题目
给定一个二叉树和其中的一个结点,请找出中序遍历顺序的下一个结点并且返回。注意,树中的结点不仅包含左右子结点,同时包含指向父结点的指针。
思路
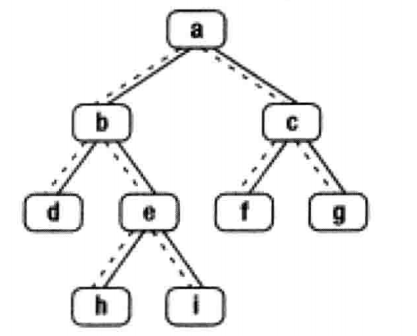
我们以上图为例进行讲解,上图二叉树的中序遍历是d,b,h,e,i,a,f,c,g。我们以这棵树为例来分析如何找出二叉树的下一个结点。
- 结点有右子树,那么它的下一个结点就是它的右子树的最左子结点。也就是说从右子结点出发一直沿着指向左子树结点的指针,我们就能找到它的下一个结点。例如,图中结点b的下一个结点是h,结点a的下一个结点是f。
- 结点没有右子树的情形。
1>如果结点是它父结点的左子结点,那么它的下一个结点就是它的父结点。例如,途中结点d的下一个结点是b,f的下一个结点是c。
2>如果一个结点既没有右子树,并且它还是父结点的右子结点,这种情形就比较复杂。我们可以沿着指向父结点的指针一直向上遍历,直到找到一个是它父结点的左子结点的结点。
如果这样的结点存 在,那么这个结点的父结点就是我们要找的下一个结点。例如,为了找到结点g的下一个结点,我们沿着指向父结点的指针向上遍历,先到达结点c。由于结点c是
父结点a的右结点,我们继续向上遍历到达结点a。由于结点a是树的根结点。它没有父结点。因此结点g没有下一个结点。
#include <iostream> using namespace std; struct node { int val; struct node *l,*r,*p; }; class BTree { public: BTree(); void create(struct node *&r); void add_parent(struct node *&r,struct node *p); node *get_next(struct node *r); struct node *root; }; BTree::BTree() { root=NULL; } void BTree::create(struct node *&r) { int x; cin>>x; if(x==0) return; else { r=new node(); r->val=x; create(r->l); create(r->r); } } void BTree::add_parent(struct node *&r,struct node *p) { if(r==nullptr) return; r->p=p; p=r; add_parent(r->l,p); add_parent(r->r,p); } node *BTree::get_next(struct node *r) { if(r==nullptr) return nullptr; if(r->r!=nullptr) { struct node *curr=r->r; while(curr->l!=nullptr) curr=curr->l; return curr; } else if(r->p!=nullptr) { struct node *curr=r; struct node *p=curr->p; while(p!=nullptr&&curr==p->r) { curr=p; p=p->p; } return curr; } return nullptr; } int main() { BTree b; b.create(b.root); b.add_parent(b.root,nullptr); struct node *t=b.get_next(b.root); //测试 if(t!=nullptr) cout<<t->val<<endl; else cout<<" 该结点无下一个结点."<<endl; return 0; }
code2
/* struct TreeLinkNode { int val; struct TreeLinkNode *left; struct TreeLinkNode *right; struct TreeLinkNode *next; TreeLinkNode(int x) :val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) { } }; */ class Solution { public: TreeLinkNode* GetNext(TreeLinkNode* node) { if(!node) return nullptr; if(node->right) { auto cur=node->right; while(cur->left) cur=cur->left; return cur; } while(node->next) { auto root=node->next; if(root->left==node) return root; node=node->next; } return nullptr; } };