我们在 Java 中经常会碰到如何把 InputStream 转换成 String 的情形,比如从文件或网络得到一个 InputStream,需要转换成字符串输出或赋给别的变量。
未真正关注这个问题之前我常用的办法就是按字节一次次读到缓冲区,或是建立 BufferedReader 逐行读取。其实大可不必费此周折,我们可以用 Apache commons IOUtils,或者是 JDK 1.5 后的 Scanner,还可用 Google Guava 库的 CharStreams。到了 JDK7,若要从文件中直接得到字符串还能用 java.nio.file.Files#readAllLines 和 java.nio.file.Files#readAllBytes 方法。
下面看各个例子,为能够实际用运,例子写在 main 方法里,并从文件获得一个 InputStream,代码中把可能要捕获的异常抛出来。再就是注意处理输入输出流时有涉及到字符集,字符集乱了就乱码了,默认字符集是 System.getProperty("file.encoding"),通常我们都用 UTF-8,异常 UnsupportedEncodingException 继承自 IOException。
下面的 6 个方法中应该有一个你能看得上的吧,用 Groovy,Scala 的除外,若未找到一个遂意的,告诉我,你有好办法更应该告诉我。
1. 使用 JDK 5 的 Scanner
package cc.unmi.test;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
*
* @author Unmi
* @Creation date: 2013-02-01
*/
public class Test {
/**
* @param args
* @throws FileNotFoundException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("d:/sample.txt");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(inputStream, "UTF-8");
String text = scanner.useDelimiter("\A").next();
System.out.println(text);
scanner.close();
}
}
2. JDK1.4 及之前的 BufferedReader 法
package cc.unmi.test;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
/**
*
* @author Unmi
* @Creation date: 2013-02-01
*/
public class Test {
/**
* @param args
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("d:/sample.txt");
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));
boolean firstLine = true;
String line = null; ;
while((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null){
if(!firstLine){
stringBuilder.append(System.getProperty("line.separator"));
}else{
firstLine = false;
}
stringBuilder.append(line);
}
System.out.println(stringBuilder.toString());
}
}
中间那些判断是不是第一行来决定是否加换行符是些杂音。
3. JDK1.4 及之前的 readBytes 法
package cc.unmi.test;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
*
* @author Unmi
* @Creation date: 2013-02-01
*/
public class Test {
/**
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("d:/sample.txt");
byte[] buffer = new byte[2048];
int readBytes = 0;
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
while((readBytes = inputStream.read(buffer)) > 0){
stringBuilder.append(new String(buffer, 0, readBytes));
}
System.out.println(stringBuilder.toString());
}
}
缓冲区的大小自己根据实际来调,比 BufferedReader 还简洁些,不需管换行符的事情。
4. Apache commons IOUtils.toString 法
package cc.unmi.test;
import java.io.*;
import org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils;
/**
*
* @author Unmi
* @Creation date: 2013-02-01
*/
public class Test {
/**
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("d:/sample.txt");
String text = IOUtils.toString(inputStream);
System.out.println(text);
}
}
第三方库就是第三方库,人家充分考虑到了你的感受,你对 JDK 库的抱怨,多简洁,一行搞定。IOUtils 还能把内容拷入其他的 Writer 中,如 IOUtils.copy(inputStream, new StringWriter())。
5. Google guava 的 CharStreams 方法
package cc.unmi.test;
import java.io.*;
import com.google.common.io.CharStreams;
/**
*
* @author Unmi
* @Creation date: 2013-02-01
*/
public class Test {
/**
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("d:/sample.txt");
String text = CharStreams.toString(new InputStreamReader(inputStream, "UTF-8"));
System.out.println(text);
}
}
CharSteams 不是直接作用在 InputSteam 上的,还要靠 InputStreamReader 拱个桥。
6. JDK 7 的 NIO readAllBytes
package cc.unmi.test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.*;
/**
*
* @author Unmi
* @Creation date: 2013-02-01
*/
public class Test {
/**
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
byte[] bytes = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("d:/sample.txt"));
String text = new String(bytes);
System.out.println(text);
}
}
这让我们相信 JDK 一直还有人在管,虽然不可能象动态语言的方法那么快捷,上面的 readAllBytes 在处理大文件时肯定会很被动的。而 Files.readAllLines 会把文件的内容读入一个 List<String> 对象中,往内存不断放东西就得掂量下内存会不会被爆。在 java.nio.file.* 还有很多新事物可供发掘。
- /**
- * 利用BufferedReader实现Inputstream转换成String <功能详细描述>
- *
- * @param in
- * @return String
- */
- public static String Inputstr2Str_Reader(InputStream in, String encode)
- {
- String str = "";
- try
- {
- if (encode == null || encode.equals(""))
- {
- // 默认以utf-8形式
- encode = "utf-8";
- }
- BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in, encode));
- StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
- while ((str = reader.readLine()) != null)
- {
- sb.append(str).append(" ");
- }
- return sb.toString();
- }
- catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e1)
- {
- e1.printStackTrace();
- }
- catch (IOException e)
- {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- return str;
- }
- /**
- * 利用byte数组转换InputStream------->String <功能详细描述>
- *
- * @param in
- * @return
- * @see [类、类#方法、类#成员]
- */
- public static String Inputstr2Str_byteArr(InputStream in, String encode)
- {
- StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
- byte[] b = new byte[1024];
- int len = 0;
- try
- {
- if (encode == null || encode.equals(""))
- {
- // 默认以utf-8形式
- encode = "utf-8";
- }
- while ((len = in.read(b)) != -1)
- {
- sb.append(new String(b, 0, len, encode));
- }
- return sb.toString();
- }
- catch (IOException e)
- {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- return "";
- }
- /**
- * 利用ByteArrayOutputStream:Inputstream------------>String <功能详细描述>
- *
- * @param in
- * @return
- * @see [类、类#方法、类#成员]
- */
- public static String Inputstr2Str_ByteArrayOutputStream(InputStream in,String encode)
- {
- ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
- byte[] b = new byte[1024];
- int len = 0;
- try
- {
- if (encode == null || encode.equals(""))
- {
- // 默认以utf-8形式
- encode = "utf-8";
- }
- while ((len = in.read(b)) > 0)
- {
- out.write(b, 0, len);
- }
- return out.toString(encode);
- }
- catch (IOException e)
- {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- return "";
- }
- /**
- * 利用ByteArrayInputStream:String------------------>InputStream <功能详细描述>
- *
- * @param inStr
- * @return
- * @see [类、类#方法、类#成员]
- */
- public static InputStream Str2Inputstr(String inStr)
- {
- try
- {
- // return new ByteArrayInputStream(inStr.getBytes());
- // return new ByteArrayInputStream(inStr.getBytes("UTF-8"));
- return new StringBufferInputStream(inStr);
- }
- catch (Exception e)
- {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- return null;
- }
=====================================
从SDCard保存的txt文件读取中文到android系统中会出现乱码问题,如何解决这个乱码问题,网上有不少解答方法,譬如说利用String temp1 =EncodingUtils.getString(strLine.getBytes(),"GB2312"); 但并非对所有的情况都适用,解决乱码问题首先要明白为什么会乱码。究其原因,是因为txt文件在win系统上保存时默认为ANSI格式,而android目前只支持UTF-8编码,因此将txt文件的中文读入android系统中会产生乱码。也有人说直接将txt另存为UTF-8编码格式来解决乱码问题,但这种方法指标不治本,不能要求用户手动去更改格式,客户第一嘛。因此还是需要想办法在程序中进行处理。
以下做了一些编码格式的测试:
测试文本: 122.11196,29.90573,北仑固废厂 测试代码段:
reader=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename));
strLine=reader.readLine() ;
String temp1 = EncodingUtils.getString(strLine.getBytes(),"GB2312");
String temp2 = EncodingUtils.getString(strLine.getBytes("utf-8"),"utf-8");
String temp3 = EncodingUtils.getString(strLine.getBytes(),"utf-8");
将文件存成 Unicode 格式
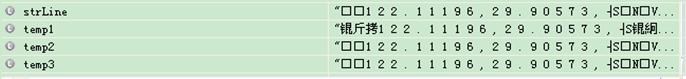
将文件存成utf-8 格式
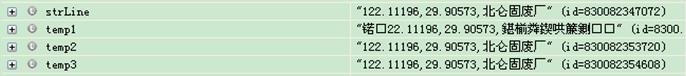
这种方式能得到非乱码的中文显示,但对于 utf-8 格式下取得的经纬度数字利用double lon = Double.parseDouble(lat); 报错 NumberFormatException,原因可能是 parseDouble(lat)方法不能处理存成utf-8格式的带标点小数。 将文件 存成 ANSI 格式

将代码改为:
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(filename),"GB2312"));
strLine=reader.readLine() ;
String temp1 = EncodingUtils.getString(strLine.getBytes(),"GB2312");
String temp2 = EncodingUtils.getString(strLine.getBytes("utf-8"),"utf-8");
String temp3 = EncodingUtils.getString(strLine.getBytes(),"utf-8");
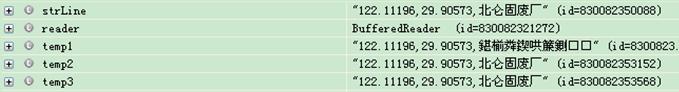
即解决了中文乱码问题,又解决了Double.parseDouble(lat)报错问题。