> <map> <entry key="name" value="陈晨"></entry> <entry key="age" value="18"></entry> </map> </property> <!--properties--> <property name="properties"> <props> <prop key="jdbc.driver">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</prop> <prop key="jdbc.username">root</prop> </props> </property> </bean> </beans>
Test测试类对应如下
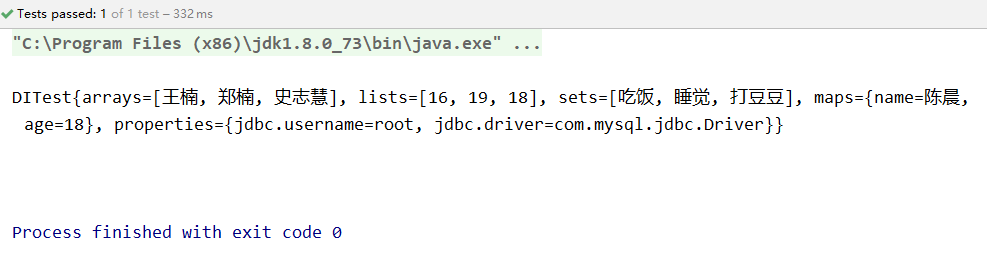
package com.spring.test; import com.spring.entity.DITest; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Idtest { @Test public void say(){ ApplicationContext cxt=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContextDITest.xml"); DITest dITest = (DITest) cxt.getBean("dITest"); System.out.println(dITest.toString()); } }
运行结果如下
3、静态代理
(1)什么是静态代理:
说白了,就是创建一个给程序调用的类(代理类),然后用代理类去吊原始对象
(2)对应的案例
创建抽象类Subject并定义其方法
package com.spring.Subject; /** * 抽象类:真实业务接口 */ public interface Subject { public void doSome(); }
创建Subject实现类RealSubject
package com.spring.Subject.impl; import com.spring.Subject.Subject; /** * 真实主题:将业务代码封装到此主题中 */ public class RealSubject implements Subject { @Override public void doSome() { System.out.println("=============真实业务============"); } }
创建中间类ProxySubject
package com.spring.ProxySubject; import com.spring.Subject.Subject; import com.spring.Subject.impl.RealSubject; /** * 代理主题:代理类 生成真实主体对象,调用真实主题的方法 * 程序就不用直接去创建真实主题了,直接调用代理对象 * * * * 静态代理:说白了,就是创建一个给程序调用的类(代理类),然后用代理类去吊原始对象 */ public class ProxySubject implements Subject { //真实主题 private Subject subject=new RealSubject(); @Override public void doSome() { //AOP思想:增强 System.out.println("前置增强==============="); subject.doSome(); System.out.println("后置增强==============="); } }
Test测试类
package com.spring.ProxyTest; import com.spring.ProxySubject.ProxySubject; public class ProxyTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //程序调用代理对象 ProxySubject proxySubject=new ProxySubject(); proxySubject.doSome(); } }
运行结果如下

4、JDK动态代理
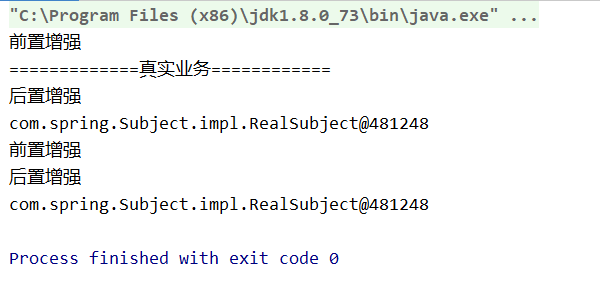
package com.spring.JDK; import com.spring.Subject.Subject; import com.spring.Subject.impl.RealSubject; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; public class JDKTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //JDK动态代理:要求必须有抽象类 //代表的是代理对象 指定对象的原始类型 /** * ClassLoader loader, 类加载器:应该是代理对象的类加载器 * Class<?>[] interfaces, 接口:原始对象实现的接口类型 * InvocationHandler h */ //创建一个原始对象 final Subject subject=new RealSubject(); Subject subjectProxy= (Subject) Proxy.newProxyInstance(subject.getClass().getClassLoader(), subject.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() { /** * * @param proxy 代理对象 * @param method 目标代理方法 * @param args 目标代理方法的参数 * @return * @throws Throwable */ @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { System.out.println("前置增强"); //如何去调用原始对象的业务方法 Object invoke=method.invoke(subject,args); System.out.println("后置增强"); return invoke; } }); subjectProxy.doSome(); System.out.println(subject); System.out.println(subjectProxy); } }
运行结果如下
5、CGLIB动态代理
(1)创建IService类
package com.spring.CGLIB; /** * 业务类 */ public class IService { public void doSome(){ System.out.println("我是实现业务的方法"); } }
(2)创建CGLIBTest类
package com.spring.CGLIB; import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Enhancer; import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor; import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class CGLIBTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //步骤一:目标对象 final IService iService=new IService(); //步骤二:通过CGLIB提供的Enhancer类生成代理 Enhancer enhancer=new Enhancer(); //步骤三:指定需要代理的目标对象模板(将目标对象放入到代理工厂中,生成代理对象) enhancer.setSuperclass(iService.getClass()); //步骤四:实现增强的处理操作 enhancer.setCallback(new MethodInterceptor() { /** * * @param o 目标对象 * @param method 目标对象的方法 * @param objects 目标对象方法内的参数 * @param methodProxy 代理目标对象方法 * @return * @throws Throwable */ @Override public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable { System.out.println("前置"); Object invoke = methodProxy.invoke(iService, objects); System.out.println("后置"); return invoke; } }); //最后一步:创建代理 IService iServiceProxy = (IService) enhancer.create(); iServiceProxy.doSome(); } }
运行结果如下
