性质
- 由很多层结构组成
- 每一层都是一个有序的链表
- 最底层(Level 1)的链表包含所有元素
- 如果一个元素出现在 Level i 的链表中,则它在 Level i 之下的链表也都会出现。
- 每个节点包含两个指针,一个指向同一链表中的下一个元素,一个指向下面一层的元素。
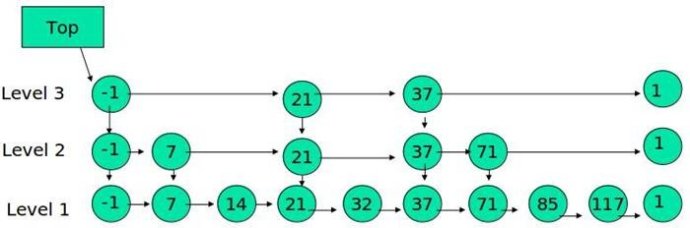
查找

- 比较 21, 比 21 大,往后面找
- 比较 37, 比 37大,比链表最大值小,从 37 的下面一层开始找
- 比较 71, 比 71 大,比链表最大值小,从 71 的下面一层开始找
- 比较 85, 比 85 大,从后面找
- 比较 117, 等于 117, 找到了节点。
插入
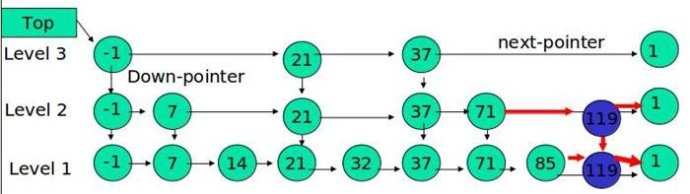
先确定该元素要占据的层数 K(采用丢硬币的方式,这完全是随机的)然后在 Level 1 ... Level K 各个层的链表都插入元素。例子:插入 119, K = 2
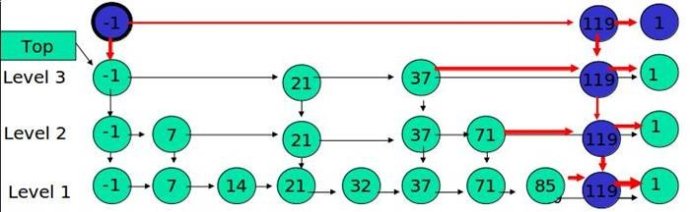
如果 K 大于链表的层数,则要添加新的层。例子:插入 119, K = 4
跳表的高度
n 个元素的跳表,每个元素插入的时候都要做一次实验,用来决定元素占据的层数 K,跳表的高度等于这 n 次实验中产生的最大 K,待续。。。
跳表的空间复杂度分析
根据上面的分析,每个元素的期望高度为 2, 一个大小为 n 的跳表,其节点数目的,期望值是 2n。
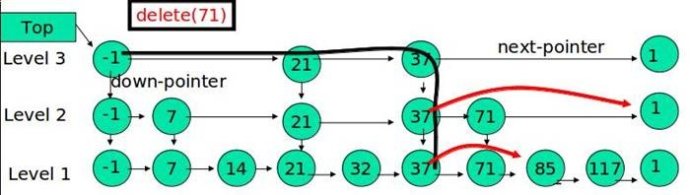
跳表的删除
在各个层中找到包含 x 的节点,使用标准的 delete from list 方法删除该节点。例子:删除 71
code
skiplist.h
#ifndef SKIPLIST_H_INCLUDED #define SKIPLIST_H_INCLUDED #include <cstdlib> #include <ctime> #include "entry.h" using namespace std; //跳表结构 template <typename T> class SkipList { private: typedef struct Entry_H//跳表头结点 { Entry_H *up; Entry_H *down; Entry<T> *right; Entry_H() { up=nullptr; down=nullptr; right=nullptr; } }Entry_H; Entry_H *head; int level; unsigned int seed; bool random(); public: SkipList():level(1),seed(time(NULL))//初始化为1层 { head=new Entry_H(); } void inserts(Entry<T> *e); bool searchs(Entry<T> *e) const; void removes(Entry<T> *e); }; //SkipList的函数 template <typename T> bool SkipList<T>::random() { srand(seed); int res=rand()%2; seed=rand(); return res==0?true:false; } template <typename T> extern void SkipList<T>::inserts(Entry<T>* e) { //先找到第一层:L1 Entry_H *cur_head=head; while(cur_head->down!=nullptr) cur_head=cur_head->down; //L1层肯定要插入数据,上面是否插入数据根据random决定 int cur_level=0; Entry<T> *temp_entry=nullptr;//保存一个已完成插入的结点 Entry<T> *cur_entry=new Entry<T>(*e);//拷贝要复制的对象 do { //层数超过了表中的最大层,创建新的头结点 ++cur_level; if(level<cur_level) { ++level; Entry_H *new_head=new Entry_H(); new_head->down=cur_head; cur_head->up=new_head; head=new_head; } if(cur_level>1)//层数大于1,向上依次添加 { cur_head=cur_head->up; cur_entry->down()=temp_entry; } temp_entry=cur_entry; //添加对象 if(cur_head->right==nullptr) { cur_head->right=cur_entry; break; } else//一个简单的在单链表中的插入操作 { Entry<T> *cursor=cur_head->right;//指向当前结点的指针 Entry<T> *pre=cur_head->right;//指向当前节点的前一节点的指针 //如果要插入的结点小于第一个结点---同一层的结点升序排列 if(*cur_entry<*cursor) { cur_entry->next()=cursor; cur_head->right=cur_entry; } else { bool flag=true; cursor=cursor->next(); while(cursor!=nullptr) { if(*cur_entry<*cursor) { cur_entry->next()=cursor; pre->next()=cur_entry; flag=false; break; } cursor=cursor->next(); pre=pre->next(); } if(flag)//记录是由什么原因跳出while循环 cursor->next()=cur_entry; } } } while(random()); delete cur_entry; } template <typename T> extern bool SkipList<T>::searchs(Entry<T>* e) const { if(head==nullptr) return false; Entry_H *cur_head=head; for(int i=0; i<level; ++i) //先找一个接入点 { if(*e<*cur_head->right) cur_head=cur_head->down; else { Entry<T> *cursor=cur_head->right; while(cursor->down()!=nullptr) { while(cursor->next()!=nullptr) { if(*e<=cursor->next()) break; cursor=cursor->next(); } cursor=cursor->down(); } while(cursor!=nullptr) { if(*e<*cursor) cursor=cursor->next(); else if(*e==*cursor) return true; } return false; } } return false;//找不到接入点 } template <typename T> extern void SkipList<T>::removes(Entry<T>* e) { if(head->right==nullptr) return; Entry_H *cur_head=head; int cur_level=level; for(int i=0; i<level; ++i) { if(*e==*cur_head->right) { Entry<T> *t=cur_head->right; cur_head->right=cur_head->right->next(); delete t; // break; } else { Entry<T> *cursor=cur_head->right; while(cursor) { if(*e==*cursor) { Entry<T> *t=cursor; cursor=cursor->next(); delete t; break; } cursor=cursor->next(); } } if(cur_head->right==nullptr) { Entry_H *t=head; cur_head=cur_head->down; head=cur_head; delete t; --level; } else cur_head=cur_head->down; } } #endif // SKIPLIST_H_INCLUDED
entry.h
#ifndef ENTRY_H_INCLUDED #define ENTRY_H_INCLUDED template <typename T> class Entry//结点类型 { private: int key; T value; Entry *Next; Entry *Down; public: Entry(int k,T v):key(k),value(v),Next(nullptr),Down(nullptr){} Entry(const Entry &e):key(e.key),value(e.value),Next(nullptr),Down(nullptr){} bool operator <(const Entry &e); bool operator <=(const Entry &e); bool operator >(const Entry &e); bool operator >=(const Entry &e); bool operator ==(const Entry &e); Entry*& next() { return Next; } Entry*& down() { return Down; } }; //Entry的函数 template <typename T> bool Entry<T>::operator<(const Entry& e) { return key<e.value; } template <typename T> bool Entry<T>::operator<=(const Entry& e) { return key<=e.value; } template <typename T> bool Entry<T>::operator>(const Entry& e) { return key>e.value; } template <typename T> bool Entry<T>::operator>=(const Entry& e) { return key>=e.value; } template <typename T> bool Entry<T>::operator==(const Entry& e) { return key==e.value; } #endif
main.cpp
#include <iostream> #include "skiplist.h" int main() { Entry<int> *e=new Entry<int>(1,2); SkipList<int> sk; sk.inserts(e); return 0; }