Spring MVC 学习 -- 创建过程
Spring MVC我们使用的时候会在web.xml中配置
1 <servlet> 2 <servlet-name>SpringMVC</servlet-name> 3 <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> 4 <init-param> 5 <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> 6 <param-value>classpath:spring/spring-web.xml</param-value> 7 </init-param> 8 </servlet> 9 <servlet-mapping> 10 <servlet-name>SpringMVC</servlet-name> 11 <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> 12 </servlet-mapping>
1.核心的类结构
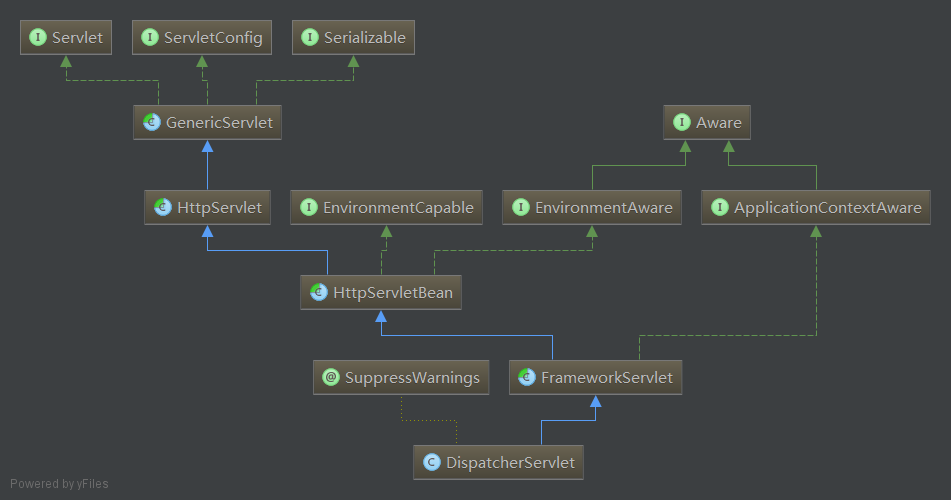
继承结构主要有五个类,GenericServlet和HttpServlet 是Java的,HttpServletBean、FrameworkServlet和DispatcherServlet是Spring MVC的。
在图中还有三个接口:EnvironmentCapable、EnvironmentAware和ApplicationContextAware~
XXXAware 在spring里标识对XXX可以感知 -- 白话的意思就是:某个类如果想要使用spring的一些东西,就可以通过实现XXXAware接口告诉spring,spring看到后会给你送过来,而接收的方式是通过实现接口唯一的setXXX
1 public interface ApplicationContextAware extends Aware { 2 3 void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException; 4 5 }
源码如上,使用的话写一个类实现ApplicationContextAware,然后实现setApplicationContext()方法就行,spring为自动调用这个方法将applicationContext传给我们。
而EnvironmentCapable是为了实现getEnvironment去拿到ServletContext、ServletConfig、JndiProperty、系统环境变量和系统属性。
2.HttpServletBean
1 public final void init() throws ServletException { 2 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 3 logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + getServletName() + "'"); 4 } 5 6 // Set bean properties from init parameters. 7 try { 8 PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties); 9 BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this); 10 ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext()); 11 bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment())); 12 initBeanWrapper(bw); 13 bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true); 14 } 15 catch (BeansException ex) { 16 logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex); 17 throw ex; 18 } 19 20 // Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like. 21 initServletBean(); 22 23 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 24 logger.debug("Servlet '" + getServletName() + "' configured successfully"); 25 } 26 }
主要看init()方法, 使用了BeanWrapper这个类对象,BeanWrapper是操作JavaBean的工具类,主要就是对属性进行操作。
3.FrameworkServlet
这个类是通过HttpServletBean中的initServletBean()方法进入的。
1 protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException { 2 getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'"); 3 if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) { 4 this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started"); 5 } 6 long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); 7 8 try { 9 this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext(); 10 initFrameworkServlet(); 11 } 12 catch (ServletException ex) { 13 this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex); 14 throw ex; 15 } 16 catch (RuntimeException ex) { 17 this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex); 18 throw ex; 19 } 20 21 if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) { 22 long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime; 23 this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " + 24 elapsedTime + " ms"); 25 } 26 }
核心代码就try里面包含的两句,很显然主要用来初始化WebApplicationContext和初始化FrameworkServlet的。
1 protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() { 2 WebApplicationContext rootContext = 3 WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext()); 4 WebApplicationContext wac = null; 5 6 if (this.webApplicationContext != null) { 7 // A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it 8 wac = this.webApplicationContext; 9 if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) { 10 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac; 11 if (!cwac.isActive()) { 12 // The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as 13 // setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc 14 if (cwac.getParent() == null) { 15 // The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set 16 // the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent 17 cwac.setParent(rootContext); 18 } 19 configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac); 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 if (wac == null) { 24 // No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one 25 // has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed 26 // that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the 27 // user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id 28 wac = findWebApplicationContext(); 29 } 30 if (wac == null) { 31 // No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one 32 wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext); 33 } 34 35 if (!this.refreshEventReceived) { 36 // Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh 37 // support or the context injected at construction time had already been 38 // refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here. 39 onRefresh(wac); 40 } 41 42 if (this.publishContext) { 43 // Publish the context as a servlet context attribute. 44 String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName(); 45 getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac); 46 if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 47 this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() + 48 "' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]"); 49 } 50 } 51 52 return wac; 53 }
主要做了三件事:
- 获取spring的根容器rootContext
- 设置webApplicationContext并根据情况调用onRefresh方法
- 将webApplicationContext设置到ServletContext中
4.DispatcherServlet
通过上面onRefresh()方法,调用initStrategies()方法,初始化策略组件。具体的内容就是用来初始化9个组件,每个组件的代码不一一贴出来了, 这几个方法都会去调用getDefaultStrategies()方法。
1 protected <T> List<T> getDefaultStrategies(ApplicationContext context, Class<T> strategyInterface) { 2 String key = strategyInterface.getName(); 3 String value = defaultStrategies.getProperty(key); 4 if (value != null) { 5 String[] classNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(value); 6 List<T> strategies = new ArrayList<T>(classNames.length); 7 for (String className : classNames) { 8 try { 9 Class<?> clazz = ClassUtils.forName(className, DispatcherServlet.class.getClassLoader()); 10 Object strategy = createDefaultStrategy(context, clazz); 11 strategies.add((T) strategy); 12 } 13 catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { 14 throw new BeanInitializationException( 15 "Could not find DispatcherServlet's default strategy class [" + className + 16 "] for interface [" + key + "]", ex); 17 } 18 catch (LinkageError err) { 19 throw new BeanInitializationException( 20 "Error loading DispatcherServlet's default strategy class [" + className + 21 "] for interface [" + key + "]: problem with class file or dependent class", err); 22 } 23 } 24 return strategies; 25 } 26 else { 27 return new LinkedList<T>(); 28 } 29 }
5.代码测试
配置内容都不再贴了,启动Tomcat,然后去请求某个controller地址,进入HttpServletBean的init()方法
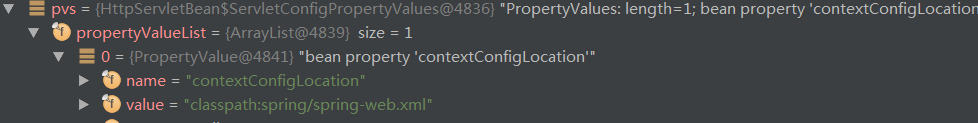
然后继续,因为WebApplicationContext是null,会进入
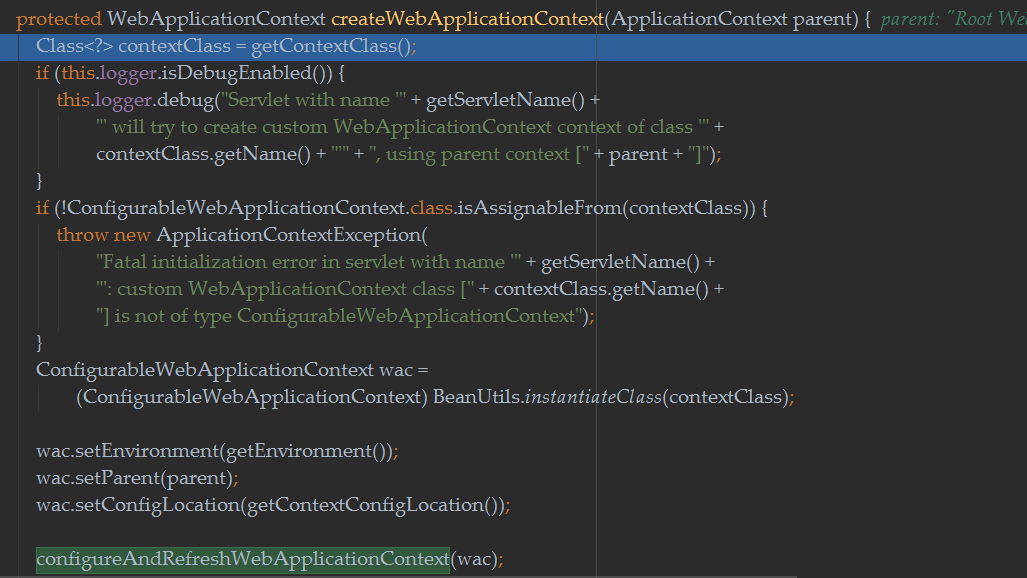
然后configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext方法中会执行refresh(),这部分可以看spring bean加载过程和实例化。