



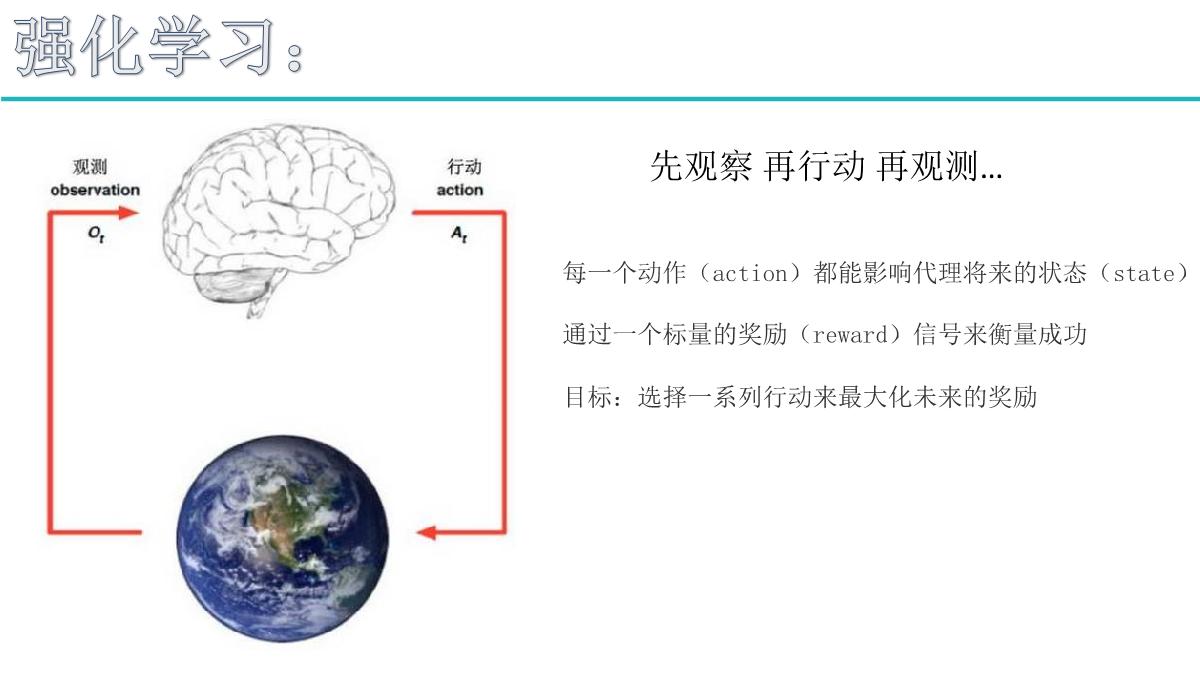

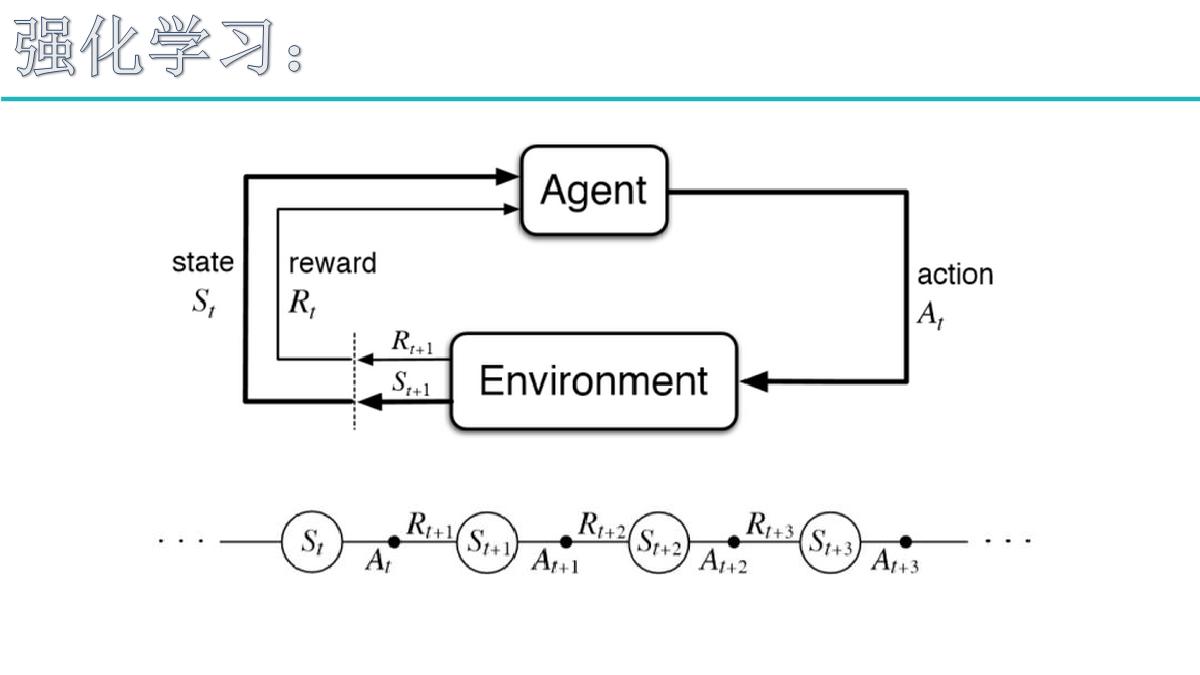


理想状态指的是有最终的目标,赢了就会有奖励。
可以多次尝试(死了重来、输了重来等)

Bellman方程:当前状态的价值和下一步的价值及当前的奖励(Reward)有关;
价值函数分解为当前的奖励和下一步的价值两部分。

注意:动作空间A,状态空间S均为有限集合!
举个例子(本例子没加折扣因子,要想加上只需要在下一步的价值公式前乘以0.6或0.8;另外这里假设a3 = a4 = 0.5):
举个例子:
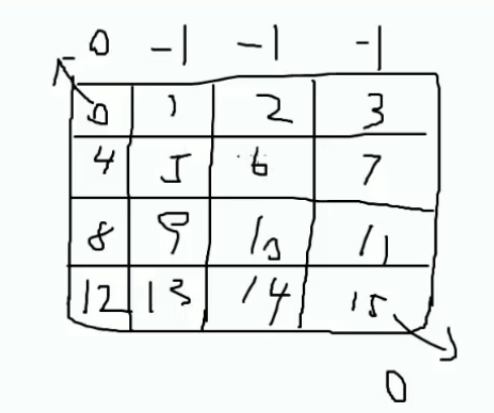
在以下棋盘上,0和15表示两个出口,在任何一个位置要想出去只能从0和15号出去,达到0或者15奖励值是“0”,到达其他位置奖励值是“-1”。想想怎么编程?
#代码实现
import numpy as np
#pip install gridworld
from gridworld import GridworldEnv#导入大环境
env = GridworldEnv()#设置大环境
def value_iteration(env, theta=0.0001, discount_factor=1.0):#迭代求解
"""
Value Iteration Algorithm.
Args:
env: OpenAI environment. env.P represents the transition probabilities of the environment.
theta:停止条件 Stopping threshold. If the value of all states changes less than theta
in one iteration we are done.
discount_factor:折扣因子 lambda time discount factor.
Returns:
A tuple (policy, V) of the optimal policy and the optimal value function.
"""
def one_step_lookahead(state, V):#一步一步进行迭代的函数,V:所有状态的状态值
"""
Helper function to calculate the value for all action in a given state.
Args:
state:当前状态 The state to consider (int)
V: The value to use as an estimator, Vector of length env.nS
Returns:
A vector of length env.nA containing the expected value of each action.
"""
A = np.zeros(env.nA)#nA = 4代表有四个方向可以走
for a in range(env.nA):#四个方向
for prob, next_state, reward, done in env.P[state][a]:#每个方向的计算
#prob:往某个某个方向移动的概率值; next_state:下一步状态; reward:奖励值; done:达到出口就是True,没有达到就是False; env.P[state][a]:当前状态下执行某个action
A[a] += prob * (reward + discount_factor * V[next_state])#Bellman方程
return A
V = np.zeros(env.nS)#env.nS = 16:16个格子。 V :16个状态值组成的array
while True:
# Stopping condition用于判断是否进行更新了
delta = 0
# Update each state...
for s in range(env.nS):#每一个状态(格子)作为开始,s指的是当前状态
# Do a one-step lookahead to find the best action
A = one_step_lookahead(s, V)
best_action_value = np.max(A)#走的最好的一步
# Calculate delta across all states seen so far
delta = max(delta, np.abs(best_action_value - V[s]))
# Update the value function
V[s] = best_action_value
# Check if we can stop
if delta < theta:
break
# Create a deterministic policy using the optimal value function
policy = np.zeros([env.nS, env.nA])
for s in range(env.nS):
# One step lookahead to find the best action for this state
A = one_step_lookahead(s, V)
best_action = np.argmax(A)
# Always take the best action
policy[s, best_action] = 1.0#某个状态最好方向为1,其他方向为0
return policy, V
policy, v = value_iteration(env)
print("Policy Probability Distribution:")
print(policy)
print("")
print("Reshaped Grid Policy (0=up, 1=right, 2=down, 3=left):")
print(np.reshape(np.argmax(policy, axis=1), env.shape))
print("")

注意:在任何一个房间,其目标都是从5号出去


注意:箭头上的0,100指的是奖励值
 注意:-1指的是通路不通。
注意:-1指的是通路不通。